How to Become a Software Testing Engineer: Complete Career Guide 2025 [₹7L Average Salary]
Master quality assurance and become the guardian of software reliability
Software testing engineers are experiencing unprecedented demand as organizations prioritize software quality and user experience, with average salaries ranging from ₹3.5-15 LPA in India and senior automation engineers earning ₹20+ LPA. As applications become more complex and user expectations rise, the ability to ensure software quality, performance, and security has become one of the most critical skills in software development.
Whether you’re a manual tester looking to upgrade to automation, a developer seeking quality assurance expertise, or a fresh graduate entering the QA field, this comprehensive guide provides the proven roadmap to building a successful software testing career. Having trained over 350 testing professionals at Frontlines EduTech with an 87% job placement rate, I’ll share the strategies that consistently deliver results in the evolving QA landscape.
What you’ll master in this guide:
- Complete testing roadmap from manual to automation expert
- Essential tools and frameworks for modern QA practices
- Portfolio projects demonstrating real-world testing scenarios
- Certification paths and interview preparation strategies
- Career advancement opportunities in testing and quality assurance
⚡ Launch Your Software Testing Career
Learn Manual + Automation Testing with our Software Testing Course
1. What is Software Testing?
Software testing is the systematic process of evaluating and verifying that software applications, systems, and components meet specified requirements and function correctly under various conditions. Modern software testing encompasses manual testing techniques, automated testing frameworks, performance optimization, security validation, and quality assurance processes that ensure reliable software delivery.
Core Responsibilities of Testing Engineers:
Manual Testing Excellence:
- Test Planning and Design – Create comprehensive test strategies, test cases, and test data
- Functional Testing – Verify application features work according to specifications
- User Experience Testing – Ensure intuitive interfaces and smooth user journeys
- Regression Testing – Validate that new changes don’t break existing functionality
Test Automation and Frameworks:
- Automation Strategy – Identify test cases suitable for automation and ROI analysis
- Framework Development – Build reusable, maintainable test automation frameworks
- CI/CD Integration – Implement automated testing in deployment pipelines
- Performance Testing – Load, stress, and scalability testing for applications
Quality Assurance and Process:
- Defect Management – Bug tracking, prioritization, and lifecycle management
- Process Improvement – Analyze testing metrics and optimize QA processes
- Tool Evaluation – Research and implement testing tools and technologies
- Stakeholder Communication – Report quality status to development teams and management
Types of Software Testing:
Functional Testing Categories:
- Unit Testing – Individual component verification by developers
- Integration Testing – Module interaction and data flow validation
- System Testing – Complete application functionality verification
- User Acceptance Testing – Business requirement validation by end users
Non-Functional Testing Areas:
- Performance Testing – Speed, scalability, and resource utilization analysis
- Security Testing – Vulnerability assessment and data protection verification
- Usability Testing – User experience and interface evaluation
- Compatibility Testing – Cross-platform, browser, and device validation
2. Why Choose Software Testing in 2025?
Growing Importance of Quality Assurance
According to World Quality Report 2025, organizations are investing 23% more in quality assurance as software failures become increasingly costly. In India specifically, the testing services market is projected to grow at 12.4% CAGR, driven by:
Digital Transformation Initiatives:
- Banking and Financial Services – HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank implementing rigorous testing for digital banking platforms
- E-commerce Growth – Flipkart, Amazon India scaling testing infrastructure for high-volume transactions
- Healthcare Digitization – Apollo Digital, 1mg requiring comprehensive testing for patient safety
- Government Services – Digital India initiatives demanding robust testing for citizen services
Quality-First Development Culture:
- Shift-Left Testing – Early involvement of testing in development lifecycle
- DevOps Integration – Continuous testing in automated deployment pipelines
- User Experience Focus – Rigorous testing for customer satisfaction and retention
- Regulatory Compliance – Banking, healthcare, and financial sectors requiring extensive validation
Competitive Salary Packages and Job Security
Testing professionals enjoy stable career growth with competitive compensation:
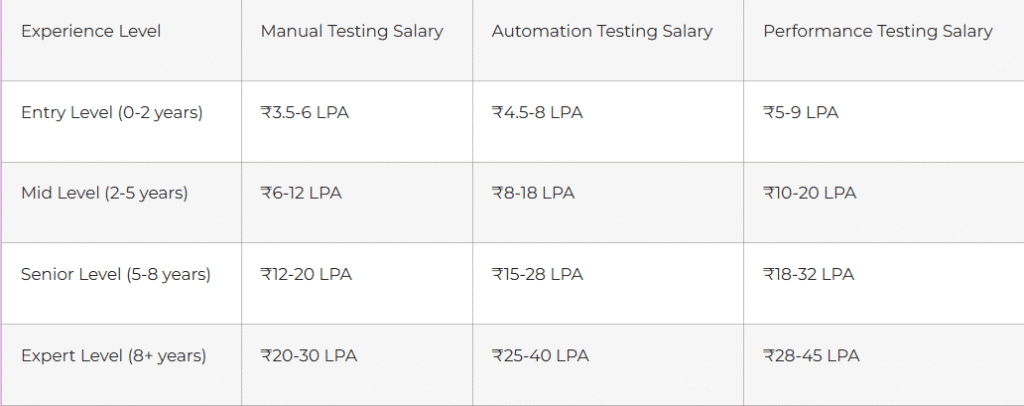
Source: PayScale India 2025, Glassdoor QA Salaries
Recession-Resistant Career Path
Software testing is considered essential for business continuity:
- Risk Mitigation – Organizations cannot afford software failures in competitive markets
- Cost of Poor Quality – Prevention is more cost-effective than post-release bug fixes
- Regulatory Requirements – Compliance mandates comprehensive testing documentation
- Customer Trust – Quality assurance directly impacts brand reputation and customer retention
Multiple Career Specialization Options
Testing offers diverse career paths:
- Test Automation Engineering – Framework development and CI/CD integration
- Performance Engineering – Scalability and optimization specialization
- Security Testing – Cybersecurity and vulnerability assessment
- Mobile Testing – iOS and Android application validation
- API Testing – Microservices and integration testing expertise
3. Complete Learning Roadmap (4-6 Months)
Phase 1: Testing Fundamentals and Manual Testing (Month 1-2)
Software Testing Basics (2-3 weeks)
Understanding testing principles is fundamental before diving into tools and automation:
- Testing Principles – Seven principles of software testing, testing objectives
- SDLC and STLC – Software development lifecycle integration, testing lifecycle phases
