SQL 90-Day Course Roadmap: From Beginner to Job-Ready Professional
Thinking about starting a career that pays well and offers endless opportunities? SQL might just be your ticket to success. Companies across India are desperately looking for skilled SQL professionals, with entry-level positions starting at ₹3.3 lakh per year and experienced developers earning upwards of ₹9 lakh annually. This comprehensive 90-day roadmap will transform you from a complete beginner into a job-ready SQL professional, equipped with real-world skills that employers actually want.
Why SQL Skills Matter in 2025
The demand for SQL professionals has exploded across major Indian cities like Bangalore, Hyderabad, Pune, and Gurgaon. Top companies including Infosys, TCS, Accenture, Capgemini, Wipro, Cognizant, IBM, and KPMG are actively hiring SQL developers right now. Whether you’re a fresh graduate, a working professional looking to switch careers, or someone from a non-IT background, SQL offers an accessible entry point into the tech industry with exceptional growth potential.
SQL developers work in diverse sectors including technology development, data science and analytics, artificial intelligence, media and entertainment, and tech startups. The beauty of SQL is that it’s not just for database administrators anymore—data analysts, business intelligence developers, data engineers, and software developers all need strong SQL skills to succeed in their roles.
🚀 Start your SQL journey with structured career Course for every tech role.
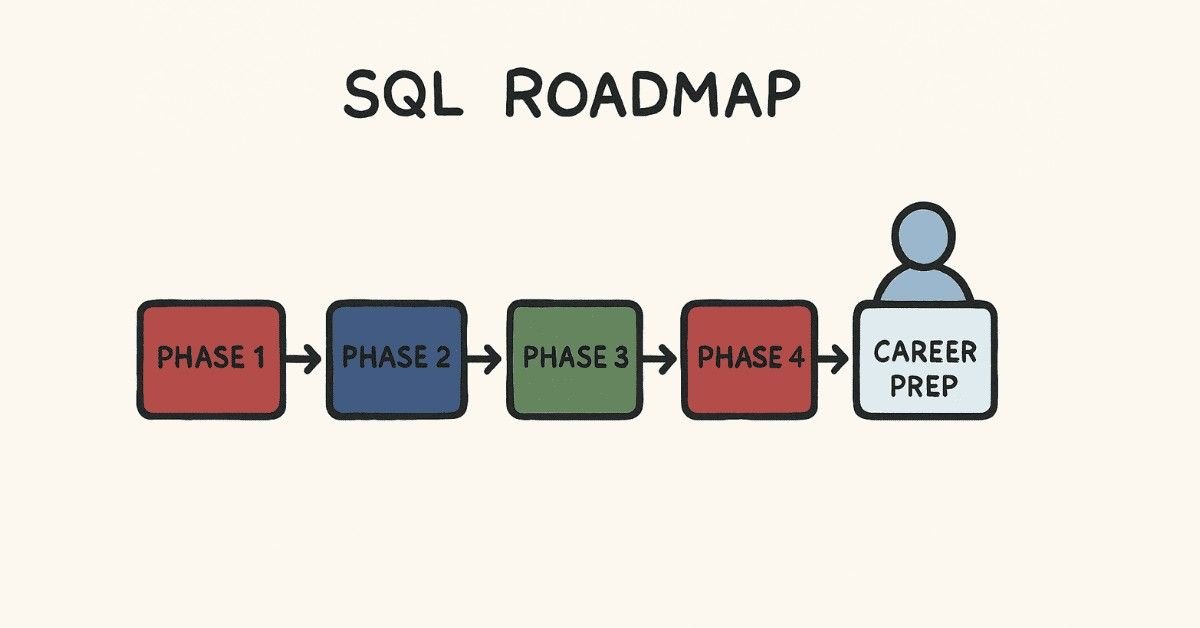
Your 90-Day Transformation Journey
This structured learning path takes you through five carefully designed phases, each building on the previous one to ensure solid understanding and practical application. You won’t just memorize commands—you’ll understand how databases work, why certain approaches are better than others, and how to solve real business problems using SQL.
PHASE 1: Foundation Building (Days 1-18)
Week 1: Understanding Databases and SQL Fundamentals
Day 1: Introduction to Database Systems
Start your journey by understanding what databases actually are and why businesses need them. Learn about relational databases—the organized way companies store customer information, sales records, employee data, and millions of other pieces of information. Think of a database as a digital filing cabinet, but infinitely more powerful and organized.
You’ll explore the difference between OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) systems that handle day-to-day business operations and OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) systems that help managers make strategic decisions. Understanding this distinction helps you grasp why companies need different database strategies for different purposes.
Day 2: Installing Your Database Environment
Get hands-on by installing SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), the professional tool used by database developers worldwide. This might seem technical at first, but the process is straightforward—you’ll be writing your first SQL commands by the end of the day. SSMS provides a visual interface that makes working with databases much easier than you might expect.
Day 3: SQL Basics and Database Creation
Learn what SQL actually stands for—Structured Query Language—and why it’s become the universal language for talking to databases. You’ll create your very first database today using Management Studio’s graphical interface. This hands-on experience demystifies databases and shows you that creating and managing them isn’t as complicated as you might think.
Day 4: Understanding Data Types
Discover how databases store different kinds of information—numbers, text, dates, and more. Just like you wouldn’t store milk in a paper bag, databases need the right container for each type of data. You’ll learn about integers for whole numbers, varchar for text, datetime for dates and times, and decimal for precise calculations like money.
