How to Become an Advanced Java Enterprise Developer: Complete Career Guide [₹15L Average Salary]

1. What is Advanced Java Enterprise Development?
Master Advanced Java Enterprise Developer and build scalable business applications
Advanced Java Enterprise Developer are among the most sought-after professionals in enterprise software development, with average salaries ranging from ₹8-25 LPA in India and senior Java architects earning ₹40+ LPA. As organizations continue to rely on Java for mission-critical enterprise applications, microservices architectures, and cloud-native solutions, the ability to design and develop sophisticated Java applications using enterprise frameworks has become one of the most valuable and well-compensated skills in software development.
Whether you’re a Advanced Java Enterprise developer seeking to advance to enterprise-level development, a software engineer wanting to specialize in backend systems, or a professional looking to master modern Java architectures, this comprehensive guide provides the proven roadmap to building a successful advanced Java career. Having trained over 320 Java professionals at Frontlines EduTechwith an 89% job placement rate, I’ll share the strategies that consistently deliver results in the competitive enterprise Java landscape.
What you’ll master in this guide:
- Complete advanced Java learning pathway from Spring Boot to microservices architecture
- Essential enterprise frameworks including Spring, Hibernate, and cloud-native technologies
- Portfolio projects demonstrating real enterprise application development
- Modern Java practices including reactive programming and containerization
- Career advancement opportunities in solution architecture and technical leadership
Advanced Java Enterprise developer encompasses the design and implementation of large-scale, mission-critical business applications using sophisticated Java frameworks, design patterns, and architectural principles. This specialization goes beyond basic Java programming to include distributed systems, microservices architecture, enterprise integration patterns, and cloud-native development practices essential for modern business applications.
Core Components of Advanced Java Enterprise Development:
Enterprise Frameworks and Technologies:
- Spring Framework Ecosystem – Spring Boot, Spring Data, Spring Security, Spring Cloud for comprehensive application development
- Java Persistence API (JPA) – Hibernate, Spring Data JPA for object-relational mapping and database operations
- Enterprise Integration – Apache Camel, Spring Integration for system-to-system communication
- Message Queues – RabbitMQ, Apache Kafka, ActiveMQ for asynchronous processing and event-driven architecture
Microservices and Distributed Systems:
- Microservices Architecture – Service decomposition, API gateway patterns, service discovery, load balancing
- Containerization – Docker containers, Kubernetes orchestration, container security and optimization
- Cloud-Native Development – 12-factor app principles, serverless functions, cloud platform integration
- Distributed Data Management – Database per service, event sourcing, CQRS patterns, eventual consistency
Enterprise Application Patterns:
- Design Patterns – Gang of Four patterns, enterprise integration patterns, architectural patterns
- Domain-Driven Design (DDD) – Bounded contexts, aggregates, entities, value objects, domain services
- Test-Driven Development (TDD) – Unit testing, integration testing, behavior-driven development
- DevOps Integration – CI/CD pipelines, infrastructure as code, monitoring and observability
Performance and Scalability:
- Reactive Programming – Spring WebFlux, Project Reactor, non-blocking I/O, backpressure handling
- Caching Strategies – Redis, Hazelcast, application-level caching, distributed caching
- Performance Tuning – JVM optimization, garbage collection tuning, profiling and monitoring
- High Availability – Circuit breaker patterns, bulkhead isolation, timeout and retry mechanisms
Advanced Java vs Basic Java Development
Basic Java Development Focus:
- Core language features, object-oriented programming concepts
- Simple database connectivity, basic web applications
- Monolithic application architecture, traditional deployment models
- Limited scalability and performance considerations
Advanced Java Enterprise Developer:
- Complex enterprise frameworks and architectural patterns
- Distributed systems design, microservices decomposition
- Cloud-native architecture, containerization, orchestration
- Advanced performance optimization, monitoring, and scalability solutions
💡 New to enterprise Java? Begin with our step-by-step interview guides on Java, Spring, Microservices & Cloud.
2. Why Choose Advanced Java?
Continued Enterprise Dominance and Market Growth
According to Stack Overflow Developer Survey 2025, Java remains the #2 most popular programming language globally, with 35.6% of professional developers using it. In India specifically, Java continues to dominate enterprise software development:
Enterprise Java Adoption:
- Banking and Financial Services – HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Axis Bank using Java for core banking systems and digital platforms
- E-commerce Platforms – Flipkart, Amazon India, Paytm leveraging Java for high-scale transaction processing
- Technology Services – TCS, Infosys, Wipro delivering Java-based enterprise solutions globally
- Fintech Innovation – Razorpay, PhonePe, CRED building next-generation financial platforms with modern Java
Modern Java Evolution:
- Cloud-Native Java – GraalVM native images, Quarkus, Spring Native for cloud optimization
- Microservices Ecosystems – Spring Cloud, Netflix OSS, service mesh integration
- Reactive Programming – Non-blocking I/O, event-driven architecture, streaming data processing
- Enterprise AI Integration – Machine learning model deployment, AI-powered business applications
Premium Compensation for Advanced Java Skills
Advanced Java Enterprise developer command significantly higher salaries than basic Java programmers:
📘 Download Java cheat sheets, OOP notes & Core Java practice projects.

Source: PayScale India 2025, Glassdoor Advanced Java Salaries
Future-Proof Technology Stack
Advanced Java skills remain highly relevant due to several factors:
- Enterprise Stability – Java’s backward compatibility and enterprise support ensure long-term viability
- Continuous Innovation – Regular Java releases introducing modern language features and performance improvements
- Cloud Integration – Native cloud support, containerization, serverless deployment options
- Open Source Ecosystem – Rich ecosystem of frameworks, tools, and libraries with active communities
Multiple Specialization and Career Paths
Advanced Java enables diverse career opportunities:
- Solution Architecture – Enterprise solution design, technical leadership, architectural decision making
- DevOps and Platform Engineering – Java application optimization, deployment automation, performance monitoring
- Product Development – SaaS platform development, API design, user experience optimization
- Consulting and Implementation – Enterprise Java consulting, system integration, digital transformation projects
🚀 Kickstart your expert-level Java journey with structured, proven Tech Roadmaps designed for fast career growth.
3. Complete Learning Roadmap (5-7 Months)
📘 Download OOP patterns, DDD cheat sheets, concurrency notes & enterprise Java PDF quick guides.