- Test Design Techniques – Equivalence partitioning, boundary value analysis, decision tables
- Testing Types – Functional vs non-functional, black box vs white box, static vs dynamic
Manual Testing Mastery (3-4 weeks)
- Test Planning – Test strategy document, test plan creation, effort estimation
- Test Case Design – Writing effective test cases, test data preparation, traceability matrix
- Test Execution – Test case execution, defect logging, test reporting
- Defect Management – Bug lifecycle, severity vs priority, defect tracking tools
Practical Manual Testing Projects:
- E-commerce Website Testing – Complete functional testing of shopping cart, payment, user registration
- Mobile App Testing – Android/iOS application testing for usability and functionality
- API Testing – RESTful service validation using Postman
Testing Documentation and Process (1-2 weeks)
- Test Documentation – Test cases, test scenarios, bug reports, test summary reports
- Testing Metrics – Defect density, test coverage, defect detection percentage
- Testing Process – Entry/exit criteria, test environment setup, release criteria
Phase 2: Test Automation Fundamentals (Month 2-3)
Programming for Testers (3-4 weeks)
Basic programming knowledge is essential for automation:
- Java/Python Basics – Variables, data types, control structures, object-oriented concepts
- Web Technologies – HTML, CSS, JavaScript basics, DOM understanding
- Database Concepts – SQL queries, database connectivity, data validation
- Version Control – Git basics, repository management, collaboration workflows
Selenium WebDriver Mastery (4-5 weeks)
- Selenium Setup – WebDriver installation, IDE configuration, browser drivers
- Locator Strategies – ID, name, class, XPath, CSS selectors, best practices
- WebDriver Actions – Click, send keys, dropdown handling, alert handling, window switching
- Synchronization – Implicit wait, explicit wait, fluent wait, custom wait conditions
Framework Development (2-3 weeks)
- Page Object Model – Design pattern for maintainable test code
- Data-Driven Testing – Excel, CSV, JSON data sources for test parameterization
- TestNG/JUnit – Test execution frameworks, annotations, parallel execution
- Reporting – ExtentReports, Allure, custom HTML reports
Automation Projects:
- E-commerce Automation Suite – Complete user journey automation with data-driven approach
- Cross-Browser Testing – Multi-browser execution using Selenium Grid
- API Automation Framework – REST API testing using RestAssured or similar tools
Phase 3: Advanced Testing Specializations (Month 3-5)
API and Microservices Testing (3-4 weeks)
- REST API Concepts – HTTP methods, status codes, request/response structures
- API Testing Tools – Postman advanced features, Newman for automation
- RestAssured Framework – Java-based API automation, JSON/XML validation
- Performance API Testing – Load testing APIs, response time validation
Performance Testing (3-4 weeks)
- Performance Testing Concepts – Load, stress, spike, volume, endurance testing
- JMeter Mastery – Test plan creation, thread groups, assertions, correlation
- Performance Analysis – Response time analysis, throughput measurement, resource utilization
- Performance Monitoring – Server monitoring, database performance, network analysis
Mobile Testing (2-3 weeks)
- Mobile Testing Types – Functional, usability, performance, security testing
- Appium Framework – Mobile automation for Android and iOS applications
- Device Testing – Real device vs simulator/emulator testing strategies
- Mobile-Specific Scenarios – Interruptions, network conditions, battery testing
Advanced Specialization Projects:
- Performance Testing Suite – Complete load testing framework with monitoring and reporting
- Mobile App Automation – Cross-platform mobile testing framework
- API Testing Framework – Comprehensive REST API validation with security testing
Phase 4: CI/CD Integration and Advanced Topics (Month 5-6)
DevOps and CI/CD Integration (2-3 weeks)
- Jenkins Integration – Automated test execution, build triggers, reporting
- Docker for Testing – Containerized test environments, parallel execution
- Cloud Testing – AWS Device Farm, BrowserStack, Sauce Labs integration
- Pipeline as Code – Jenkinsfile, GitLab CI, Azure DevOps YAML pipelines
Security Testing Basics (2-3 weeks)
- Security Testing Concepts – Authentication, authorization, data validation
- OWASP Top 10 – Common security vulnerabilities and testing approaches
- Security Testing Tools – Burp Suite, OWASP ZAP, security scanning integration
- Compliance Testing – GDPR, PCI DSS, SOX compliance validation requirements
Test Management and Leadership (1-2 weeks)
- Test Strategy – Organizational test strategy, risk-based testing
- Team Management – Test team coordination, skill development, resource planning
- Stakeholder Management – Communication with developers, product owners, management
- Process Improvement – Test process optimization, metrics analysis, tool evaluation
🗺️ Follow the Complete Testing Roadmap
Beginner → Manual → Automation → Advanced QA. Your structured path Open Roadmap →
4. Essential Tools and Technologies
Core Testing Tools
Manual Testing Tools:
- Test Management: JIRA, TestRail, Zephyr, qTest for test case management
- Bug Tracking: JIRA, Bugzilla, Mantis for defect lifecycle management
- API Testing: Postman, Insomnia for manual API validation
- Browser Testing: Chrome DevTools, Firefox Developer Tools for debugging
Test Automation Frameworks:
- Selenium WebDriver – Most popular web automation framework
- Appium – Mobile application automation for iOS and Android
- Cypress – Modern web testing framework with advanced debugging
- Playwright – Cross-browser automation with advanced capabilities
Programming Languages for Testing
Java (Most Popular):
- Advantages: Strong ecosystem, enterprise adoption, extensive libraries
- Frameworks: TestNG, JUnit, RestAssured, Selenium
- Learning Resources: Oracle documentation, extensive community support
Python (Growing Adoption):
- Advantages: Easy syntax, rapid development, data analysis capabilities
- Frameworks: PyTest, unittest, requests, Selenium Python bindings
- Use Cases: API testing, data validation, machine learning integration
JavaScript/TypeScript:
- Advantages: Native web technology, modern framework support
- Frameworks: Jest, Mocha, WebdriverIO, Cypress, Playwright
- Use Cases: Frontend testing, Node.js API testing, modern web applications
Performance Testing Tools
Apache JMeter:
- Open Source – Free performance testing with extensive plugin ecosystem
- Protocol Support – HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SOAP, REST API testing
- Scalability – Distributed testing for high-load scenarios
- Reporting – Comprehensive performance analysis and reporting
Commercial Tools:
- LoadRunner – Enterprise-grade performance testing platform
- BlazeMeter – Cloud-based load testing with JMeter compatibility
- Gatling – High-performance load testing with Scala-based scripts
CI/CD Integration Tools
Jenkins:
- Open Source – Free automation server with extensive plugin library
- Pipeline Support – Declarative and scripted pipeline configurations
- Integration – Git, Docker, cloud platforms, notification systems
- Scalability – Master-slave architecture for distributed builds
Cloud-Based Solutions:
- GitHub Actions – Integrated CI/CD with GitHub repositories
- Azure DevOps – Microsoft ecosystem integration with comprehensive tooling
- GitLab CI – Built-in CI/CD with GitLab source control
5. Building Your Testing Portfolio
Portfolio Strategy and Structure
Comprehensive Testing Expertise:
Demonstrate versatility across different testing types and technologies:
- Manual Testing Documentation – Test plans, test cases, bug reports, test metrics
- Automation Frameworks – Reusable, maintainable test automation solutions
- Performance Testing – Load testing scenarios with analysis and recommendations
- API Testing – REST API validation with security and performance considerations
Foundation Level Projects (Months 1-2)
- E-commerce Website Manual Testing
- Test Scope: User registration, product search, shopping cart, payment processing, order management
- Deliverables: Test plan, 100+ test cases, traceability matrix, bug reports
- Tools Used: Excel/Google Sheets for test case management, browser developer tools
- Business Value: Comprehensive functional validation ensuring user experience quality
- Documentation: Test strategy document, test execution summary, defect analysis report
- Mobile Application Testing
- Platforms: Android and iOS native applications
- Testing Types: Functional, usability, compatibility, performance, security
- Test Scenarios: Device-specific testing, network conditions, interruption scenarios
- Tools: Android Studio, Xcode, Charles Proxy for network simulation
- Outcomes: Mobile testing checklist, device compatibility matrix, performance benchmarks
Intermediate Level Projects (Months 3-4)
- Selenium Automation Framework
- Framework Architecture: Page Object Model with Page Factory pattern
- Technology Stack: Java, Selenium WebDriver, TestNG, Maven, ExtentReports
- Features: Cross-browser execution, data-driven testing, parallel execution, reporting
- CI/CD Integration: Jenkins pipeline for automated execution and reporting
Implementation Example:
// Page Object Model implementation
public class LoginPage extends BasePage {
@FindBy(id = “username”)
private WebElement usernameField;
@FindBy(id = “password”)
private WebElement passwordField;
@FindBy(xpath = “//button[@type=’submit’]”)
private WebElement loginButton;
public void login(String username, String password) {
waitForElement(usernameField);
usernameField.sendKeys(username);
passwordField.sendKeys(password);
loginButton.click();
}
public boolean isLoginSuccessful() {
return driver.getCurrentUrl().contains(“/dashboard”);
}
}
// Test class with TestNG
public class LoginTests extends BaseTest {
@Test(dataProvider = “loginData”)
public void testValidLogin(String username, String password) {
LoginPage loginPage = new LoginPage(driver);
loginPage.login(username, password);
Assert.assertTrue(loginPage.isLoginSuccessful(),
“Login failed for valid credentials”);
}
@DataProvider(name = “loginData”)
public Object[][] getLoginData() {
return ExcelUtils.getTestData(“login_data.xlsx”, “ValidLogins”);
}
}
- API Testing Framework
- Technology Stack: RestAssured, TestNG, JSON Schema Validation, Allure Reports
- Test Coverage: CRUD operations, authentication, error handling, data validation
- Security Testing: SQL injection, XSS prevention, authentication bypass attempts
- Performance Integration: Response time validation, concurrent user simulation
Advanced Level Projects (Months 5-6)
- Performance Testing Suite
- Application Under Test: Web application with database backend
- Test Scenarios: Load testing, stress testing, spike testing, endurance testing
- Monitoring: Server resources, database performance, network utilization
- Analysis and Reporting: Performance bottleneck identification, scalability recommendations
JMeter Test Plan Structure:
Performance Test Plan
├── Thread Groups
│ ├── Normal Load (100 users, 10 minutes)
│ ├── Peak Load (500 users, 5 minutes)
│ └── Stress Load (1000 users, 3 minutes)
├── HTTP Request Samplers
│ ├── Login Request
│ ├── Search Products
│ ├── Add to Cart
│ └── Checkout Process
├── Listeners
│ ├── Response Time Graph
│ ├── Throughput Monitor
│ └── Error Rate Analysis
└── Assertions
├── Response Time < 3000ms
├── Success Rate > 95%
└── Error Rate < 1%
- CI/CD Integrated Testing Pipeline
- Pipeline Components: Source control integration, automated build, test execution, reporting, deployment
- Testing Stages: Unit tests, integration tests, UI automation, API tests, performance tests
- Quality Gates: Code coverage thresholds, test pass rates, performance benchmarks
- Notification System: Email reports, Slack integration, dashboard visualization
Portfolio Presentation and Documentation
GitHub Repository Structure:
testing-portfolio/
├── README.md (Portfolio overview and navigation)
├── manual-testing/
│ ├── test-plans/
│ ├── test-cases/
│ ├── bug-reports/
│ └── test-metrics/
├── automation-frameworks/
│ ├── selenium-java-framework/
│ ├── api-testing-framework/
│ └── mobile-automation/
├── performance-testing/
│ ├── jmeter-scripts/
│ ├── performance-reports/
│ └── monitoring-setup/
├── ci-cd-integration/
│ ├── jenkins-pipelines/
│ ├── docker-configs/
│ └── cloud-integration/
└── certifications/
├── istqb-foundation.pdf
└── selenium-certification.pdf
Professional Documentation Standards:
- Test Strategy Documents – Comprehensive approach and methodology
- Framework Architecture – Design decisions and implementation guidelines
- Execution Reports – Test results with analysis and recommendations
- Performance Analysis – Bottleneck identification and optimization suggestions
- Lessons Learned – Challenges faced, solutions implemented, best practices
Live Demo Environment:
- Deployed Applications – Live applications for testing demonstration
- Automation Execution – Real-time test execution with reporting
- Performance Dashboards – Live monitoring and metrics visualization
CI/CD Pipeline – Working pipeline with automated quality gates
🧠 Crack Your QA Interviews Faster
Get 200+ Manual, Automation & API Testing interview questions View Interview Guide →
6. Job Search Strategy

Resume Optimization for Testing Roles
Technical Skills Section:
Testing Expertise:
• Manual Testing: Test Planning, Test Case Design, Defect Management, Regression Testing
• Test Automation: Selenium WebDriver, TestNG, JUnit, Page Object Model, Data-Driven Testing
• API Testing: REST/SOAP, Postman, RestAssured, JSON/XML Validation, Security Testing
• Performance Testing: JMeter, Load Testing, Stress Testing, Performance Analysis
• Mobile Testing: Android, iOS, Appium, Device Testing, Cross-Platform Validation
Tools & Technologies:
• Programming: Java, Python, JavaScript, SQL for test automation and data validation
• Frameworks: Selenium, TestNG, JUnit, Cucumber, RestAssured, Appium
• CI/CD: Jenkins, Git, Maven, Docker, Pipeline Integration
• Management: JIRA, TestRail, Confluence, Defect Tracking, Test Reporting
Project Experience Examples:
E-commerce Platform Automation Testing
- Challenge: Manual regression testing taking 40+ hours per release, delaying deployments
- Solution: Developed comprehensive Selenium automation framework with 300+ test cases covering critical user journeys
- Technologies: Java, Selenium WebDriver, TestNG, Maven, Jenkins, ExtentReports
- Results: Reduced regression testing time by 85%, improved defect detection by 32%, enabled daily deployments
API Testing Framework for Microservices
- Challenge: Complex microservices architecture with 25+ APIs requiring comprehensive validation
- Solution: Built RestAssured-based framework with automated contract testing and security validation
- Technologies: Java, RestAssured, TestNG, JSON Schema Validation, Performance Testing
- Impact: Achieved 95% API test coverage, reduced integration defects by 67%, improved release confidence
Testing Job Market Analysis
High-Demand Role Categories:
- Test Automation Engineer (All Levels)
- Salary Range: ₹4.5-25 LPA
- Open Positions: 4,200+ across India
- Key Skills: Selenium, API testing, CI/CD integration, framework development
- Growth Path: Senior Automation Engineer → Automation Architect → QA Manager
- Performance Testing Engineer (Specialized)
- Salary Range: ₹6-30 LPA
- Open Positions: 1,800+ across India
- Key Skills: JMeter, LoadRunner, performance analysis, scalability testing
- Growth Path: Senior Performance Engineer → Performance Architect → Site Reliability Engineer
- QA Lead/Manager (Leadership Track)
- Salary Range: ₹12-35 LPA
- Open Positions: 2,500+ across India
- Key Skills: Team management, process improvement, strategy development
- Growth Path: QA Manager → QA Director → VP Quality Engineering
Top Hiring Companies and Opportunities
Technology Product Companies:
- Microsoft India – Windows, Office, Azure product testing teams
- Google India – Search, Android, Cloud product validation
- Amazon India – E-commerce platform, AWS services testing
- Flipkart – E-commerce, logistics, payment platform quality assurance
Financial Services and Fintech:
- Paytm – Payment platform, financial services testing
- PhonePe – UPI payments, merchant platform validation
- HDFC Bank – Digital banking, mobile app testing
- ICICI Bank – Online banking, loan processing systems
Consulting and Services:
- Accenture – Client testing services, test automation solutions
- Cognizant – Quality engineering services for global clients
- TCS – Testing centers of excellence, domain-specific testing
- Infosys – Digital quality assurance, automation frameworks
Interview Preparation Framework
Manual Testing Competency:
Test Design and Planning:
- “How would you test a login functionality?”
- Positive Scenarios: Valid credentials, remember me, forgot password
- Negative Scenarios: Invalid credentials, empty fields, SQL injection
- Edge Cases: Special characters, maximum length, concurrent sessions
- Non-Functional: Performance under load, security validation, accessibility
- “Explain your approach to testing a payment gateway integration”
- Functional Testing: Payment methods, transaction processing, refunds
- Security Testing: Data encryption, PCI compliance, fraud detection
- Integration Testing: Bank API connectivity, error handling, timeout scenarios
- Performance Testing: High transaction volumes, concurrent payments
Test Automation Technical Questions:
- “How do you handle dynamic elements in Selenium automation?”
// Dynamic element handling strategies
// 1. Explicit Wait with Expected Conditions
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, Duration.ofSeconds(10));
WebElement dynamicElement = wait.until(
ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(By.id(“dynamic-button”))
);
// 2. Custom Wait Condition
wait.until(new ExpectedCondition<Boolean>() {
public Boolean apply(WebDriver driver) {
List<WebElement> elements = driver.findElements(By.className(“loading”));
return elements.size() == 0;
}
});
// 3. Fluent Wait for Complex Scenarios
FluentWait<WebDriver> fluentWait = new FluentWait<>(driver)
.withTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(30))
.pollingEvery(Duration.ofSeconds(2))
.ignoring(NoSuchElementException.class);
- “Design a test automation framework architecture”
- Layer Structure: Driver layer, page object layer, test layer, utility layer
- Design Patterns: Page Object Model, Factory Pattern, Singleton Pattern
- Configuration Management: Property files, environment-specific configs
- Reporting and Logging: ExtentReports, Log4j integration, screenshots
- Data Management: Excel, JSON, database connectivity for test data
API Testing Scenarios:
5. “How do you perform end-to-end API testing?”