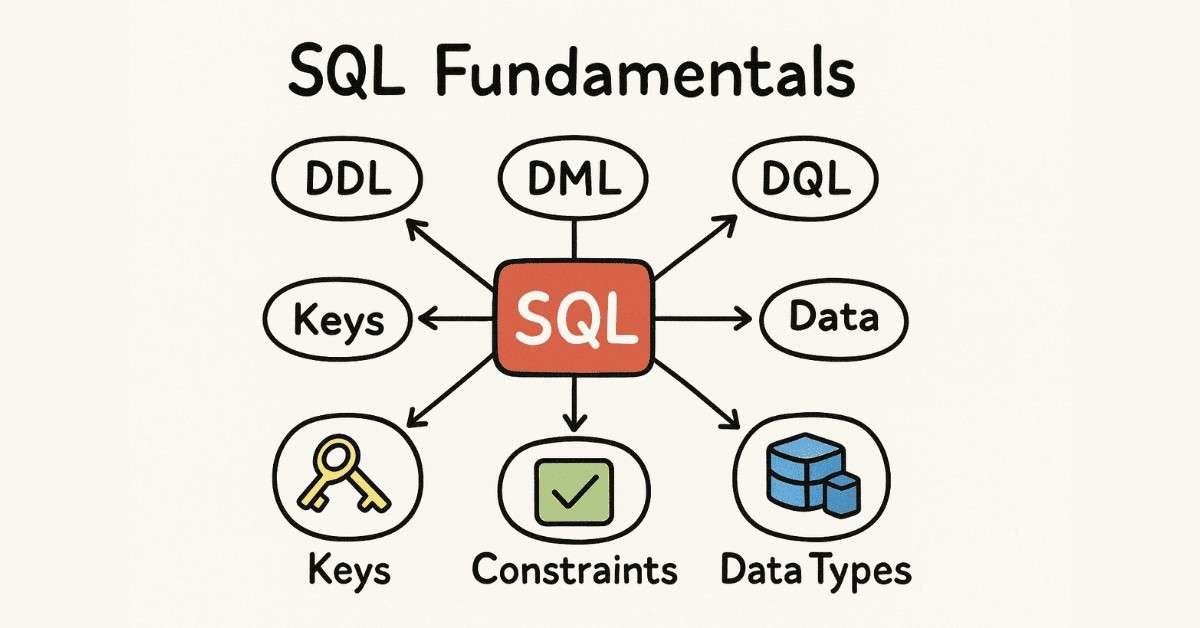
Day 5: DDL Commands – Creating Your First Tables
DDL (Data Definition Language) commands let you build the structure of your database. Today you’ll create your first table using the CREATE command, learning how to define columns, set data types, and establish the basic framework that holds data. You’ll also learn how to modify existing tables with ALTER and remove them with DROP commands.
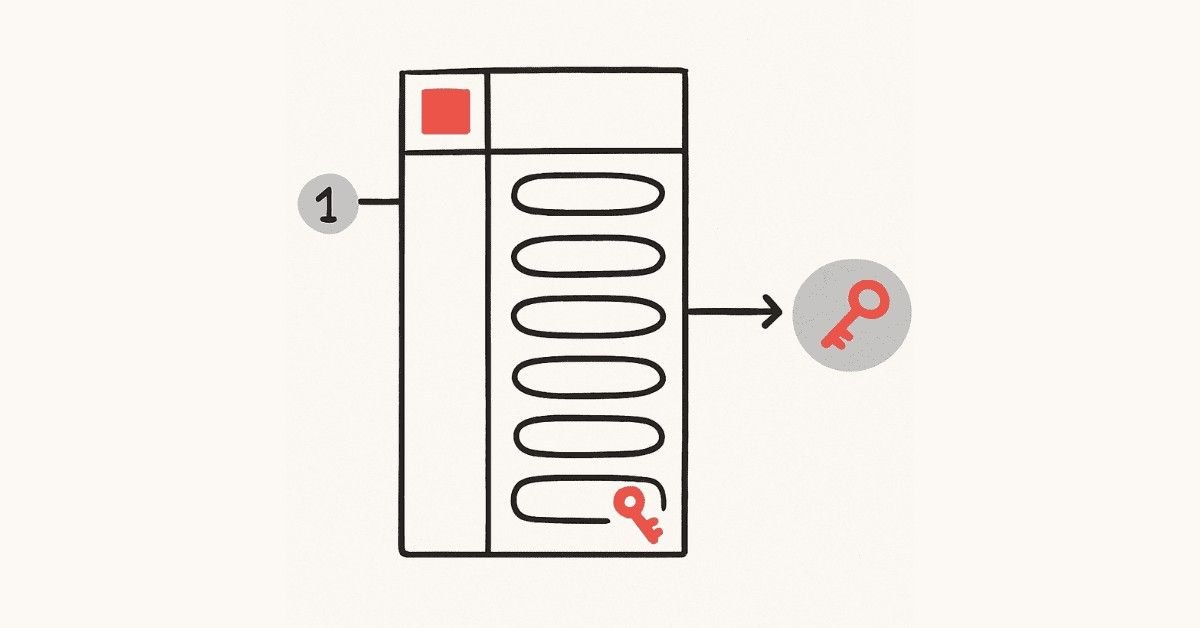
Day 6: Understanding Keys and Constraints
Keys are like identification numbers that make sure your data stays organized and accurate. Primary keys uniquely identify each record in a table—think of them like your Aadhar number. Foreign keys create relationships between tables, connecting customer orders to customer information, for example. Constraints are rules that keep bad data out of your database.
Day 7: Practice Project – Building Your First Database
Put everything together by designing a simple student database with tables for students, courses, and enrollments. This project reinforces all the concepts from Week 1 and gives you something tangible to show for your learning. You’ll encounter real challenges and solve them, building confidence in your new skills.
📘 New to SQL? Learn installation, setup & basics with beginner-friendly How-to Guides.
Week 2: Manipulating Data
Day 8: DML Commands – INSERT Statements
DML (Data Manipulation Language) commands let you actually work with data. The INSERT command adds new records to your tables—like adding a new customer to your system. You’ll learn multiple ways to insert data, including adding single records, multiple records at once, and inserting data from other tables.
Day 9: UPDATE and DELETE Operations
Learn how to modify existing records with UPDATE and remove records with DELETE. These powerful commands require careful use—you’ll learn safety techniques to avoid accidentally changing or deleting the wrong data. Understanding WHERE clauses becomes crucial here, as they specify exactly which records to update or delete.
Day 10: TRUNCATE and Data Management
Discover the TRUNCATE statement, which quickly removes all data from a table while keeping the table structure intact. You’ll understand when to use TRUNCATE versus DELETE, and why TRUNCATE is faster for removing large amounts of data. This knowledge helps you manage databases efficiently in real-world scenarios.
Day 11: Basic SELECT Queries
SELECT is the most commonly used SQL command—you’ll probably write thousands of SELECT queries in your career. Learn how to retrieve data from tables, select specific columns, and use the WHERE clause to filter results. This fundamental skill forms the foundation for everything else you’ll learn.
Day 12: Filtering and Comparison Operators
Master the art of finding exactly the data you need using comparison operators (=, <, >, <=, >=, !=). Learn logical operators (AND, OR, NOT) that let you combine multiple conditions. These tools help you answer business questions like “Which customers in Mumbai spent more than ₹50,000 last quarter?”.
Day 13: Advanced Filtering – BETWEEN, IN, LIKE
Expand your filtering toolkit with specialized operators. BETWEEN finds values within a range, IN checks against a list of values, and LIKE performs pattern matching for partial text searches. These operators make complex queries much simpler to write and understand.
Day 14: Sorting and Limiting Results
Learn to organize query results using ORDER BY to sort data alphabetically or numerically, ascending or descending. The LIMIT clause (or TOP in SQL Server) restricts results to a specific number of records. These commands are essential for creating reports and displaying data in meaningful ways.