Phase 1: Advanced Java Fundamentals and Enterprise Patterns (Month 1-2)
Java 17+ Modern Features (2-3 weeks)
Mastering modern Java is essential for enterprise development:
- Functional Programming – Streams, lambdas, optional, method references, functional interfaces
- Modern Java Features – Records, sealed classes, pattern matching, text blocks, switch expressions
- Concurrency and Threading – ExecutorService, CompletableFuture, parallel streams, virtual threads (Project Loom)
- Module System (JPMS) – Module declarations, module path, modular application design
Enterprise Design Patterns (2-3 weeks)
- Creational Patterns – Singleton, Factory, Builder, Prototype patterns in enterprise context
- Structural Patterns – Adapter, Decorator, Facade, Proxy patterns for system integration
- Behavioral Patterns – Observer, Strategy, Command, State patterns for business logic
- Enterprise Integration Patterns – Message routing, transformation, aggregation, event-driven architecture
Advanced Object-Oriented Design (1-2 weeks)
- SOLID Principles – Single responsibility, open/closed, Liskov substitution, interface segregation, dependency inversion
- Clean Code Practices – Code readability, refactoring techniques, technical debt management
- Domain-Driven Design – Bounded contexts, aggregates, entities, value objects, domain services
- Dependency Injection – Inversion of control, dependency injection patterns, container management
Foundation Projects:
- Enterprise Library Management System – Advanced OOP design with design patterns and clean architecture
- Event-Driven Order Processing – Implementation of enterprise integration patterns with messaging
- Multi-threaded File Processing Engine – Concurrent programming with modern Java concurrency utilities
Phase 2: Spring Framework Mastery (Month 2-4)
Spring Core and Boot Fundamentals (3-4 weeks)
- Spring IoC Container – Bean lifecycle, configuration, profiles, conditional beans
- Spring Boot – Auto-configuration, starters, actuator, configuration properties, testing
- Spring MVC – RESTful web services, request mapping, validation, exception handling
- Spring Data – Repository patterns, query methods, custom implementations, transactions
Spring Security and Advanced Features (3-4 weeks)
- Authentication and Authorization – JWT tokens, OAuth2, method-level security, role-based access
- Spring Cloud – Service discovery, circuit breakers, configuration management, API gateway
- Spring Integration – Message channels, endpoints, transformers, enterprise integration patterns
- Spring Batch – Large-scale data processing, job scheduling, transaction management, error handling
Database Integration and JPA (2-3 weeks)
- Hibernate and JPA – Entity mapping, relationships, JPQL, criteria API, caching strategies
- Spring Data JPA – Repository interfaces, custom queries, specifications, auditing
- Database Migrations – Flyway, Liquibase for version control and schema management
- Performance Optimization – Query optimization, N+1 problem solutions, connection pooling
Spring Framework Projects:
- E-commerce REST API – Complete Spring Boot application with security, data persistence, and validation
- Microservices Communication – Spring Cloud implementation with service discovery and circuit breakers
- Enterprise Batch Processing – Spring Batch job for large-scale data processing with error handling
Phase 3: Microservices and Distributed Systems (Month 4-5)
Microservices Architecture Design (4-5 weeks)
- Service Decomposition – Domain-driven decomposition, bounded contexts, service boundaries
- API Gateway Patterns – Spring Cloud Gateway, request routing, load balancing, security
- Service Discovery – Eureka, Consul, service registration and discovery patterns
- Inter-Service Communication – RESTful APIs, message queues, event-driven architecture
Distributed Data Management (3-4 weeks)
- Database Per Service – Data consistency, transaction boundaries, eventual consistency
- Event Sourcing – Event store implementation, event replay, snapshotting
- CQRS Pattern – Command query responsibility segregation, read/write model separation
- Distributed Transactions – Saga patterns, two-phase commit, compensating transactions
Monitoring and Observability (2-3 weeks)
- Distributed Tracing – Spring Cloud Sleuth, Zipkin, Jaeger for request tracing
- Metrics and Monitoring – Micrometer, Prometheus, Grafana for application metrics
- Health Checks – Spring Boot Actuator, custom health indicators, readiness/liveness probes
- Centralized Logging – ELK stack, log aggregation, structured logging
Microservices Implementation Projects:
- Distributed E-commerce Platform – Multiple microservices with API gateway, service discovery, and monitoring
- Event-Driven Order Management – Event sourcing and CQRS implementation with Kafka
- Observability Dashboard – Comprehensive monitoring solution with metrics, tracing, and alerting
Phase 4: Cloud-Native and DevOps Integration (Month 5-6)
Containerization and Orchestration (4-5 weeks)
- Docker Mastery – Multi-stage builds, image optimization, security scanning, registry management
- Kubernetes Deployment – Pods, services, deployments, config maps, secrets, ingress controllers
- Helm Charts – Package management, templating, dependency management, release management
- Service Mesh – Istio, Linkerd for traffic management, security, observability
Cloud Platform Integration (3-4 weeks)
- AWS Integration – EC2, RDS, SQS, SNS, Lambda, ECS, EKS for comprehensive cloud deployment
- Azure Integration – Azure App Service, Azure Database, Service Bus, Functions, AKS
- Google Cloud Platform – Compute Engine, Cloud SQL, Pub/Sub, Cloud Functions, GKE
- Cloud-Native Patterns – 12-factor app principles, stateless design, configuration management
CI/CD and DevOps Practices (2-3 weeks)
- Jenkins Pipeline – Declarative pipelines, parallel execution, artifact management, deployment automation
- GitLab CI/CD – Pipeline configuration, Docker integration, environment management
- Infrastructure as Code – Terraform, CloudFormation for reproducible infrastructure
- Monitoring and Alerting – Application performance monitoring, error tracking, incident response
Cloud-Native Projects:
- Kubernetes-Native Application – Complete containerized microservices deployment with Helm
- Multi-Cloud Deployment – Application deployment across multiple cloud providers with Terraform
- CI/CD Pipeline Implementation – End-to-end automation from code commit to production deployment
Phase 5: Advanced Topics and Specialization (Month 6-7)
Choose Advanced Specialization Track:
Solution Architecture Track:
- Enterprise architecture patterns and frameworks
- Technology selection and architectural decision making
- Performance engineering and scalability planning
- Technical leadership and team coordination
Performance Engineering Track:
- JVM tuning and garbage collection optimization
- Application profiling and performance analysis
- Distributed systems performance optimization
- Load testing and capacity planning
Cloud-Native Specialist Track:
- Serverless architecture with Java (GraalVM, Quarkus)
- Container optimization and security
- Service mesh implementation and management
- Cloud cost optimization and resource management
Enterprise Integration Track:
- Apache Camel and enterprise integration patterns
- Message broker implementation and optimization
- API management and governance
- Legacy system modernization and migration
⚙️ Build scalable apps with confidence—Access microservices patterns, Kafka examples & real-world architecture diagrams.
4. Essential Java Technologies and Frameworks

Core Java Platform and JVM
OpenJDK and Oracle JDK:
- Java 17 LTS – Current long-term support version with modern language features
- Java 21 LTS – Latest LTS with virtual threads, pattern matching, and performance improvements
- GraalVM – High-performance runtime with native image compilation for cloud-native deployments
- JVM Tuning – Garbage collection optimization, memory management, performance monitoring
Build Tools and Dependency Management:
- Apache Maven – Project structure, dependency management, lifecycle management, plugin ecosystem
- Gradle – Build automation, dependency resolution, multi-project builds, performance optimization
- SBT – Scala Build Tool for mixed Java/Scala projects and advanced build configurations
- Bazel – Google’s build tool for large-scale Java projects with advanced caching and parallelization
Spring Framework Ecosystem
Core Spring Framework:
- Spring Framework 6 – Latest version with modern Java support and improved performance
- Spring Boot 3 – Production-ready applications with minimal configuration and native compilation
- Spring Data – Consistent data access across relational and NoSQL databases