- Functional Testing: Request/response validation, status codes, data integrity
- Security Testing: Authentication, authorization, input validation
- Performance Testing: Response time, throughput, concurrent users
- Contract Testing: Schema validation, backward compatibility
Performance Testing Questions:
6. “Explain your approach to performance test planning”
- Requirement Analysis: SLA definition, user load patterns, performance criteria
- Test Environment: Production-like setup, data volume, network simulation
- Test Scenarios: Load, stress, spike, volume, endurance testing
- Monitoring Strategy: Application metrics, server resources, database performance
Salary Negotiation and Career Advancement
Market Research and Positioning:
- Skill Premium – Automation skills command 30-50% higher salaries than manual testing
- Domain Expertise – Banking, healthcare, e-commerce domains offer 10-20% premiums
- Certification Value – ISTQB, Selenium, performance testing certifications add 15-25% value
- Leadership Skills – Test management and team leadership significantly increase earning potential
Negotiation Strategy:
Total Compensation Package:
Base Salary: ₹X LPA (Fixed annual compensation)
Variable Pay: X% of base (Performance bonuses, project completion bonuses)
Learning Budget: ₹25,000-50,000 annually (Certification reimbursement, conference attendance)
Flexible Benefits: Work from home allowance, health insurance, professional development
Stock Options: For startup and growth-stage companies
Value Proposition Framework:
- Technical Expertise – Automation frameworks, performance testing, API validation capabilities
- Process Improvement – Quantified improvements in test efficiency, defect detection, release quality
- Cross-Functional Skills – Collaboration with developers, product managers, business stakeholders
- Continuous Learning – Commitment to staying current with testing tools and methodologies
- Leadership Potential – Mentoring experience, process standardization, team coordination
7. Salary Expectations and Career Growth
2025 Compensation Benchmarks
Entry Level (0-2 years):
- Manual Tester: ₹3.5-6 LPA
- Junior Automation Engineer: ₹4.5-8 LPA
- API Testing Specialist: ₹5-9 LPA
- Performance Testing Associate: ₹5.5-10 LPA
Mid Level (2-5 years):
- Senior Manual Tester: ₹6-12 LPA
- Automation Engineer: ₹8-18 LPA
- API Testing Engineer: ₹10-16 LPA
- Performance Testing Engineer: ₹12-22 LPA
Senior Level (5-8 years):
- Lead QA Engineer: ₹15-25 LPA
- Senior Automation Architect: ₹20-32 LPA
- Performance Testing Lead: ₹22-35 LPA
- QA Manager: ₹18-30 LPA
Expert Level (8+ years):
- Principal QA Engineer: ₹25-40 LPA
- QA Architect: ₹30-45 LPA
- Director of Quality Engineering: ₹35-55 LPA
- VP Quality Assurance: ₹45-70 LPA
Industry and Geographic Salary Variations
High-Paying Industries:
- Financial Services – 20-30% premium for compliance and security testing expertise
- Healthcare Technology – 15-25% premium for regulatory and patient safety validation
- E-commerce Platforms – 10-20% premium for scale and performance testing skills
- Gaming and Entertainment – 15-25% premium for specialized performance and compatibility testing
Geographic Distribution:
- Bangalore – Highest concentration of testing jobs, 12-18% above national average
- Pune – Strong automotive and manufacturing testing market, 8-15% above average
- Mumbai – Financial services testing hub, 10-16% above national average
- Hyderabad – Government and pharma testing opportunities, 6-12% above average
Career Progression Pathways
Technical Excellence Track:
Junior Tester (0-2 years)
↓
Test Automation Engineer (1-4 years)
↓
Senior Automation Engineer (3-7 years)
↓
Test Automation Architect (5-10 years)
↓
Principal QA Engineer (8+ years)
Management and Leadership Track:
Senior Tester (2-5 years)
↓
Test Lead (4-7 years)
↓
QA Manager (6-10 years)
↓
QA Director (8-15 years)
↓
VP Quality Engineering (12+ years)
Specialization Track:
Testing Engineer (1-3 years)
↓
Performance Testing Specialist (2-6 years)
↓
Performance Architect (5-9 years)
↓
Site Reliability Engineer (7-12 years)
↓
Infrastructure Architect (10+ years)
Skills for Accelerated Career Growth
Technical Mastery (Years 1-3):
- Multi-Tool Proficiency – Selenium, API testing, performance testing, security testing
- Programming Skills – Strong programming foundation in Java/Python/JavaScript
- CI/CD Integration – Jenkins, Docker, cloud platform integration
- Test Architecture – Framework design, scalable automation solutions
Leadership and Process (Years 3-6):
- Team Coordination – Cross-functional collaboration, agile/scrum participation
- Process Improvement – Metrics analysis, efficiency optimization, tool evaluation
- Stakeholder Management – Business communication, requirement analysis
- Mentoring Skills – Knowledge transfer, junior team member development
Strategic Impact (Years 6+):
- Quality Strategy – Organizational test strategy, risk-based testing approaches
- Innovation Leadership – Emerging technology adoption, competitive advantage creation
- Business Partnership – Quality impact on business outcomes, ROI demonstration
- Industry Expertise – Deep domain knowledge, regulatory compliance understanding
Emerging Opportunities and Future Trends
High-Growth Testing Specializations:
- AI/ML Testing – Model validation, data quality, algorithmic bias testing
- IoT Testing – Device connectivity, edge computing, sensor validation
- Blockchain Testing – Smart contract validation, consensus mechanism testing
- Cloud-Native Testing – Microservices, serverless, container testing
- Accessibility Testing – ADA compliance, inclusive design validation
Market Trends Creating New Opportunities:
- Shift-Left Testing – Early testing integration in development process
- Test-Driven Development – Developer and tester collaboration
- Continuous Testing – DevOps pipeline integration, automated quality gates
- Risk-Based Testing – AI-powered test prioritization and optimization
8. Success Stories from Our Students

Sneha Reddy – From Manual Tester to Automation Architect
Background: 4 years as manual tester with limited programming knowledge
Challenge: Career stagnation with repetitive manual testing tasks, low growth potential
Transformation Strategy: Systematic progression from manual to automation expertise
Timeline: 12 months from course enrollment to automation architect role
Current Position: Senior Test Automation Architect at Wipro Digital
Salary Progression: ₹6.8 LPA → ₹12.5 LPA → ₹18.2 LPA → ₹26.8 LPA (over 24 months)
Sneha’s Strategic Approach:
- Programming Foundation – Dedicated 3 months to Java fundamentals and OOP concepts
- Framework Development – Built 3 different automation frameworks during learning phase
- Domain Specialization – Focused on banking and financial services testing expertise
- Community Contribution – Created open-source testing utilities, gained recognition
Key Success Factors:
- Practical Application – “I didn’t just learn Selenium—I built complete frameworks that solved real testing challenges. My portfolio showed actual solutions I could implement immediately.”