💡 Download practice databases, insert/update datasets & SQL starter resources.
Week 3: Data Analysis Fundamentals
Day 15: Aggregate Functions – COUNT and SUM
Aggregate functions perform calculations across multiple rows of data. COUNT tells you how many records exist, while SUM adds up numeric values. These functions answer questions like “How many orders did we receive today?” or “What’s our total revenue this month?”.
Day 16: MIN, MAX, and AVG Functions
Discover functions that find minimum values, maximum values, and calculate averages. These analytical tools help you understand your data’s range and central tendencies. Business analysts use these functions constantly to identify trends and outliers.
Day 17: GROUP BY Clause
GROUP BY is where SQL starts feeling like magic. This powerful clause lets you organize data into categories and perform calculations for each category. You can answer questions like “What’s the average order value for each customer?” or “How many sales did each salesperson make?”.
Day 18: HAVING Clause and String Functions
While WHERE filters individual rows, HAVING filters grouped results. Learn the crucial difference and when to use each. String functions like CONCAT, SUBSTRING, REPLACE, and LENGTH let you manipulate text data. These skills are essential for cleaning and formatting data.

Want to see how these skills translate into real job opportunities? Check out our comprehensive Career Guide for SQL Professionals to understand salary expectations, job roles, and growth paths.
🧩 Strengthen your analysis skills—Access GROUP BY, HAVING & string function guides.
PHASE 2: Advanced Querying (Days 19-36)
Week 4: Mastering Joins
Day 19: Understanding Table Relationships
Before diving into joins, understand why tables are connected in the first place. Real-world databases split information across multiple tables to avoid duplication and maintain data integrity. You’ll learn about one-to-many, many-to-many, and one-to-one relationships that mirror how businesses actually organize information.
Day 20: INNER JOIN Deep Dive
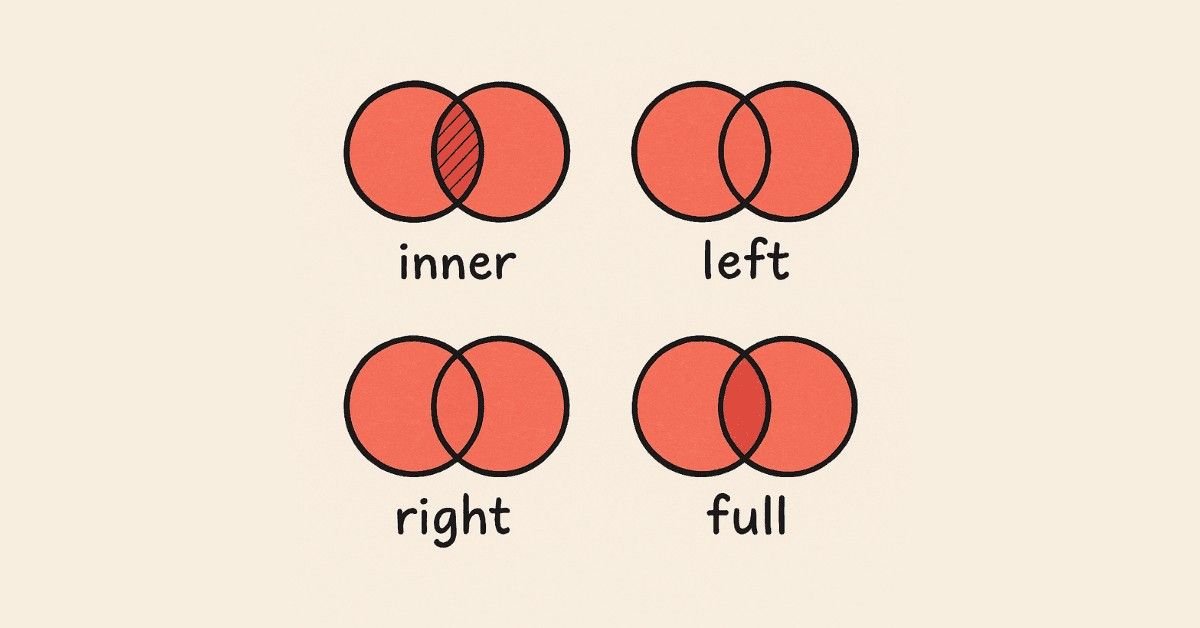
INNER JOIN is your go-to tool for combining related data from multiple tables. Learn how to match customer information with their orders, or connect employees to their departments. You’ll understand the syntax, practice with real-world scenarios, and build queries that pull together complete information from separate tables.
Day 21: LEFT JOIN and RIGHT JOIN
LEFT JOIN returns all records from the left table plus matching records from the right table. This is crucial when you want to include all customers even if they haven’t placed orders yet, for example. RIGHT JOIN works similarly but from the opposite direction. Master these to handle incomplete data gracefully.
Day 22: FULL OUTER JOIN
FULL JOIN returns all records from both tables, whether they match or not. This less common but powerful join type helps you identify mismatches and orphaned records. You’ll learn when full joins are necessary and how to interpret their sometimes surprising results.
Day 23: Self Joins and Multiple Joins
Self joins connect a table to itself—useful for hierarchical data like employee-manager relationships. Multiple joins combine data from three or more tables in a single query. These advanced techniques let you answer complex business questions that require information from across your entire database.
Day 24: SELECT with DISTINCT
The DISTINCT keyword eliminates duplicate rows from your results. Learn when duplicates occur, why they might be problematic, and how DISTINCT solves these issues. You’ll also learn about its performance implications and when to use other approaches instead.
Day 25: Practice Project – Multi-Table Analysis
Build a complete database for an e-commerce system with customers, products, orders, and order details tables. Write queries that join these tables to generate sales reports, identify top customers, and analyze product performance. This real-world project solidifies your understanding of joins and prepares you for actual job scenarios.
🎯 Want to prepare for real SQL jobs? Explore SQL Interview Q&A & scenario-based problems.
Week 5: Subqueries and Advanced Filtering
Day 26: Introduction to Subqueries
Subqueries are queries nested inside other queries. They let you break complex problems into manageable pieces. Learn to write subqueries in WHERE clauses to filter data based on calculated values or results from other tables. This logical approach mirrors how business analysts actually think about data problems.
Day 27: Subqueries in SELECT and FROM
Discover how subqueries in the SELECT clause can add calculated columns to your results. Subqueries in FROM clauses (also called derived tables) let you treat query results as if they were actual tables. These techniques enable sophisticated data transformations and complex calculations.
Day 28: Correlated Subqueries
Unlike regular subqueries, correlated subqueries reference columns from the outer query. They execute once for each row in the outer query, enabling row-by-row comparisons. Learn when correlated subqueries are necessary and when they should be avoided for performance reasons.