- Spring Security – Comprehensive security framework with OAuth2, JWT, and method-level security
Spring Cloud Stack:
- Spring Cloud Gateway – API gateway with routing, filtering, and load balancing capabilities
- Spring Cloud Config – Centralized configuration management with Git backend
- Spring Cloud Netflix – Service discovery (Eureka), circuit breakers (Hystrix), client-side load balancing
- Spring Cloud Stream – Event-driven microservices with message broker abstraction
Database Technologies and Persistence
Relational Databases:
- PostgreSQL – Advanced open-source database with JSON support and full-text search
- MySQL – High-performance database with clustering and replication capabilities
- Oracle Database – Enterprise database with advanced features and performance optimization
- Microsoft SQL Server – Integrated business intelligence and advanced analytics capabilities
NoSQL and Big Data:
- MongoDB – Document database with flexible schema and horizontal scaling
- Redis – In-memory data structure store for caching and session management
- Apache Cassandra – Distributed database for large-scale data with high availability
- Elasticsearch – Search and analytics engine for full-text search and log analysis
Message Brokers and Event Streaming
Message Queue Systems:
- Apache Kafka – Distributed streaming platform for high-throughput event processing
- RabbitMQ – Reliable message broker with advanced routing and clustering capabilities
- Apache ActiveMQ – Java-based message broker with JMS support and multiple protocols
- Amazon SQS/SNS – Cloud-native message queuing and notification services
Event Processing:
- Apache Storm – Real-time stream processing with low latency guarantees
- Apache Flink – Stream processing engine with event time processing and exactly-once semantics
- Kafka Streams – Library for building streaming applications with Kafka integration
- Spring Cloud Stream – Framework for building event-driven microservices
5. Building Your Enterprise Java Portfolio
Portfolio Strategy and Architecture
Enterprise Java Portfolio Objectives:
- Demonstrate Technical Depth – Show mastery of advanced Java frameworks and architectural patterns
- Highlight Scalability Solutions – Display ability to design and implement high-performance systems
- Showcase Modern Practices – Present cloud-native, containerized, and DevOps-integrated solutions
- Present Business Value – Quantify performance improvements, cost savings, and efficiency gains
Foundation Level Projects (Months 1-3)
- Enterprise Customer Management System
- Architecture: Spring Boot application with microservices-ready design and comprehensive security
- Technical Stack: Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring Data JPA, PostgreSQL, Redis caching
- Advanced Features: JWT authentication, role-based authorization, audit logging, comprehensive testing
- Performance Optimization: Connection pooling, query optimization, caching strategies, async processing
- DevOps Integration: Docker containerization, CI/CD pipeline, monitoring and health checks
Technical Implementation Example:
@RestController
@RequestMapping(“/api/v1/customers”)
@Validated
@Slf4j
public class CustomerController {
private final CustomerService customerService;
private final CustomerMapper customerMapper;
public CustomerController(CustomerService customerService, CustomerMapper customerMapper) {
this.customerService = customerService;
this.customerMapper = customerMapper;
}
@GetMapping(“/{id}”)
@PreAuthorize(“hasRole(‘USER’) or hasRole(‘ADMIN’)”)
@Cacheable(value = “customers”, key = “#id”)
public ResponseEntity<CustomerResponse> getCustomer(@PathVariable UUID id) {
log.debug(“Fetching customer with id: {}”, id);
Customer customer = customerService.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new CustomerNotFoundException(“Customer not found with id: ” + id));
CustomerResponse response = customerMapper.toResponse(customer);
return ResponseEntity.ok(response);
}
@PostMapping
@PreAuthorize(“hasRole(‘ADMIN’)”)
@Transactional
public ResponseEntity<CustomerResponse> createCustomer(
@Valid @RequestBody CreateCustomerRequest request) {
log.info(“Creating new customer: {}”, request.getEmail());
Customer customer = customerMapper.toEntity(request);
Customer savedCustomer = customerService.save(customer);
CustomerResponse response = customerMapper.toResponse(savedCustomer);
// Publish customer created event for downstream services
customerEventPublisher.publishCustomerCreated(savedCustomer);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(response);
}
@PutMapping(“/{id}”)
@PreAuthorize(“hasRole(‘ADMIN’) or @customerService.isOwner(#id, authentication.name)”)
@CacheEvict(value = “customers”, key = “#id”)
public ResponseEntity<CustomerResponse> updateCustomer(
@PathVariable UUID id,
@Valid @RequestBody UpdateCustomerRequest request) {
Customer updatedCustomer = customerService.update(id, request);
CustomerResponse response = customerMapper.toResponse(updatedCustomer);
return ResponseEntity.ok(response);
}
}
@Service
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
@Slf4j
public class CustomerService {
private final CustomerRepository customerRepository;
private final CustomerEventPublisher eventPublisher;
private final RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
public CustomerService(CustomerRepository customerRepository,
CustomerEventPublisher eventPublisher,
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) {
this.customerRepository = customerRepository;
this.eventPublisher = eventPublisher;
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
@Transactional
public Customer save(Customer customer) {
// Business validation
validateCustomerData(customer);
// Check for duplicate email
if (customerRepository.existsByEmail(customer.getEmail())) {
throw new DuplicateCustomerException(“Customer already exists with email: ” + customer.getEmail());
}
// Set audit fields
customer.setCreatedAt(Instant.now());
customer.setUpdatedAt(Instant.now());
Customer savedCustomer = customerRepository.save(customer);
// Clear cache
redisTemplate.delete(“customers::*”);
log.info(“Customer created successfully: {}”, savedCustomer.getId());
return savedCustomer;
}
@Retryable(value = {DataAccessException.class}, maxAttempts = 3, backoff = @Backoff(delay = 1000))
public Optional<Customer> findById(UUID id) {
return customerRepository.findById(id);
}
private void validateCustomerData(Customer customer) {
// Complex business validation logic
if (customer.getAge() < 18) {
throw new InvalidCustomerDataException(“Customer must be at least 18 years old”);
}
// Additional validation rules
validatePhoneNumber(customer.getPhoneNumber());
validateAddress(customer.getAddress());
}
}
Intermediate Level Projects (Months 3-5)
- Microservices E-commerce Platform
- Architecture: Multiple Spring Boot microservices with API gateway and service discovery
- Services: User service, Product service, Order service, Payment service, Notification service
- Communication: REST APIs, asynchronous messaging with RabbitMQ, event-driven architecture
- Data Management: Database per service, distributed transactions with Saga pattern
- Infrastructure: Docker containers, Kubernetes deployment, service mesh with Istio
Microservices Architecture Example:
// Order Service – Domain Model
@Entity
@Table(name = “orders”)
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
public class Order {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = “UUID”)
private UUID id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private UUID customerId;
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
private OrderStatus status = OrderStatus.PENDING;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = “order”, cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
private List<OrderItem> items = new ArrayList<>();
@Column(nullable = false)
private BigDecimal totalAmount = BigDecimal.ZERO;
@CreatedDate
private Instant createdAt;
@LastModifiedDate
private Instant updatedAt;
// Domain methods
public void addItem(Product product, int quantity) {
OrderItem item = new OrderItem(this, product, quantity);
items.add(item);
recalculateTotal();
}
public void confirm() {
if (status != OrderStatus.PENDING) {
throw new InvalidOrderStateException(“Order can only be confirmed from PENDING state”);
}
status = OrderStatus.CONFIRMED;
}
private void recalculateTotal() {
totalAmount = items.stream()
.map(item -> item.getPrice().multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(item.getQuantity())))
.reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add);
}
}
// Order Service Implementation with Saga Pattern
@Service
@Transactional
@Slf4j
public class OrderService {