- Business Understanding – “Understanding the banking domain helped me design better test scenarios and communicate effectively with business stakeholders.”
- Continuous Learning – “I spent 1 hour daily learning new tools and techniques. The testing field evolves rapidly, so staying current is essential.”
Current Impact: Leading automation initiatives for Fortune 500 banking clients, managing frameworks used by 50+ testers across multiple countries, responsible for quality strategy affecting $10M+ annual revenue.
Raj Patel – From Fresher to Performance Testing Lead
Background: Recent engineering graduate with computer science degree but no industry experience
Challenge: Competitive fresher market with thousands of applicants for basic testing positions
Strategic Focus: Performance testing specialization to differentiate from general testing candidates
Timeline: 18 months from graduation to performance testing leadership role
Career Trajectory: Trainee → Junior Performance Tester → Performance Engineer → Performance Lead
Current Role: Performance Testing Lead at PhonePe
Compensation and Growth:
- Year 1: ₹4.5 LPA (Trainee at mid-size company)
- Year 2: ₹8.2 LPA (Performance Engineer at fintech startup)
- Current: ₹19.8 LPA + equity (Performance Lead at PhonePe)
- Additional Income: ₹3-5 LPA from weekend consulting projects
Raj’s Performance Testing Mastery:
- Technical Expertise – JMeter, LoadRunner, Gatling, cloud-based load testing platforms
- Scale Expertise – Designed performance tests for applications handling 10M+ daily transactions
- Monitoring Integration – Comprehensive APM setup with Dynatrace, AppDynamics, custom dashboards
- Business Impact – Performance optimizations saving ₹2.4 crores annually in infrastructure costs
Innovation and Recognition:
- Framework Development – Created performance testing accelerators reducing test creation time by 60%
- Industry Recognition – Speaker at 5 performance testing conferences, published research papers
- Team Building – Built performance testing center of excellence with 8 specialists
- Knowledge Sharing – Internal training programs, mentored 15+ junior performance engineers
Success Insights: “Performance testing is highly specialized and in huge demand. While everyone was competing for basic automation roles, I focused on performance testing where there were fewer candidates but higher-paying opportunities. The combination of technical skills and business impact measurement accelerated my career significantly.”
Priya Singh – From Developer to QA Manager
Background: 5 years as Java developer wanting to transition into quality assurance and leadership
Challenge: Career transition from development to testing while aiming for management track
Strategic Approach: Leverage development experience while building testing expertise and leadership skills
Timeline: 20 months from career transition decision to QA Manager role
Career Evolution: Java Developer → Test Automation Engineer → Senior QA Engineer → QA Manager
Current Position: QA Manager at Razorpay managing 12-person testing team
Leadership and Compensation Growth:
- Pre-transition: ₹11.2 LPA (Senior Java Developer)
- Transition Year: ₹13.8 LPA (Test Automation Engineer)
- Leadership Role: ₹22.5 LPA (QA Manager) + performance bonuses
- Total Package: ₹28+ LPA including stock options and leadership incentives
Priya’s Management Transformation:
- Technical Leadership – Established automation standards, implemented CI/CD testing integration
- Process Innovation – Reduced release cycle time from 2 weeks to 2 days through testing optimization
- Team Development – Built high-performing QA team with 95% retention rate, internal promotion focus
- Strategic Planning – Quality roadmap alignment with business objectives, risk-based testing strategy
Business Impact and Recognition:
- Cost Optimization – Testing process improvements saving ₹1.8 crores annually in development costs
- Quality Metrics – Achieved 99.2% uptime for payment platform, industry-leading quality scores
- Innovation Leadership – Implemented AI-powered test case generation, predictive quality analytics
- Industry Recognition – Featured in QA leadership articles, invited speaker at testing conferences
Management Philosophy: “My development background gave me unique insights into how testing should integrate with development workflows. I could speak both languages—technical implementation and business impact. This bridge perspective was essential for successful team leadership and stakeholder management.”