Day 29: EXISTS and NOT EXISTS
The EXISTS operator checks whether a subquery returns any results. It’s more efficient than IN for many scenarios and expresses certain logical conditions more naturally. NOT EXISTS finds records that don’t have corresponding entries in another table. These operators are favorites among experienced SQL developers.
Day 30: UNION and Set Operations
UNION combines results from multiple queries into a single result set. Learn the difference between UNION (which removes duplicates) and UNION ALL (which keeps them). Set operations like INTERSECT and EXCEPT (where supported) provide additional ways to compare and combine query results.
Day 31: CASE Statements
CASE statements bring if-then logic into SQL. Create custom categories, handle null values gracefully, and transform data on the fly. CASE is indispensable for creating readable reports and performing conditional calculations. You’ll use this in almost every complex query you write.
Day 32: NULL Handling and Coalesce
NULL represents missing or unknown data, but it behaves differently from other values. Learn how NULL affects comparisons, calculations, and joins. The COALESCE function provides default values when data is missing, making your queries more robust. Proper NULL handling separates good SQL developers from great ones.
Week 6: Data Transformation Techniques
Day 33: Date and Time Functions
Working with dates is crucial in business analysis. Learn to extract parts of dates (year, month, day), calculate date differences, and format dates for reports. Time zone handling, date arithmetic, and period comparisons become second nature. These skills are essential for trend analysis and time-based reporting.
Day 34: Conversion and Casting
Data doesn’t always come in the format you need. CAST and CONVERT functions transform data types—turning text into numbers, formatting dates, or adjusting decimal precision. Learn when explicit conversion is necessary and how implicit conversion can cause unexpected problems.
Day 35: Window Functions Introduction
Window functions perform calculations across sets of rows that are related to the current row. Unlike GROUP BY, window functions don’t collapse rows—you see both individual records and aggregate calculations. ROW_NUMBER, RANK, and DENSE_RANK help you identify top performers, create numbered lists, and handle ties.
Day 36: Practice Project – Advanced Analysis Dashboard
Create a comprehensive sales analysis system using all the techniques from Phase 2. Write queries that identify trends, compare periods, rank products and salespeople, and generate executive summaries. This capstone project demonstrates your ability to tackle real business intelligence challenges.

Ready to understand your career trajectory? Download our SQL Career Roadmap Guide to see exactly how these skills map to different job roles and salary levels.
🔥 Master advanced SQL faster—Download cheat sheets, join charts & DML/DQL PDFs.
PHASE 3: Database Design & Optimization (Days 37-54)
Week 7: Understanding Data Warehousing Concepts
Day 37: Introduction to Data Warehousing
Data warehouses are specialized databases designed for analysis rather than daily transactions. Unlike operational databases that handle orders and customer updates, data warehouses store historical information for business intelligence and reporting. You’ll learn the fundamental difference between OLTP (handling live transactions) and OLAP (analyzing historical trends). This knowledge helps you understand why companies maintain separate systems for operations and analytics.
Day 38: Star Schema and Snowflake Schema
Database design patterns called schemas determine how efficiently you can analyze data. The star schema organizes facts (like sales transactions) surrounded by dimension tables (like customer info, product details, time periods). Snowflake schemas normalize dimensions further for storage efficiency. These design choices significantly impact query performance and how easily business users can understand the data.
Day 39: Fact Tables and Dimension Tables
Fact tables contain measurable business events—sales amounts, quantities, durations—while dimension tables describe the who, what, where, when of those events. Learn to identify which data belongs in facts versus dimensions. This fundamental concept underlies all business intelligence and analytics work. Proper fact and dimension design makes complex queries simpler and faster.
Day 40: Slowly Changing Dimensions
Customer addresses change, product prices fluctuate, and organizations reorganize—how do you track these changes historically? Slowly Changing Dimensions (SCDs) provide strategies for maintaining accurate historical records while accommodating real-world changes. Type 1 overwrites old data, Type 2 creates new records for each change, and Type 3 keeps limited history. Understanding SCDs is crucial for accurate trend analysis.
Day 41: Query Optimization Fundamentals
Even perfect SQL syntax can produce slow queries if not optimized. Learn how databases execute queries through execution plans. Understand why some queries take seconds while others take hours on the same data. Query optimization separates junior developers from senior ones—it’s the skill that makes you indispensable when databases grow large.
Day 42: Indexing Strategies
Indexes are like book indexes—they help databases find information without scanning every page. Learn when indexes speed up queries and when they slow down updates. Understand clustered versus non-clustered indexes, composite indexes, and covering indexes. Poor indexing strategies can cripple database performance, while smart indexing makes everything faster.
Day 43: Practice Project – Data Warehouse Design
Design a complete data warehouse for a retail business with sales facts, customer dimensions, product dimensions, and time dimensions. Implement slowly changing dimensions for customers and products. Create appropriate indexes and write optimized queries for common business questions. This real-world project demonstrates your understanding of analytical database design.
Week 8: Advanced SQL Techniques
Day 44: Common Table Expressions (CTEs)
CTEs make complex queries readable by breaking them into named, reusable parts. Instead of nested subqueries that hurt readability, CTEs present logical steps sequentially. Learn when CTEs improve performance and when they’re just for clarity. Most importantly, discover how CTEs make your code maintainable—you’ll thank yourself when revisiting queries months later.
Day 45: Recursive CTEs
Recursive CTEs solve hierarchical problems like organizational charts, bill of materials, or category trees. They repeatedly reference themselves until a condition is met. This powerful technique handles parent-child relationships that would require multiple queries or application code otherwise. Master recursive CTEs and you’ll solve problems that baffle other developers.
Day 46: Pivot and Unpivot Operations
Business reports often need data rotated from rows to columns (pivot) or columns to rows (unpivot). Learn how to transform monthly sales data from rows into columnar format for comparison. These transformations make reports more readable and enable analyses that would be difficult with standard queries.
Day 47: Stored Procedures Introduction
Stored procedures are pre-compiled SQL code saved in the database. They improve performance, enhance security by controlling data access, and reduce network traffic. Learn to create procedures with parameters, return values, and error handling. Stored procedures are standard in enterprise environments.
Day 48: Variables and Control Flow
Bring programming logic into SQL with variables, IF statements, WHILE loops, and CASE expressions. Build dynamic queries that adapt to different conditions. Control flow statements enable complex business logic within the database layer. These skills bridge the gap between SQL and traditional programming.