private final OrderRepository orderRepository;
private final PaymentServiceClient paymentServiceClient;
private final InventoryServiceClient inventoryServiceClient;
private final ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;
public OrderService(OrderRepository orderRepository,
PaymentServiceClient paymentServiceClient,
InventoryServiceClient inventoryServiceClient,
ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher) {
this.orderRepository = orderRepository;
this.paymentServiceClient = paymentServiceClient;
this.inventoryServiceClient = inventoryServiceClient;
this.eventPublisher = eventPublisher;
}
public Order processOrder(CreateOrderRequest request) {
// Create order
Order order = createOrder(request);
try {
// Start saga
SagaTransaction saga = new SagaTransaction(order.getId());
// Step 1: Reserve inventory
ReservationResult reservation = inventoryServiceClient.reserveItems(order.getItems());
saga.addCompensation(() -> inventoryServiceClient.releaseReservation(reservation.getId()));
// Step 2: Process payment
PaymentResult payment = paymentServiceClient.processPayment(
order.getCustomerId(), order.getTotalAmount());
saga.addCompensation(() -> paymentServiceClient.refundPayment(payment.getId()));
// Step 3: Confirm order
order.confirm();
orderRepository.save(order);
// Publish success event
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new OrderConfirmedEvent(order.getId()));
log.info(“Order processed successfully: {}”, order.getId());
return order;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(“Order processing failed: {}”, order.getId(), e);
// Execute compensations in reverse order
saga.compensate();
order.cancel();
orderRepository.save(order);
throw new OrderProcessingException(“Failed to process order: ” + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
// Event-Driven Communication
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = “order.events”)
@Slf4j
public class OrderEventHandler {
private final NotificationService notificationService;
private final AnalyticsService analyticsService;
public OrderEventHandler(NotificationService notificationService,
AnalyticsService analyticsService) {
this.notificationService = notificationService;
this.analyticsService = analyticsService;
}
@RabbitHandler
public void handleOrderConfirmed(OrderConfirmedEvent event) {
log.info(“Processing order confirmed event: {}”, event.getOrderId());
// Send confirmation notification
notificationService.sendOrderConfirmation(event.getOrderId());
// Update analytics
analyticsService.recordOrderConfirmation(event);
}
@RabbitHandler
public void handleOrderCancelled(OrderCancelledEvent event) {
log.info(“Processing order cancelled event: {}”, event.getOrderId());
// Send cancellation notification
notificationService.sendOrderCancellation(event.getOrderId());
// Update analytics
analyticsService.recordOrderCancellation(event);
}
}
Advanced Level Projects (Months 5-7)
- High-Performance Trading Platform
- Requirements: Low-latency order processing, real-time market data streaming, high availability
- Architecture: Reactive programming with Spring WebFlux, event sourcing, CQRS implementation
- Performance: Sub-millisecond response times, millions of transactions per second capability
- Scalability: Horizontal scaling, distributed caching, database sharding strategies
- Monitoring: Comprehensive observability with metrics, tracing, and real-time alerting
- Cloud-Native Data Processing Pipeline
- Challenge: Large-scale data ingestion, transformation, and analytics for business intelligence
- Technology Stack: Spring Boot, Apache Kafka, Apache Spark, Elasticsearch, Kubernetes
- Features: Real-time stream processing, batch processing, machine learning integration
- Cloud Integration: Multi-cloud deployment with auto-scaling and cost optimization
- DevOps: Complete GitOps workflow with infrastructure as code and automated deployment
Portfolio Presentation Standards
Professional Documentation Framework:
Enterprise Java Project Documentation:
Architecture Overview:
– System architecture diagram with service interactions
– Technology stack justification and selection rationale
– Scalability and performance considerations
– Security implementation and data protection measures
Technical Implementation:
– Design patterns utilized and architectural decisions
– Database design with entity relationship diagrams
– API documentation with OpenAPI specifications
– Code samples demonstrating advanced Java features
Performance and Scalability:
– Load testing results and performance benchmarks
– Scalability testing with concurrent user simulations
– Memory usage analysis and optimization strategies
– Response time improvements and throughput metrics
DevOps and Deployment:
– Containerization strategy with Docker optimization
– Kubernetes deployment with helm charts
– CI/CD pipeline implementation and automation
– Monitoring and observability implementation
Business Impact:
– Problem solved and business value delivered
– Performance improvements and efficiency gains
– Cost savings through optimization and automation
– User experience improvements and satisfaction metrics
6. Job Search Strategy
Resume Optimization for Advanced Java Roles
Technical Skills Section:

🧠 Prepare for top companies—Practice 200+ Java, Spring, Microservices, and System Design interview questions.
Project Experience Examples:
High-Performance Microservices Platform
- Challenge: Monolithic e-commerce application unable to scale during peak traffic, frequent downtime during promotions
- Solution: Redesigned as microservices architecture with Spring Boot, implemented event-driven communication
- Technical Implementation: 12 microservices with API gateway, service discovery, circuit breakers, distributed caching
- Business Impact: Improved system availability to 99.9%, reduced response times by 65%, enabled independent service scaling
Real-Time Financial Trading System
- Challenge: Legacy trading platform with 500ms+ latency unable to compete in high-frequency trading market
- Solution: Reactive programming with Spring WebFlux, event sourcing, CQRS pattern implementation
- Advanced Features: Sub-millisecond order processing, real-time risk management, distributed market data feeds
- Results: Achieved <10ms average latency, processed 1M+ orders per second, increased trading volume by 180%
Advanced Java Job Market Analysis
High-Demand Role Categories:
- Senior Java Developer (Advanced Skills)
- Salary Range: ₹12-35 LPA
- Open Positions: 8,500+ across India
- Key Skills: Spring Boot, microservices, cloud platforms, performance optimization
- Growth Path: Senior Developer → Technical Lead → Solution Architect → VP Engineering
- Java Solution Architect (Leadership Role)
- Salary Range: ₹25-50 LPA
- Open Positions: 2,100+ across India
- Key Skills: System design, architectural patterns, technology strategy, team leadership
- Growth Path: Solution Architect → Enterprise Architect → CTO → Technical Founder
- Java Performance Engineer (Specialized)
- Salary Range: ₹18-40 LPA
- Open Positions: 1,200+ across India
- Key Skills: JVM tuning, profiling, distributed systems optimization, scalability engineering
- Growth Path: Performance Engineer → Staff Engineer → Principal Engineer → Distinguished Engineer
- Cloud Java Developer (Modern Focus)
- Salary Range: ₹15-38 LPA
- Open Positions: 3,800+ across India
- Key Skills: Kubernetes, serverless, cloud-native patterns, container optimization
- Growth Path: Cloud Developer → Cloud Architect → Platform Engineer → VP Platform
Top Hiring Companies and Opportunities
Technology Product Companies:
- Google India – Large-scale distributed systems, cloud platform development, performance engineering
- Microsoft India – Azure platform services, enterprise Java applications, cloud-native solutions
- Amazon India – E-commerce platform, AWS services, high-scale system development
- Oracle India – Database technologies, enterprise software, cloud infrastructure development
Financial Services and Fintech:
- Goldman Sachs – High-frequency trading systems, risk management platforms, quantitative applications
- JP Morgan Chase – Core banking systems, payment processing, regulatory compliance systems
- Paytm – Payment gateway, wallet services, merchant platform development
- Razorpay – Payment processing, financial APIs, B2B platform development
Indian IT Services and Product Companies:
- TCS – Enterprise Java development, client delivery, digital transformation projects
- Infosys – Java-based consulting, platform development, industry-specific solutions
- Flipkart – E-commerce platform, supply chain systems, customer experience applications
- Ola – Ride-sharing platform, logistics optimization, real-time processing systems