✨ Follow Your Testing Learning Path
Go from beginner → Manual Tester → Automation Engineer with a guided path View Learning Path →
9. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them

Challenge 1: Transition from Manual to Automation Testing
Problem: Many testers struggle with programming concepts and automation framework development
Impact: Career stagnation, lower salary growth, limited job opportunities in automation-focused market
Symptoms: Fear of coding, difficulty understanding automation architecture, poor framework design
Systematic Transition Strategy:
Phase 1: Programming Foundation (4-6 weeks)
- Start with Basics – Variables, data types, control structures using interactive platforms
- Practice Daily – Solve simple programming problems on HackerRank or CodeChef
- Focus on Concepts – Object-oriented programming, exception handling, collections
- Apply to Testing – Write simple test scenarios in code format
Programming Learning Path:
// Week 1-2: Basic syntax and concepts
public class TestingBasics {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Practice variables and data types
String testCaseName = “Login Test”;
boolean testResult = true;
int executionTime = 30; // seconds
// Practice control structures
if (testResult) {
System.out.println(testCaseName + ” passed in ” + executionTime + ” seconds”);
} else {
System.out.println(testCaseName + ” failed”);
}
}
}
// Week 3-4: Object-oriented concepts applied to testing
public class TestCase {
private String testName;
private String expectedResult;
private String actualResult;
public TestCase(String name, String expected) {
this.testName = name;
this.expectedResult = expected;
}
public boolean execute() {
// Test execution logic
return expectedResult.equals(actualResult);
}
}
Phase 2: Tool-Specific Learning (6-8 weeks)
- Selenium Basics – Locators, basic actions, simple scripts
- Framework Concepts – Page Object Model, data-driven testing
- Build Tools – Maven/Gradle for dependency management
- Version Control – Git for code management and collaboration
Challenge 2: Designing Effective Test Cases and Test Data
Problem: Many testers create ineffective test cases that miss critical scenarios or contain redundant validations
Impact: Poor defect detection, inefficient testing process, missed production issues
Solution: Systematic test design techniques and risk-based testing approaches
Test Design Excellence Framework:
Requirement Analysis Process:
- Functional Decomposition – Break down requirements into testable components
- Business Rule Identification – Extract validation rules and constraints
- User Journey Mapping – Understand end-to-end user workflows
- Risk Assessment – Identify high-risk areas requiring thorough testing
Test Case Design Techniques:
Example: Testing an ATM withdrawal function
Equivalence Partitioning:
– Valid withdrawal amounts: $20, $50, $100, $200
– Invalid amounts: $0, negative values, amounts > account balance
– Account balance ranges: Low balance, sufficient balance, high balance
Boundary Value Analysis:
– Minimum withdrawal: $20 (exact boundary)
– Maximum withdrawal: Account balance (exact boundary)
– Just above/below boundaries: $19, $21, balance+$1, balance-$1
Decision Table:
Conditions: Valid PIN, Sufficient Balance, Card Valid, Network Available
Actions: Dispense cash, Update balance, Print receipt, Return card
Test Data Management Strategy:
- Realistic Data Sets – Use production-like data while maintaining privacy
- Edge Case Coverage – Include boundary conditions, special characters, null values
- Negative Testing – Invalid inputs, malformed requests, security test cases
- Performance Data – Large datasets for volume and stress testing scenarios
Challenge 3: Keeping Up with Rapidly Evolving Testing Tools
Problem: Testing tools and frameworks evolve rapidly, creating continuous learning pressure
Challenge: Fear of skill obsolescence, difficulty choosing which tools to learn
Solution: Strategic tool evaluation and incremental learning approach
Tool Selection Framework:
Evaluation Criteria:
1. Industry Adoption – Job market demand and community support
2. Learning Curve – Time investment required for proficiency
3. Integration Capabilities – CI/CD, existing tool ecosystem compatibility
4. Maintenance Overhead – Long-term support and update frequency
5. ROI Potential – Career advancement and salary impact
Priority Matrix:
High Impact, Low Effort: Selenium, Postman, JMeter, Jenkins
High Impact, High Effort: Cypress, Playwright, Kubernetes testing
Low Impact, Low Effort: Browser extensions, simple utilities
Low Impact, High Effort: Niche tools with limited adoption
Continuous Learning Strategy:
- Core Tools Mastery (70% effort) – Focus on widely adopted, stable tools
- Emerging Technology Exploration (20% effort) – Experiment with new tools and frameworks
- Industry Trend Monitoring (10% effort) – Stay informed about tool landscape evolution
Challenge 4: Demonstrating Business Value and ROI of Testing
Problem: Testing is often viewed as cost center rather than value generator
Impact: Limited budget for testing tools, reduced team sizes, undervaluation of QA contributions
Solution: Quantify testing impact using business metrics and stakeholder communication
Business Value Measurement Framework:
Cost of Quality Metrics:
- Prevention Costs – Testing effort, tool investments, training costs
- Appraisal Costs – Review activities, audit costs, testing execution
- Internal Failure Costs – Rework, debugging, delayed releases
- External Failure Costs – Customer complaints, warranty claims, reputation damage
ROI Calculation Examples:
Automation ROI Calculation:
Investment:
– Framework development: 200 hours @ ₹2000/hour = ₹4,00,000
– Tool licenses: ₹50,000 annually
– Training and setup: ₹75,000
Total Investment: ₹5,25,000
Returns (Annual):
– Manual testing time saved: 1000 hours @ ₹1500/hour = ₹15,00,000
– Defect prevention value: 50 defects @ ₹10,000 each = ₹5,00,000
– Faster release cycles: 6 additional releases = ₹3,00,000
Total Returns: ₹23,00,000
ROI = (Returns – Investment) / Investment * 100 = 338%
Stakeholder Communication Strategy:
- Executive Dashboards – Quality metrics tied to business KPIs
- Risk Communication – Potential business impact of quality issues
- Success Stories – Quantified examples of testing preventing major issues
- Competitive Analysis – Quality compared to industry benchmarks
💰 Aim for High-Paying QA Jobs?