Day 49: Error Handling with TRY-CATCH
Professional SQL code anticipates and handles errors gracefully. TRY-CATCH blocks prevent crashes, log problems, and provide meaningful error messages. Learn to identify error types, roll back problematic transactions, and maintain data integrity even when things go wrong. Error handling demonstrates maturity and professionalism in your code.
Day 50: Transactions and ACID Properties
Transactions ensure database operations either complete entirely or not at all—no halfway states. ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) guarantee data reliability even when systems crash or multiple users access data simultaneously. Understanding transactions is essential for applications handling money, inventory, or any critical data.
⚙️ Improve performance—Access optimization guides, index strategies & execution plan tutorials.
Week 9: Performance and Security
Day 51: Query Performance Analysis
Use execution plans to diagnose slow queries. Learn to identify table scans, missing indexes, and inefficient joins. Tools like SQL Profiler and Database Tuning Advisor reveal performance bottlenecks. This diagnostic skill makes you the go-to person when queries need optimization.
Day 52: Writing Efficient Queries
Apply best practices for fast queries—select only needed columns, filter early, avoid unnecessary functions on indexed columns. Learn why some query patterns perform poorly and their faster alternatives. Small changes can reduce query time from minutes to seconds. Efficient queries save company resources and improve user experience.
Day 53: Database Security Basics
Learn about SQL injection attacks and how to prevent them with parameterized queries. Understand user permissions, roles, and the principle of least privilege. Security isn’t just the DBA’s job—every developer must write secure SQL code. Data breaches destroy companies; security knowledge protects your employer and users.
Day 54: Backup, Recovery, and Best Practices
Understand backup strategies—full backups, differential backups, transaction log backups. Learn recovery models and point-in-time restoration. Know best practices for naming conventions, code documentation, and version control for database objects. Professional database work requires reliability and disaster preparedness.
🎯 Checkpoint Milestone: You’ve completed advanced SQL training covering data warehousing, optimization, and professional development practices. These enterprise-level skills qualify you for mid-level SQL developer and business intelligence positions with salaries ranging from ₹5-7 lakhs annually. You can now design efficient databases, optimize complex queries, and implement secure, reliable database solutions.
Wondering how to showcase these advanced skills? Access our Portfolio Building Guide for SQL Professionals to create projects that impress hiring managers.
PHASE 4: Business Intelligence Integration (Days 55-72)
Week 10: Introduction to Power BI with SQL
Day 55: Overview of Power BI
Power BI transforms raw SQL data into interactive visualizations that business users love. Learn how Power BI connects to SQL Server and other databases. Understand licensing options and when to use Power BI Desktop versus Power BI Service. This integration between SQL and visualization tools makes you a complete data professional.
Day 56: Connecting Power BI to SQL Databases
Master different connection modes—Import brings data into Power BI, while DirectQuery keeps data in SQL Server. Learn when each approach works best. Configure data source settings, manage credentials, and handle connection errors. Proper connectivity ensures reports always reflect current data.
Day 57: Power Query Editor Basics
Power Query provides a visual interface for data transformation. Learn to clean data, remove duplicates, split columns, and merge queries without writing complex SQL. Understand how Power Query M language works behind the scenes. These skills complement your SQL knowledge with user-friendly data preparation tools.
Day 58: Data Modeling in Power BI
Create relationships between tables imported from your SQL database. Understand cardinality (one-to-many, many-to-many), cross-filtering direction, and active versus inactive relationships. Good data models make visualizations intuitive and calculations accurate. This bridges your SQL design skills with business intelligence requirements.
Day 59: DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) Fundamentals
DAX is Power BI’s formula language for creating calculated columns and measures. Learn basic functions for aggregation, date manipulation, and filtering. Understand the difference between calculated columns (computed row-by-row) and measures (computed based on context). DAX complements SQL for analytical calculations.
Day 60: Creating Basic Visualizations
Build charts, tables, and cards that communicate data insights effectively. Learn which visualization types suit different data—bar charts for comparisons, line charts for trends, pie charts for composition. Format visuals professionally with appropriate colors, labels, and titles. Visual communication skills make your SQL expertise accessible to non-technical stakeholders.
Day 61: Advanced Visualizations and Interactivity
Implement drill-down, drill-through, and tooltips that let users explore data. Add slicers and filters for interactive analysis. Create bookmarks and buttons for guided navigation through reports. Advanced interactivity transforms static reports into exploratory analytical tools.
Week 11: Dashboard Development
Day 62: Dashboard Design Principles
Learn visual design principles—layout, color theory, information hierarchy. Understand how business users consume information and design accordingly. Bad dashboards overwhelm users with clutter, while good dashboards highlight key insights immediately. Design skills differentiate adequate reports from exceptional ones.
Day 63: Building Sales Dashboards
Create comprehensive sales dashboards combining SQL data with Power BI visualizations. Track revenue, identify top products, analyze regional performance, and monitor trends. Include year-over-year comparisons and target achievement indicators. Sales dashboards are the most common deliverable in business intelligence roles.
Day 64: Creating Operational Dashboards
Build real-time monitoring dashboards for operational metrics. Display current inventory levels, order processing status, or system performance indicators. Implement refresh schedules to keep data current. Operational dashboards help businesses respond quickly to changing conditions.
Day 65: Publishing and Sharing Reports
Learn to publish reports to Power BI Service workspaces. Configure refresh schedules using Power BI Gateway. Share reports and dashboards with colleagues through apps or direct links. Manage permissions to control who sees what data. Publishing skills ensure your work reaches stakeholders effectively.
Day 66: Row-Level Security Implementation
Implement row-level security (RLS) to show different users different data based on their roles. Sales managers see only their region’s data, while executives see everything. RLS combines SQL security principles with Power BI’s flexibility. This enterprise feature is essential for multi-user reporting environments.
Day 67: Performance Optimization in Power BI
Use Performance Analyzer to identify slow visuals. Optimize DAX measures and reduce data model size. Balance functionality with speed—users won’t use sluggish reports. Performance optimization ensures dashboards remain useful as data volumes grow.
Day 68: Practice Project – Complete BI Solution
Build an end-to-end business intelligence solution. Design and populate a SQL database, create an optimized data model in Power BI, develop interactive dashboards, implement security, and publish to Power BI Service. This capstone project demonstrates your ability to deliver complete BI solutions.
Week 12: Real-World Applications
Day 69: Industry-Specific SQL Applications
Explore how different industries use SQL—e-commerce for order management, healthcare for patient records, finance for transaction processing, logistics for inventory tracking. Learn industry-specific terminology and common reporting requirements. Understanding industry contexts helps you communicate with business stakeholders.
Day 70: ETL Processes and Data Integration
Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes move data from source systems into data warehouses. Learn basic ETL concepts—data extraction strategies, transformation logic, load patterns, and scheduling. ETL knowledge helps you understand where data comes from and how it’s prepared for analysis.