Consulting and System Integration:
- ThoughtWorks – Agile development, modern Java practices, client consulting
- Accenture – Enterprise transformations, Java modernization, cloud migration projects
- Deloitte – Digital consulting, enterprise architecture, technology implementation
- Cognizant – Application modernization, Java development services, maintenance
Interview Preparation Framework
System Design and Architecture:
- “Design a high-scale e-commerce system handling millions of concurrent users”
- Microservices decomposition and service boundaries
- Database sharding and caching strategies
- Load balancing and auto-scaling implementation
- Performance optimization and bottleneck identification
- “Implement a distributed transaction across multiple microservices”
// Saga Pattern Implementation
@Component
public class OrderSagaOrchestrator {
private final PaymentService paymentService;
private final InventoryService inventoryService;
private final ShippingService shippingService;
@SagaOrchestrationStart
public void processOrder(OrderCreatedEvent event) {
SagaManager saga = SagaManager.create(event.getOrderId());
try {
// Step 1: Reserve inventory
saga.choreography()
.step(“reserveInventory”)
.invoke(() -> inventoryService.reserve(event.getItems()))
.compensate(() -> inventoryService.release(event.getItems()))
.and()
// Step 2: Process payment
.step(“processPayment”)
.invoke(() -> paymentService.charge(event.getPayment()))
.compensate(() -> paymentService.refund(event.getPayment()))
.and()
// Step 3: Schedule shipping
.step(“scheduleShipping”)
.invoke(() -> shippingService.schedule(event.getShippingInfo()))
.compensate(() -> shippingService.cancel(event.getShippingInfo()))
.execute();
} catch (SagaExecutionException e) {
log.error(“Order saga failed: {}”, event.getOrderId(), e);
saga.compensate();
}
}
}
Performance and Optimization:
3. “Optimize a Java application experiencing high latency and memory issues”
- JVM profiling and analysis techniques
- Memory leak detection and garbage collection tuning
- Query optimization and database performance
- Caching strategies and implementation
Modern Java and Frameworks:
4. “Implement reactive programming with Spring WebFlux for high-throughput scenarios”
@RestController
public class ReactiveOrderController {
private final OrderService orderService;
@GetMapping(value = “/orders/stream”, produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<OrderEvent> streamOrders() {
return orderService.getOrderStream()
.delayElements(Duration.ofSeconds(1))
.doOnNext(order -> log.info(“Streaming order: {}”, order.getId()))
.onErrorResume(error -> {
log.error(“Error streaming orders”, error);
return Flux.empty();
});
}
@PostMapping(“/orders”)
public Mono<ResponseEntity<Order>> createOrder(@RequestBody CreateOrderRequest request) {
return orderService.createOrder(request)
.map(order -> ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(order))
.onErrorReturn(ResponseEntity.badRequest().build());
}
}
Cloud and DevOps Integration:
5. “Deploy a Java microservices application to Kubernetes with proper monitoring”
- Containerization best practices and optimization
- Kubernetes deployment strategies and service mesh
- Observability implementation with metrics and tracing
- Auto-scaling and resource management
Salary Negotiation and Career Advancement
Advanced Java Value Propositions:
- Technical Leadership – Ability to architect complex systems and mentor development teams
- Performance Expertise – Proven track record of optimizing high-scale applications
- Modern Practices – Experience with cloud-native, containerized, and DevOps-integrated development
- Business Impact – Demonstrated ability to translate business requirements into technical solutions
Negotiation Strategy:
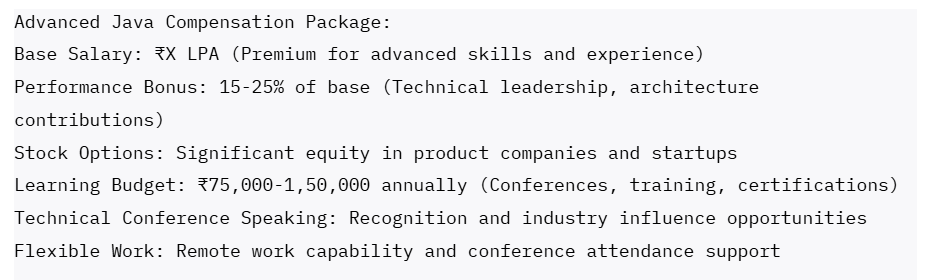
Career Advancement Factors:
- Technical Depth – Advanced Excel mastery with VBA programming and BI tool integration
- Business Acumen – Industry knowledge, financial understanding, strategic thinking
- Communication Skills – Executive presentation, stakeholder management, training delivery
- Process Improvement – Efficiency gains, automation development, best practice establishment
- Continuous Learning – Stay current with Excel updates, new analytical techniques, industry trends
7. Salary Expectations and Career Growth

2025 Compensation Benchmarks by Specialization and Experience
Senior Java Developer Track:
- Senior Java Developer (3-6 years): ₹12-22 LPA
- Lead Java Developer (5-8 years): ₹20-32 LPA
- Principal Java Developer (7-12 years): ₹30-45 LPA
- Distinguished Engineer (10+ years): ₹45-65 LPA
Java Solution Architect Track:
- Solution Architect (5-8 years): ₹25-35 LPA
- Senior Solution Architect (7-12 years): ₹35-50 LPA
- Enterprise Architect (10-15 years): ₹50-70 LPA
- Chief Technology Officer (15+ years): ₹70-120 LPA
Performance Engineering Track:
- Performance Engineer (4-7 years): ₹18-28 LPA
- Senior Performance Engineer (6-10 years): ₹28-40 LPA
- Staff Performance Engineer (8-12 years): ₹40-55 LPA
- Principal Engineer (12+ years): ₹55-80 LPA
Cloud Java Specialist Track:
- Cloud Java Developer (3-6 years): ₹15-25 LPA
- Senior Cloud Developer (5-8 years): ₹25-38 LPA
- Cloud Architect (7-12 years): ₹35-55 LPA
- VP Platform Engineering (12+ years): ₹55-85 LPA
Industry and Geographic Salary Variations
High-Paying Industries:
- Financial Services and Investment Banking – 30-40% premium for low-latency, high-availability systems
- Technology Product Companies – 25-35% premium for platform engineering and scale challenges
- Fintech and Digital Payments – 20-30% premium for security and compliance expertise
- E-commerce and Marketplace – 15-25% premium for high-scale customer-facing applications
Geographic Salary Distribution:
- Bangalore – Technology hub with highest concentration, 20-25% above national average
- Mumbai – Financial services center, 15-22% above national average for fintech roles
- Delhi/NCR – Corporate headquarters and consulting hub, 12-18% above national average
- Pune – Growing tech center, 8-15% above national average with lower cost of living
Career Progression Pathways
Individual Contributor Track:
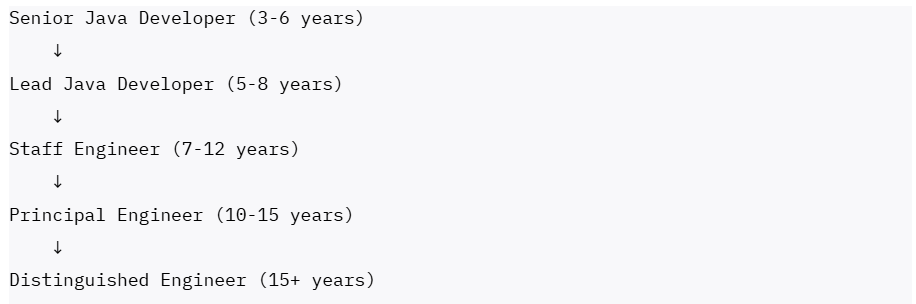
Architecture and Leadership Track:
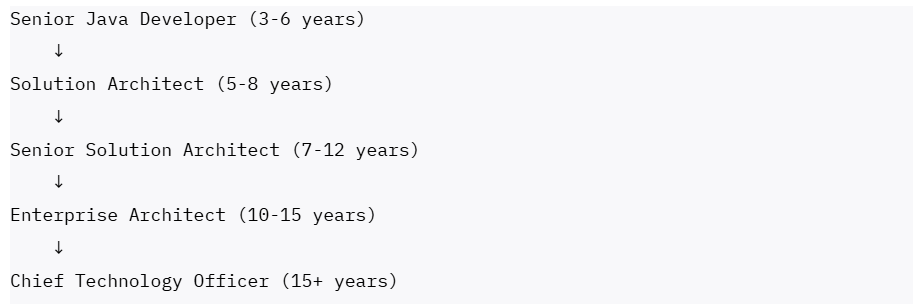
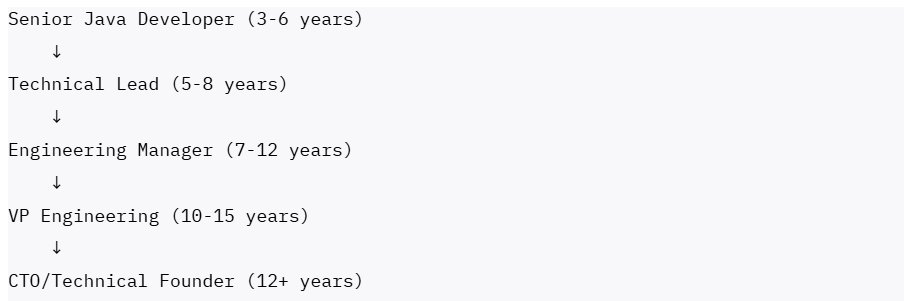
Product and Startup Track:
Skills for Accelerated Career Growth
Technical Mastery (Years 3-6):
- Advanced Spring Ecosystem – Spring Boot, Cloud, Security, WebFlux with performance optimization
- Microservices Architecture – Service design, distributed systems, event-driven architecture
- Cloud-Native Development – Kubernetes, serverless, container optimization, infrastructure as code
- Performance Engineering – JVM tuning, profiling, scalability testing, optimization techniques
System Design and Architecture (Years 6-10):
- Distributed Systems Design – CAP theorem, consistency patterns, fault tolerance, scalability
- Technology Strategy – Architecture decision making, technology evaluation, migration planning
- Cross-Cutting Concerns – Security architecture, observability, developer productivity
- Business Alignment – Translating business requirements into technical architecture decisions
Leadership and Innovation (Years 10+):
- Technical Leadership – Team building, mentoring, technical vision, culture development
- Strategic Planning – Technology roadmap, innovation planning, competitive analysis
- Organization Building – Engineering practices, process improvement, talent development
- Industry Influence – Open source contribution, conference speaking, thought leadership
Emerging Opportunities and Future Trends
High-Growth Advanced Java Specializations:
- Cloud-Native Java – GraalVM native images, Quarkus, serverless Java, container optimization
- Reactive Systems – Event-driven architecture, reactive streams, back-pressure handling
- AI/ML Integration – Java-based ML pipelines, model serving, intelligent applications
- Edge Computing – IoT applications, distributed computing, real-time processing
- Blockchain and DeFi – Distributed ledger applications, smart contracts, cryptocurrency platforms
Market Trends Creating New Opportunities:
- Platform Engineering – Developer productivity platforms, internal developer tools, DevOps automation
- Observability Engineering – Application monitoring, distributed tracing, performance analysis
- Security Engineering – Application security, DevSecOps, compliance automation
- Developer Experience – Tooling, frameworks, and platforms improving developer productivity
📈 Advance your career strategically—Get expert-curated roadmaps for Java Architect, Cloud Engineer & Performance Engineer roles.