Become job-ready with our Software Testing Course
10. Your Next Steps

Week 1: Foundation and Environment Setup
Day 1-2: Testing Fundamentals and Career Planning
- Download Testing Tools – Install browsers, Postman, basic testing utilities
- Create Learning Accounts – GitHub for portfolio, LinkedIn for networking
- Join Testing Communities – Reddit r/QualityAssurance, Stack Overflow, Facebook groups
- Set Learning Goals – Define 30, 60, 90-day milestones for skill development
Day 3-4: Manual Testing Practice
- Practice Test Case Writing – Use any website/application for functional testing
- Bug Report Creation – Document defects with proper severity and priority
- Explore Testing Types – Functional, usability, compatibility testing on different platforms
- Study SDLC Integration – Understand how testing fits into development process
Day 5-7: Tool Exploration and Community Engagement
- Postman API Testing – Learn basic API testing with public APIs
- Browser Developer Tools – Understand HTML, CSS, JavaScript basics for testing
- Join Local Meetups – Find testing user groups in your city
- Create Study Schedule – Allocate daily learning time and weekend projects
Month 1: Manual Testing Mastery and Documentation
Week 1-2: Test Planning and Design
- Test Strategy Creation – Learn to write comprehensive test plans
- Test Case Design Techniques – Equivalence partitioning, boundary value analysis
- Defect Management – Bug lifecycle, severity vs priority, tracking tools
- Testing Metrics – Coverage, defect density, test effectiveness measurement
Week 3-4: Practical Testing Projects
- Web Application Testing – Complete functional testing of e-commerce site
- Mobile Application Testing – Android/iOS app validation and usability
- Cross-Platform Testing – Browser compatibility, device responsiveness
- Documentation Standards – Professional test case and bug report formats
Month-End Achievement:
- Complete Manual Testing Project – Well-documented testing of complex application
- Professional Test Documentation – Test plans, cases, execution reports
- Basic Tool Proficiency – Comfortable with testing tools and processes
- Testing Fundamentals Certification – Consider ISTQB Foundation Level
Month 2: Programming and Automation Introduction
Week 1-2: Programming Fundamentals
- Java/Python Basics – Syntax, variables, control structures, object-oriented concepts
- Web Technologies – HTML, CSS, JavaScript understanding for test automation
- Database Concepts – SQL queries for test data validation and setup
- Version Control – Git basics for code management and collaboration
Week 3-4: Selenium Introduction
- Selenium Setup – WebDriver installation, IDE configuration, first automation script
- Element Identification – Locator strategies, XPath, CSS selectors
- Basic Automation – Click, type, dropdown, alert handling, navigation
- Simple Framework – Page Object Model basics, TestNG/JUnit introduction
Programming Practice Focus:
- Daily Coding – 30-45 minutes of programming practice daily
- Testing Context – Apply programming concepts to testing scenarios
- Code Quality – Learn debugging, error handling, code organization
- Collaboration – Use GitHub for version control and portfolio building
Month 3: Test Automation Framework Development
Week 1-2: Advanced Selenium and Framework Design
- Advanced WebDriver – Synchronization, window handling, file upload/download
- Framework Architecture – Page Object Model, Page Factory, Base classes
- Data-Driven Testing – Excel, CSV, JSON data sources for test parameterization
- Reporting Integration – ExtentReports, TestNG reports, custom reporting
Week 3-4: CI/CD Integration and Best Practices
- Build Tools – Maven/Gradle for project management and dependency handling
- Jenkins Integration – Automated test execution, build triggers, result reporting
- Code Quality – Clean code practices, code reviews, maintainable automation
- Framework Documentation – Architecture documentation, setup guides, best practices
Advanced Learning Goals:
- Complete Automation Framework – Production-ready framework with proper architecture
- CI/CD Pipeline – Integrated automation execution with reporting
- Code Portfolio – Well-documented GitHub repository with multiple projects
- Community Participation – Contribute to forums, answer questions, share knowledge
Long-Term Milestones (6-12 Months)
Professional Skill Development:
- Specialization Choice – API testing, performance testing, mobile testing, or security testing
- Advanced Certifications – ISTQB Advanced Level, tool-specific certifications
- Industry Knowledge – Domain expertise in banking, healthcare, e-commerce, or other verticals
- Leadership Skills – Team coordination, process improvement, stakeholder management
Career Transition Activities:
- Resume Optimization – Highlight projects, certifications, quantifiable achievements
- Interview Preparation – Technical scenarios, problem-solving, communication skills
- Professional Network – Connections through conferences, meetups, online communities
- Salary Research – Market rates, negotiation preparation, career path planning
Portfolio and Professional Presence:
- Comprehensive Portfolio – 5-7 testing projects demonstrating various skills and tools
- Technical Writing – Blog posts, articles, documentation of learning journey
- Community Contribution – Open source contributions, forum participation, knowledge sharing
Continuous Learning – Stay updated with testing trends, tools, and methodologies
Conclusion
Software testing represents a stable, rewarding, and intellectually challenging career path that plays a crucial role in ensuring software quality and user satisfaction. As digital transformation accelerates across all industries, the demand for skilled testing professionals continues to grow, offering excellent job security and competitive compensation packages.
The journey from manual testing beginner to automation expert typically requires 4-6 months of dedicated learning and hands-on practice, but the investment delivers both immediate employment opportunities and long-term career growth potential. Unlike many technology roles that require extensive programming backgrounds, testing offers multiple entry points for professionals with diverse educational and career backgrounds.
Critical Success Factors for Testing Career Excellence:
- Balanced Skill Development – Combine manual testing fundamentals with automation expertise
- Business Understanding – Focus on testing’s impact on user experience and business outcomes
- Continuous Learning – Stay current with evolving tools, frameworks, and testing methodologies
- Quality Mindset – Develop instinct for identifying risks, edge cases, and potential failure points
- Communication Skills – Effectively collaborate with developers, product managers, and stakeholders
The most successful testing professionals combine technical proficiency with analytical thinking and stakeholder management capabilities. As organizations adopt agile methodologies and DevOps practices, testing engineers increasingly work as quality advocates embedded within cross-functional teams rather than isolated QA departments.
Whether you choose manual testing specialization, automation engineering, performance testing, or QA leadership tracks, testing skills provide a foundation for long-term career growth and the satisfaction of ensuring software quality that impacts millions of users.
Ready to launch your software testing career and become a guardian of software quality?
Explore our comprehensive Software Testing Engineering Program designed for career changers and aspiring QA professionals:
4-month intensive curriculum covering manual testing, automation, API testing, and performance testing
Hands-on framework development with Selenium, TestNG, and CI/CD integration
Industry-standard tools training including JIRA, Postman, JMeter, and Jenkins
ISTQB certification preparation with practice exams and study materials
Job placement assistance with resume optimization, interview coaching, and employer connections
Real-world project portfolio with comprehensive documentation and live demonstrations
Lifetime learning support including tool updates, industry trends, and career guidance
Uncertain about which testing specialization matches your background and interests? Schedule a free testing career consultation with our QA experts to receive personalized guidance and a customized learning roadmap.
Connect with our testing community: Join our Software Testing Engineers WhatsApp Group with 320+ students, alumni, and working testing professionals for daily learning support, project collaboration, and job referrals.