Day 71: SQL in DevOps and Automation
Discover how SQL scripts automate database deployments, testing, and maintenance. Learn about version control for database objects and continuous integration for SQL code. Modern development practices apply to databases too. Automation skills make you valuable in agile development environments.
Day 72: Cloud Databases Overview
Get introduced to cloud database platforms—Azure SQL Database, Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL. Understand benefits of cloud databases—scalability, managed backups, automatic updates. Learn basic cloud concepts without diving too deep. Cloud knowledge positions you for future-ready career opportunities.

Ready to put these skills to work? Download our Interview Preparation Guide for SQL + BI Professionals with 100+ real interview questions and model answers.
📊 Upgrade your BI skills—Get Power BI project files, dashboards, and SQL-to-BI practice sets.
PHASE 5: Career Preparation & Professional Development (Days 73-90)
Week 13: Profile Optimization and Job Search Strategy
Day 73: Building a Professional LinkedIn Profile
Your LinkedIn profile is your digital resume and networking tool combined . Learn to craft a compelling headline that immediately communicates your SQL expertise—something like “SQL Developer | Business Intelligence Specialist | Helping Businesses Turn Data into Insights” . Write a summary that tells your story—why you chose SQL, what problems you solve, and what makes you unique . Include specific technologies you’ve mastered: SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Power BI, data warehousing, query optimization .
Add your Frontlines Edutech course completion certificate prominently in the Licenses & Certifications section. List projects you completed during training—describe the business problems you solved, technologies used, and measurable outcomes. Request recommendations from instructors and peers who can vouch for your technical skills and work ethic. Optimize your profile with industry keywords so recruiters find you when searching for SQL talent.
Day 74: Crafting Your SQL Developer Resume
Structure your resume to highlight relevant skills and projects prominently. Start with a summary statement emphasizing your SQL proficiency, analytical mindset, and business intelligence capabilities. Create a dedicated Technical Skills section listing SQL, database systems, BI tools, and complementary technologies. Include specific versions where relevant—SQL Server 2019, MySQL 8.0, Power BI Desktop.
Your projects section becomes crucial when you lack professional experience. Detail the data warehouse design project, the e-commerce analytics dashboard, and the sales reporting system you built. Quantify achievements where possible—”Optimized queries reducing execution time by 75%” or “Designed database supporting 10,000+ daily transactions”. Even if these are training projects, they demonstrate practical application of your skills.
Looking for proven resume templates? Access our SQL Developer Resume Template Pack with ATS-optimized formats tailored for different experience levels.
Day 75: Creating an Impressive GitHub Portfolio
Employers want to see your code, not just read about it. Create a GitHub repository showcasing your best SQL projects. Include well-documented queries solving real business problems—customer segmentation analysis, sales trend identification, inventory optimization. Add README files explaining the business context, your approach, and key insights discovered.
Upload your database design diagrams, ER models, and schema documentation. Include Power BI files demonstrating your visualization skills. Organize repositories logically with clear naming conventions. A professional GitHub presence differentiates you from candidates who only have certificates. Link your GitHub prominently on your LinkedIn profile and resume.
Day 76: Job Search Platforms and Strategies
Know where SQL jobs are posted—LinkedIn Jobs, Naukri, Indeed, Monster, Glassdoor, and company career pages. Set up job alerts for keywords like “SQL Developer,” “Database Developer,” “Business Intelligence Analyst,” and “Data Analyst”. Don’t limit yourself to exact job title matches—many roles need SQL skills even if they’re not primarily database positions.
Research companies actively hiring SQL professionals in your target cities—Bangalore, Hyderabad, Pune, Mumbai, Chennai, Gurgaon. Top employers include IT services firms (TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Cognizant), consulting companies (Accenture, Capgemini, Deloitte), product companies (Microsoft, Amazon, Flipkart), and specialized BI firms. Target a mix of large established companies (for structure and training) and startups (for diverse experience and rapid growth).
Day 77: Networking and Personal Branding
Join SQL and database communities on LinkedIn—follow hashtags like #SQLServer, #DatabaseDevelopment, #BusinessIntelligence. Engage with posts by commenting thoughtfully on industry discussions. Share your own insights—”Here’s how I optimized a complex join operation” or “Five SQL mistakes beginners make”. Consistent visibility builds recognition among recruiters and hiring managers.
Attend virtual meetups, webinars, and conferences focused on data and analytics. Participate in SQL forums like Stack Overflow, Database Administrators Stack Exchange, and Reddit’s r/SQL community. Helping others with their SQL problems demonstrates expertise while building your professional network. Personal branding doesn’t require massive following—thoughtful contributions to your niche community matter more.
Day 78: Understanding Salary Expectations and Negotiation
Entry-level SQL developers in India earn between ₹2.5-4 lakhs annually, while those with 1-3 years experience command ₹4-6 lakhs. Mid-level developers with 3-5 years earn ₹6-9 lakhs, and senior developers with specialized skills exceed ₹10 lakhs. Location significantly impacts compensation—Bangalore and Hyderabad typically pay 15-25% more than tier-2 cities.
Skills beyond basic SQL increase your market value. Power BI proficiency adds ₹1-2 lakhs to your expected salary. Cloud database experience (Azure, AWS) commands premium compensation. Performance tuning expertise is highly valued since it directly saves companies money. When negotiating, emphasize your complete skill set—not just SQL but also BI tools, data warehousing, and business understanding.
Research specific companies’ salary ranges using Glassdoor, AmbitionBox, and Levels.fyi. During negotiations, focus on total compensation including performance bonuses, benefits, and learning opportunities. For your first role, prioritizing good mentorship and skill development over marginal salary differences often proves wiser long-term.
Day 79: Remote Work Opportunities and Freelancing
SQL skills translate exceptionally well to remote work. Many companies hire remote database developers and BI analysts. Platforms like Upwork, Freelancer, and Toptal offer SQL freelancing opportunities. Start with smaller projects—database design reviews, query optimization, report development—to build ratings and portfolio.
Remote work requires additional skills beyond technical expertise—clear written communication, self-management, and proactive status updates. Build a home office setup that supports productive work. Freelancing offers flexibility and potentially higher hourly rates, but requires hustling for projects and managing inconsistent income. Consider part-time freelancing while employed to test whether independent work suits you.
Week 14: Interview Preparation Mastery
Day 80: Technical Interview Fundamentals
SQL interviews typically include three components—theoretical concepts, practical coding, and problem-solving scenarios. Interviewers assess not just whether you know SQL syntax, but whether you can apply it to solve business problems efficiently. Expect questions ranging from basic SELECT statements to complex multi-table joins, subqueries, and optimization challenges.