8. Success Stories from Our Students
Arjun Mehta – From Junior Developer to Solution Architect
Background: 2 years as junior Java developer with basic Spring knowledge and limited enterprise experience
Challenge: Career stagnation in maintenance projects, wanted to work on challenging architecture problems
Transformation Strategy: Systematic progression through advanced Java topics with focus on microservices and cloud
Timeline: 18 months from course completion to solution architect role
Current Position: Principal Solution Architect at Goldman Sachs India
Salary Progression: ₹6.8 LPA → ₹12.5 LPA → ₹22.8 LPA → ₹38.5 LPA (over 32 months)
Arjun’s Technical Evolution:
- Modern Java Mastery – Upgraded from Java 8 to Java 17+ with functional programming and modern features
- Spring Ecosystem Expertise – Deep knowledge of Spring Boot, Cloud, Security, and reactive programming
- Microservices Architecture – Led decomposition of monolithic applications into scalable microservices
- Performance Engineering – Specialized in high-frequency trading systems requiring sub-millisecond latency
Key Success Factors:
- Hands-On Learning – “I built every concept from scratch, creating real applications that solved actual business problems.”
- Architecture Focus – “I shifted from thinking about individual features to designing complete systems that could scale and evolve.”
- Performance Orientation – “In financial services, performance isn’t optional. I learned to optimize everything from JVM settings to database queries.”
Current Impact: Leading architecture for trading platforms processing $50+ billion daily volume, managing team of 15 senior developers, defining technology strategy for next-generation trading systems.
Priya Sharma – From Support Engineer to Cloud Java Architect
Background: 4 years in production support and maintenance with limited development experience
Challenge: Wanted to transition from support to active development and eventually architecture roles
Strategic Approach: Combined existing system troubleshooting skills with modern cloud-native Java development
Timeline: 22 months from basic Java to cloud architect position
Career Trajectory: Support Engineer → Java Developer → Senior Developer → Cloud Architect
Current Role: Senior Cloud Java Architect at Microsoft India
Compensation and Skill Growth:
- Pre-transition: ₹5.2 LPA (Production Support Engineer)
- Year 1: ₹9.8 LPA (Java Developer with cloud focus)
- Year 2: ₹16.5 LPA (Senior Java Developer with microservices expertise)
- Current: ₹32.8 LPA + stock options (Cloud Architect at Microsoft)
Priya’s Cloud-Native Journey:
- Containerization Expertise – Became expert in Docker, Kubernetes, and container orchestration
- Azure Platform Mastery – Deep knowledge of Azure services with Java integration and optimization
- DevOps Integration – Built CI/CD pipelines and infrastructure as code for Java applications
- Performance at Scale – Optimized applications for cloud environments with auto-scaling and cost efficiency
Cloud Architecture Achievements:
- Migration Leadership – Led migration of 20+ legacy Java applications to cloud-native architecture
- Cost Optimization – Achieved 60% reduction in cloud infrastructure costs through optimization
- Performance Improvement – Improved application response times by 75% through cloud-native patterns
- Team Development – Built and led team of 8 cloud engineers supporting multiple product teams
Success Philosophy: “My support background taught me to think about systems holistically. When I learned modern Java development, I could see how to build applications that were not just functional, but operationally excellent.”
Vikram Patel – From Traditional Enterprise to Fintech Entrepreneur
Background: 6 years as Java developer in traditional enterprise with monolithic applications
Challenge: Felt limited by legacy technologies, wanted to work with cutting-edge fintech solutions
Entrepreneurial Vision: Building real-time payment processing platform for small businesses
Timeline: 24 months from advanced Java learning to successful fintech startup
Business Evolution: Enterprise Developer → Fintech Developer → Technical Co-founder → CEO
Technical Innovation and Business Growth:
- Real-Time Processing – Built payment platform processing 100,000+ transactions per minute
- Regulatory Compliance – Implemented PCI DSS, RBI compliance with automated monitoring
- Scalable Architecture – Event-driven microservices handling peak loads with 99.99% uptime
- AI Integration – Machine learning fraud detection and risk scoring algorithms
Business Achievements:
- Revenue Growth – ₹12 crores ARR within 18 months of product launch
- Client Acquisition – 2,500+ merchant partners across 15 Indian cities
- Team Building – Assembled team of 25 engineers, product managers, and business developers
- Funding Success – Raised ₹8 crores Series A funding from tier-1 venture capital firm
Compensation Evolution:
- Pre-startup: ₹14.8 LPA (Senior Java Developer at enterprise company)
- 6 months: ₹18.5 LPA (Technical Lead at fintech startup)
- 12 months: ₹28.5 LPA + equity (Technical Co-founder)
- Current: ₹45+ LPA equivalent (CEO with significant equity value)
Entrepreneurial Insights: “Advanced Java skills gave me the technical confidence to build a fintech platform that could compete with established players. Understanding performance, security, and scalability from the ground up was crucial for earning customer and investor trust.”
9. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Challenge 1: Transitioning from Legacy Java to Modern Enterprise Development
Problem: Many Java developers are stuck with older versions and frameworks, limiting career growth
Impact: Reduced job opportunities, lower salary potential, difficulty with modern project requirements
Symptoms: Using Java 8 or older, unfamiliarity with Spring Boot, monolithic thinking, limited cloud knowledge
Modernization Strategy:
Phase 1: Modern Java Language Features (4-6 weeks)
// Legacy Java 8 approach
List<String> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (Customer customer : customers) {
if (customer.isActive() && customer.getOrderCount() > 10) {
results.add(customer.getName().toUpperCase());
}
}
// Modern Java 17+ approach with streams and modern features
var results = customers.stream()
.filter(Customer::isActive)
.filter(customer -> customer.getOrderCount() > 10)
.map(customer -> customer.getName().toUpperCase())
.toList(); // Java 16+ feature
// Using modern Java features
public record CustomerSummary(String name, int orderCount, boolean active) {
public CustomerSummary {
if (orderCount < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(“Order count cannot be negative”);
}
}
}
// Pattern matching (Java 17+)
public String processPayment(Payment payment) {
return switch (payment) {
case CreditCardPayment(var number, var cvv) ->
“Processing credit card ending in ” + number.substring(number.length() – 4);
case DigitalWalletPayment(var walletId) ->
“Processing digital wallet payment: ” + walletId;
case BankTransferPayment(var accountNumber, var routingNumber) ->
“Processing bank transfer from account: ” + accountNumber;
default -> “Unknown payment type”;
};
}
Phase 2: Spring Boot Migration (6-8 weeks)
- Configuration Modernization – Move from XML configuration to annotation-based and auto-configuration
- Dependency Management – Migrate to Spring Boot starters and simplified dependency management
- Testing Improvements – Adopt Spring Boot Test annotations and modern testing practices
- Monitoring Integration – Implement Actuator endpoints and production monitoring
Challenge 2: Designing Scalable Microservices Architecture
Problem: Difficulty decomposing monolithic applications into well-designed microservices
Challenge: Service boundaries, data consistency, inter-service communication, operational complexity
Solution: Systematic approach to microservices design and implementation
Microservices Design Framework:
Domain-Driven Decomposition:
// Bounded Context Implementation
@Entity
@Table(name = “orders”)
public class Order {
// Order aggregate root with business invariants
private UUID customerId; // Reference to Customer bounded context
private List<OrderItem> items;
private OrderStatus status;
private Money totalAmount;
// Business methods that maintain invariants
public void addItem(ProductId productId, Quantity quantity, Money unitPrice) {
if (status != OrderStatus.DRAFT) {
throw new OrderModificationException(“Cannot modify confirmed order”);
}
items.add(new OrderItem(productId, quantity, unitPrice));
recalculateTotal();
// Publish domain event
DomainEventPublisher.publish(new ItemAddedToOrder(this.id, productId, quantity));
}
public void confirm() {
if (items.isEmpty()) {
throw new OrderValidationException(“Cannot confirm empty order”);
}
status = OrderStatus.CONFIRMED;
DomainEventPublisher.publish(new OrderConfirmed(this.id, customerId, totalAmount));
}
}
// Service Interface with Circuit Breaker
@Component
public class PaymentService {
private final PaymentClient paymentClient;
private final CircuitBreaker circuitBreaker;
@Retryable(value = {TransientPaymentException.class}, maxAttempts = 3)
@CircuitBreaker(name = “payment-service”, fallbackMethod = “fallbackPayment”)
public PaymentResult processPayment(PaymentRequest request) {
return circuitBreaker.executeSupplier(() -> {
return paymentClient.processPayment(request);
});
}
public PaymentResult fallbackPayment(PaymentRequest request, Exception ex) {
// Queue for later processing or use alternative payment method
paymentQueue.enqueue(request);
return PaymentResult.queued(request.getOrderId());
}
}
Challenge 3: Achieving High Performance in Java Applications
Problem: Java applications not meeting performance requirements for enterprise workloads
Impact: Poor user experience, increased infrastructure costs, scalability limitations
Solution: Systematic performance engineering approach
Performance Optimization Framework:
JVM Optimization:
# Modern JVM flags for high-performance applications
-XX:+UseG1GC
-XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=50
-XX:+UseStringDeduplication
-XX:+OptimizeStringConcat
-Xms4g -Xmx4g # Consistent heap size
-XX:+AlwaysPreTouch # Pre-touch memory
-XX:+UseLargePages # Use large memory pages
-XX:+FlightRecorder # Enable profiling
Application-Level Optimization:
// Efficient data processing with parallel streams
@Service
public class OrderAnalyticsService {
@Cacheable(value = “order-analytics”, key = “#criteria.hashCode()”)
public OrderAnalytics calculateAnalytics(AnalyticsCriteria criteria) {
return orders.parallelStream()
.filter(criteria::matches)
.collect(Collectors.teeing(
Collectors.summingDouble(Order::getTotalAmount),
Collectors.counting(),
(totalRevenue, orderCount) -> new OrderAnalytics(totalRevenue, orderCount)
));
}
// Reactive programming for high-throughput scenarios
@GetMapping(value = “/orders/stream”, produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<OrderDto> streamOrders(@RequestParam String customerId) {
return orderService.findOrdersByCustomerId(customerId)
.subscribeOn(Schedulers.boundedElastic())
.map(orderMapper::toDto)
.onBackpressureBuffer(1000)
.doOnError(error -> log.error(“Error streaming orders”, error));
}
}
// Database optimization with proper indexing and queries
@Repository
public class OrderRepository {
@Query(value = “””
SELECT o FROM Order o
JOIN FETCH o.items i
JOIN FETCH i.product
WHERE o.customerId = :customerId
AND o.createdAt >= :fromDate
ORDER BY o.createdAt DESC
“””)
List<Order> findRecentOrdersWithItems(@Param(“customerId”) UUID customerId,
@Param(“fromDate”) LocalDateTime fromDate);
// Native query for complex analytics
@Query(value = “””
SELECT
DATE_TRUNC(‘day’, created_at) as order_date,
COUNT(*) as order_count,
SUM(total_amount) as total_revenue
FROM orders
WHERE created_at >= :fromDate
GROUP BY DATE_TRUNC(‘day’, created_at)
ORDER BY order_date
“””, nativeQuery = true)
List<DailyOrderStats> getDailyOrderStatistics(@Param(“fromDate”) LocalDateTime fromDate);
}
Challenge 4: Implementing Comprehensive Testing Strategies
Problem: Inadequate testing leading to production bugs and difficulty refactoring
Challenge: Complex enterprise applications, microservices testing, integration testing
Solution: Multi-layered testing approach with modern tools
Comprehensive Testing Strategy:
// Unit testing with modern approaches
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
class OrderServiceTest {
@Mock
private OrderRepository orderRepository;
@Mock
private PaymentService paymentService;
@InjectMocks
private OrderService orderService;
@Test
void shouldCreateOrderSuccessfully() {
// Given
var createRequest = new CreateOrderRequest(
UUID.randomUUID(),
List.of(new OrderItemRequest(“product-1”, 2, BigDecimal.valueOf(100)))
);
var savedOrder = Order.builder()
.id(UUID.randomUUID())
.customerId(createRequest.customerId())
.status(OrderStatus.CONFIRMED)
.build();
when(orderRepository.save(any(Order.class))).thenReturn(savedOrder);
when(paymentService.processPayment(any())).thenReturn(PaymentResult.success());
// When
var result = orderService.createOrder(createRequest);
// Then
assertThat(result.getStatus()).isEqualTo(OrderStatus.CONFIRMED);
verify(paymentService).processPayment(any());
}
}
// Integration testing with Spring Boot Test
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@Testcontainers
class OrderControllerIntegrationTest {
@Container
static PostgreSQLContainer<?> postgres = new PostgreSQLContainer<>(“postgres:14”)
.withDatabaseName(“testdb”)
.withUsername(“test”)
.withPassword(“test”);
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate restTemplate;
@DynamicPropertySource
static void configureProperties(DynamicPropertyRegistry registry) {
registry.add(“spring.datasource.url”, postgres::getJdbcUrl);
registry.add(“spring.datasource.username”, postgres::getUsername);
registry.add(“spring.datasource.password”, postgres::getPassword);
}
@Test
void shouldCreateOrderEndToEnd() {
// Given
var request = new CreateOrderRequest(
UUID.randomUUID(),
List.of(new OrderItemRequest(“product-1”, 1, BigDecimal.valueOf(50)))
);
// When
var response = restTemplate.postForEntity(“/api/v1/orders”, request, OrderResponse.class);
// Then
assertThat(response.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.CREATED);
assertThat(response.getBody().getStatus()).isEqualTo(OrderStatus.CONFIRMED);
}
}
10. Getting Started: Your Action Plan
Week 1: Assessment and Modern Java Setup
Day 1-2: Java Environment and Tools Setup
- Modern Java Installation – Install OpenJDK 17 or 21 with proper JAVA_HOME configuration
- IDE Configuration – IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate or VS Code with Java extensions
- Build Tools – Maven 3.8+ and Gradle 7+ installation and configuration