Practice explaining your thought process aloud while solving problems. Interviewers want to understand your approach—how you break down complex problems, what considerations guide your decisions, and how you debug when things go wrong. Thinking aloud feels awkward initially but becomes natural with practice. This communication skill often matters more than perfect syntax.
Clarify requirements before diving into code. Repeat the question back to the interviewer to confirm understanding. Ask about edge cases—what happens with NULL values, empty tables, or duplicate records. Interviewers appreciate candidates who think comprehensively rather than rushing to code.
Day 81: Common SQL Interview Questions – Basics
Master foundational questions that appear in virtually every SQL interview. Explain the difference between WHERE and HAVING clauses—WHERE filters before grouping, HAVING filters after. Describe various JOIN types with examples—INNER JOIN returns only matches, LEFT JOIN includes all left table records, RIGHT JOIN includes all right table records, FULL OUTER JOIN includes all records from both tables.
Understand PRIMARY KEY versus FOREIGN KEY—primary keys uniquely identify records within a table, foreign keys reference primary keys in other tables to establish relationships. Explain NULL handling—NULL represents unknown values and requires special operators like IS NULL rather than equals comparisons. Define normalization and why it matters—organizing data to reduce redundancy and improve integrity.
Practice writing queries for common scenarios—finding duplicate records, calculating running totals, identifying top N records per category, finding records without matches in another table. These patterns appear repeatedly in interviews because they’re genuinely useful in real work.
Day 82: Advanced SQL Interview Questions
Prepare for sophisticated questions testing deeper understanding. Explain window functions and when to use them instead of GROUP BY. Describe the execution order of SQL clauses—FROM, WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING, SELECT, ORDER BY, LIMIT. Discuss query optimization techniques—appropriate indexing strategies, avoiding SELECT *, filtering early in joins.
Be ready to write recursive CTEs for hierarchical queries. Explain transaction isolation levels and their implications—READ UNCOMMITTED, READ COMMITTED, REPEATABLE READ, SERIALIZABLE. Discuss the difference between DELETE, TRUNCATE, and DROP—DELETE removes specific rows and can be rolled back, TRUNCATE removes all rows quickly but can’t be rolled back easily, DROP removes the entire table structure.
Practice optimizing poorly written queries provided by interviewers. Explain your reasoning—”This query scans the entire table because there’s no index on the WHERE clause column” or “These nested subqueries should be rewritten as joins for better performance”. Optimization questions reveal your depth of understanding beyond basic syntax.
Need comprehensive interview question bank? Access our Complete SQL Interview Preparation Guide with 200+ questions, model answers, and coding challenges categorized by difficulty.
Day 83: Behavioral Interview Preparation
Technical skills get you interviews, but behavioral skills get you hired. Prepare stories demonstrating teamwork, problem-solving, learning agility, and handling pressure. Use the STAR method—Situation, Task, Action, Result—to structure responses. Concrete examples resonate more than generic claims about being a “team player” or “fast learner”.
Common behavioral questions include “Tell me about a time you debugged a complex problem,” “Describe a situation where you had to learn a new technology quickly,” or “How do you handle disagreements about technical approaches?”. Prepare 5-6 versatile stories from your training projects that can address multiple questions. Even without professional experience, you can discuss challenges during training—debugging complex queries, collaborating on group projects, or explaining technical concepts to non-technical peers.
Research the company and role thoroughly before interviews. Understand their products, industry, and recent news. Prepare thoughtful questions about their tech stack, team structure, data challenges, and growth opportunities. Asking intelligent questions demonstrates genuine interest and helps you evaluate whether the role fits your goals.
Day 84: Whiteboard Coding and Online Assessments
Many interviews require writing SQL code on whiteboards or in basic text editors without database access. This tests whether you truly understand SQL rather than relying on tools for error detection. Practice writing queries on paper or in plain text editors to build comfort with this format.
Write clean, readable code even under pressure. Use consistent indentation, meaningful aliases, and descriptive names. Comment your thinking where helpful—”– Filter to active customers only”. Readable code communicates your professionalism and makes debugging easier if something goes wrong.
For online assessments on platforms like HackerRank or LeetCode, read instructions carefully. Pay attention to output format requirements—column names, sort order, handling of NULL values. Test with provided sample data before submitting. Most platforms show expected versus actual output, making debugging manageable.
Day 85: Mock Interviews and Practice
Conduct mock interviews with peers or mentors simulating real interview conditions. Practice answering questions aloud within time constraints. Get feedback on your communication style, technical accuracy, and code quality. Mock interviews reveal gaps in your knowledge while you can still address them.
Use online platforms like InterviewBit, DataLemur, StrataScratch, and SQLPad for structured practice. Many platforms include questions actually asked at specific companies. Focus on understanding concepts rather than memorizing answers—variations of the same problem appear across interviews.
Join study groups with other SQL learners preparing for interviews. Explain concepts to each other—teaching solidifies your own understanding. Share experiences, resources, and encouragement. Interview preparation feels less daunting with a support community.
Day 86: Interview Day Best Practices
Technical preparation matters, but so does practical preparation. Test your internet connection and backup options for virtual interviews. Ensure your environment is quiet and professional. Have SQL reference materials nearby (but don’t obviously rely on them). Keep water handy—talking extensively causes dry mouth.
If you don’t know an answer, admit it honestly rather than bluffing. Follow up with your thought process—”I’m not familiar with that specific function, but I’d approach it by…”. Interviewers appreciate honesty and problem-solving mindset. Many questions intentionally push beyond your knowledge to see how you handle uncertainty.
Take a moment to think before responding to complex questions. Pausing briefly demonstrates thoughtfulness rather than nervousness. Outline your approach before coding. If you get stuck, ask clarifying questions or talk through your thought process—interviewers often provide hints. Remember, interviews are conversations, not interrogations.
Week 15: Continuous Learning and Career Growth
Day 87: Advanced Certifications and Specializations
After landing your first SQL role, consider Microsoft certifications like Azure Database Administrator Associate or Azure Data Engineer Associate. Oracle offers MySQL and Oracle Database certifications recognized globally. These credentials validate expertise and often correlate with salary increases. Certifications aren’t necessary for beginners but become valuable for mid-career advancement.
Specialize in high-demand areas—cloud databases (Azure SQL, AWS RDS), big data technologies (Hadoop, Spark), or specific industries (healthcare analytics, financial services). Specialization increases your market value and narrows job competition. Choose specializations based on market demand and personal interest—you’ll excel in areas that genuinely engage you.
Day 88: Building Your Professional Network
Networking accelerates career growth more than any other factor. Maintain relationships with Frontlines Edutech instructors and classmates—they’re your professional community. Attend data and analytics meetups in your city. Join professional associations and online communities. Most job opportunities come through referrals rather than applications.
Give back by mentoring new SQL learners once you’re established. Write blog posts sharing solutions to problems you’ve solved. Contribute to open-source projects involving databases or analytics. Teaching others solidifies your own knowledge while building reputation. A generous, collaborative approach to career development benefits everyone.
Day 89: Staying Current with Database Technologies
Database technology evolves constantly—new features, optimization techniques, and best practices emerge regularly. Follow database blogs, podcasts, and YouTube channels. Subscribe to newsletters from Microsoft, Oracle, and major database platforms. Experiment with beta features and new database systems in personal projects.
Learn complementary technologies expanding your capabilities—Python for data analysis, cloud platforms for scalability, machine learning for advanced analytics. Full-stack data skills—from database design through analysis to visualization—make you invaluable. But don’t sacrifice SQL depth for breadth—expert-level SQL skills remain your foundation.
Day 90: Reflection and Next Steps
You’ve completed an intensive 90-day transformation from complete beginner to job-ready SQL professional. You understand database fundamentals, write complex queries, optimize performance, design data warehouses, create business intelligence solutions, and communicate technical concepts effectively. These are genuine professional skills that companies desperately need.
Your learning journey doesn’t end here—it’s just beginning. Every job brings new challenges, unfamiliar data, and opportunities to deepen expertise. Approach your career with curiosity, humility, and persistence. The first job might take time to land, but your Frontlines Edutech training has prepared you thoroughly. Trust your preparation, apply consistently, and you will succeed.
🧠 Ace SQL interviews with 200+ technical, advanced & scenario-based questions.
Frontlines Edutech Private Limited has earned the trust of thousands of learners by bridging the gap between academic theory and industry requirements. Our mission focuses on eliminating unemployment by transforming motivated learners into skilled professionals that top companies actively seek. We understand the frustration of being qualified on paper but unprepared for real work—our courses fix exactly that problem.
What Sets Our SQL Course Apart
Industry-Standard Training by Practicing Professionals
Our instructors aren’t just teachers—they’re working professionals from top companies who use SQL daily. They understand current industry practices, common pitfalls, and skills employers actually value. You’ll learn practical techniques used in real production environments, not just textbook theory.
Hands-On Learning from Day One
Forget passive video watching—our approach emphasizes doing. You’ll write hundreds of queries, design multiple databases, and build complete analytical solutions. Daily assignments reinforce each day’s learning while building your portfolio. By course end, you’ll have multiple projects demonstrating your capabilities to potential employers.
Complete Career Support
Technical training is just the beginning. We provide resume building assistance ensuring your skills are presented compellingly. LinkedIn profile optimization helps recruiters find you. Interview guidance prepares you for common technical and behavioral questions. Placement updates connect you with hiring opportunities. On-demand video access lets you review concepts as needed. Course completion certificates validate your training. Downloadable resources support your continued learning.
Special Support for Non-IT Backgrounds
Coming from commerce, arts, or other non-technical backgrounds? We’ve trained hundreds of career switchers successfully. Our beginner-friendly approach assumes no prior technical knowledge. We take extra care ensuring everyone masters fundamentals before advancing. The diversity of our learner community enriches discussions and provides multiple perspectives on problem-solving.
Affordable and Transparent
Quality education shouldn’t require crushing debt. Our SQL course is priced affordably for students and early-career professionals. No hidden fees or surprise charges—transparent pricing from day one. The return on investment is clear—most students land positions paying significantly more than the course cost within months of completion.
Your Success Is Our Mission
We measure success not by course enrollments but by learner outcomes. Thousands of Frontlines Edutech graduates now work at Infosys, TCS, Accenture, Capgemini, Wipro, Cognizant, IBM, KPMG, and other leading companies across India. They started where you are now—curious, motivated, but lacking practical skills. Our proven training methodology transformed them into confident professionals ready to contribute from day one.
You receive more than technical instruction—you join a community committed to your growth. We’re success trainers, mentors, and motivators passionate about helping you reach your full potential. Our approach blends warmth with rigor, support with accountability, and fun with focus. Learning should be powerful but also enjoyable—we ensure every step of your growth journey feels meaningful and engaging.
Companies Actively Hiring Our Graduates
Major technology services companies like TCS, Infosys, and Wipro hire SQL developers for client projects across industries. Consulting firms including Accenture, Capgemini, and Cognizant need SQL expertise for enterprise implementations. Global technology leaders like IBM and Microsoft require database professionals for their products and services. Professional services firms including KPMG and Deloitte use SQL for data analytics and auditing.
Beyond these household names, countless startups, mid-sized companies, and specialized firms need SQL skills. The SQL job market in India is expanding rapidly, particularly in technology hubs like Bangalore, Hyderabad, Pune, Mumbai, Chennai, Gurgaon, and Noida. Key sectors driving SQL demand include technology development, data science and analytics, artificial intelligence, media and entertainment, and the startup ecosystem.
Take the First Step Toward Your SQL Career Today
You now have a complete roadmap for transforming yourself into a job-ready SQL professional in just 90 days. This structured, proven path has worked for thousands of learners before you. The question isn’t whether it works—the question is whether you’re ready to commit to your transformation.
The Indian job market desperately needs skilled SQL professionals. Entry-level positions start at comfortable salaries with clear growth paths toward significantly higher earnings. SQL skills open doors across industries, from technology to healthcare to finance. This is a career with stability, growth potential, and the satisfaction of solving real business problems.
But knowledge alone isn’t enough—you need structured training, hands-on practice, expert guidance, and career support. Frontlines Edutech provides the complete ecosystem for your success. Our SQL course combines comprehensive technical training with practical project work and professional development. We’ve refined this curriculum through thousands of successful student outcomes.
Don’t let another month pass wishing you had marketable skills. Start your 90-day transformation today.
Enroll in Frontlines Edutech’s SQL Course and begin building the career you deserve.
Contact us at +91-83330 77727 or email media.frontlines@gmail.com for enrollment details and upcoming batch schedules. Visit www.frontlinesedutech.com to learn more about our courses and success stories. Follow us on LinkedIn (Frontlines Edutech) and social media (Frontlines Media) for daily insights, tips, and opportunities.
Your future self will thank you for taking action today. Join the thousands of successful Frontlines Edutech graduates who transformed their careers through dedicated learning and expert guidance. Your 90-day journey to SQL mastery and career success starts now.
Building Trust & Careers Since Inception | Frontlines Edutech Private Limited
The ultimate SQL course roadmap designed specifically for Indian students and working professionals seeking career transformation through practical, industry-aligned training.