- Version Control – Git setup with proper .gitignore templates for Java projects
Day 3-4: Current Skills Assessment and Gap Analysis
- Java Knowledge Audit – Assess current Java version knowledge and framework familiarity
- Spring Framework Evaluation – Identify gaps in Spring Boot, Data, Security knowledge
- Architecture Understanding – Evaluate experience with microservices, distributed systems
- Cloud and DevOps Readiness – Assess containerization and cloud platform knowledge
Day 5-7: Learning Environment and Project Setup
- Practice Environment – Set up local development environment with databases and message queues
- Sample Project Template – Create Spring Boot project template with common dependencies
- Learning Resources – Bookmark official documentation, tutorials, and community resources
- Professional Network – Join Java communities, LinkedIn groups, and local meetups
Month 1: Modern Java and Spring Boot Mastery
Week 1-2: Java 17+ Modern Features
- Functional Programming – Streams, lambdas, optional, method references, collector patterns
- Modern Language Features – Records, sealed classes, pattern matching, text blocks
- Concurrent Programming – CompletableFuture, parallel streams, virtual threads concepts
- Performance Considerations – Memory management, garbage collection basics, profiling introduction
Week 3-4: Spring Boot Foundation
- Spring Boot Basics – Auto-configuration, starters, profiles, configuration properties
- Web Development – RESTful APIs, validation, exception handling, content negotiation
- Data Access – Spring Data JPA, repository patterns, query methods, transaction management
- Testing – Unit testing, integration testing, test slices, mock frameworks
Month-End Project: “Modern Spring Boot REST API”
- Build comprehensive REST API with modern Java features
- Implement proper validation, exception handling, and security
- Add comprehensive testing with unit and integration tests
- Document API with OpenAPI and deploy with proper configuration
Month 2: Advanced Spring Framework and Database Integration
Week 1-2: Advanced Spring Features
- Spring Security – Authentication, authorization, JWT tokens, method-level security
- Spring Data Advanced – Custom repositories, specifications, auditing, projections
- Caching – Spring Cache abstraction, Redis integration, cache strategies
- Async Processing – @Async, TaskExecutor, event-driven programming
Week 3-4: Database Design and Optimization
- JPA and Hibernate – Advanced mapping, lazy loading, N+1 problem solutions
- Database Performance – Query optimization, indexing strategies, connection pooling
- Data Migration – Flyway integration, versioned schema changes, data transformation
- Transaction Management – Isolation levels, propagation, distributed transactions
Advanced Learning Goals:
- Enterprise Patterns – Implement repository, service layer, and DTO patterns
- Performance Optimization – Profile and optimize database queries and application performance
- Security Implementation – Comprehensive authentication and authorization system
- Production Readiness – Logging, monitoring, health checks, configuration management
Month 3: Microservices and Distributed Systems
Week 1-2: Microservices Architecture
- Service Decomposition – Domain-driven design, bounded contexts, service boundaries
- Spring Cloud – Service discovery, circuit breakers, configuration management
- API Gateway – Request routing, load balancing, authentication, rate limiting
- Inter-Service Communication – REST clients, service mesh, async messaging
Week 3-4: Event-Driven Architecture
- Message Queues – RabbitMQ, Apache Kafka integration with Spring
- Event Sourcing – Event store implementation, event replay, snapshotting
- Saga Patterns – Distributed transaction management, compensating actions
- CQRS Implementation – Command query separation, read/write model optimization
Practical Implementation Focus:
- Microservices Platform – Build multiple services with proper communication patterns
- Distributed Data Management – Implement eventual consistency and saga patterns
- Observability – Add distributed tracing, metrics, and centralized logging
- Resilience Patterns – Circuit breakers, bulkheads, timeouts, and retry mechanisms
Long-Term Milestones (6-12 Months)
Advanced Technical Expertise:
- Cloud-Native Development – Kubernetes deployment, serverless integration, cloud platform mastery
- Performance Engineering – JVM tuning, application profiling, scalability optimization
- Solution Architecture – Enterprise system design, technology selection, architectural decision making
- DevOps Integration – CI/CD pipelines, infrastructure as code, monitoring and alerting
Professional Development and Portfolio:
- Enterprise Portfolio – 4-6 comprehensive projects demonstrating advanced Java capabilities
- Open Source Contribution – Contribute to Spring projects or create useful Java libraries
- Technical Leadership – Mentor junior developers, lead technical discussions, present at meetups
- Industry Recognition – Speak at conferences, write technical articles, build professional brand
Career Advancement Preparation:
- System Design Mastery – Ability to architect complex distributed systems
- Performance Expertise – Proven track record optimizing high-scale applications
- Technology Leadership – Experience evaluating and adopting new technologies and practices
- Business Impact Focus – Portfolio demonstrating measurable business outcomes from technical work
Conclusion
Advanced Java Enterprise developer represents the pinnacle of Java expertise, combining deep technical knowledge with architectural thinking and business acumen to create sophisticated, scalable enterprise solutions. As organizations continue to rely on Java for their most critical business applications and digital transformation initiatives, advanced Java professionals enjoy exceptional career opportunities, premium compensation, and the satisfaction of solving complex technical challenges that directly impact business success.
The journey from basic Java developer to Advanced Java Enterprise developer architect typically requires 5-7 months of intensive learning and hands-on practice, but the investment delivers exceptional returns through immediate career advancement opportunities and long-term growth potential. Unlike basic Java development that focuses on individual features, Advanced Java Enterprise developer encompasses system design, performance optimization, and architectural decision-making that shapes entire platforms and business capabilities.
Critical Success Factors for Advanced Java Excellence:
- Modern Technology Adoption – Master current Java versions, Spring Boot ecosystem, and cloud-native patterns
- System Design Thinking – Develop ability to architect scalable, maintainable distributed systems
- Performance Focus – Build expertise in optimization, monitoring, and scalability engineering
- Business Impact Orientation – Connect technical decisions to measurable business outcomes and competitive advantages
- Continuous Learning Commitment – Stay current with rapid evolution in Java ecosystem and enterprise patterns
The most successful advanced Java enterprise developer combine deep technical expertise with architectural vision and business understanding. As enterprises increasingly adopt microservices, cloud-native architectures, and real-time processing requirements, Java professionals who can design and implement sophisticated solutions will be most valued by organizations.
Whether you choose solution architecture leadership, performance engineering specialization, cloud-native platform development, or technical product management, advanced Java skills provide a foundation for the highest levels of technical leadership and compensation in software development.
Ready to advance your Java career and become an enterprise architecture expert?
Explore our comprehensive Advanced Java Enterprise Program designed for experienced Java developers seeking architectural expertise:
5-month intensive curriculum covering modern Java, Spring ecosystem, microservices, and cloud-native development
Hands-on architecture projects with real enterprise scenarios, performance optimization, and scalability challenges
Industry-standard tools and practices including Docker, Kubernetes, CI/CD, monitoring, and observability
Portfolio development with complex distributed systems, high-performance applications, and architectural documentation
Job placement assistance with resume optimization, system design interview preparation, and architect-level role connections
Expert mentorship from senior Java architects and principal engineers with 15+ years enterprise experience
Lifetime learning support including Java ecosystem updates, architectural pattern evolution, and career advancement guidance
Unsure which advanced Java specialization aligns with your experience and career goals? Schedule a free Java architecture consultation with our senior Java architects to receive personalized guidance and a customized learning roadmap.
Connect with our advanced Java community: Join our Advanced Java Developer WhatsApp Group with 180+ experienced developers, architects, and technical leads for advanced discussions, architecture reviews, and career guidance.
