Pega Developer: Your Complete 90-Day Career Transformation Roadmap
Starting a career in Pega development isn’t just about learning another technology—it’s about stepping into one of the most lucrative and in-demand fields in the IT industry today. With Pega professionals earning an average salary of ₹21 lakhs per year in India, and top performers making upwards of ₹78 lakhs annually, this 90-day journey could be your gateway to financial freedom and career stability.
The Business Process Management market is exploding, projected to grow from $21.51 billion in 2025 to $70.93 billion by 2032, creating thousands of job opportunities for skilled Pega developers. Companies across banking, insurance, healthcare, and IT sectors are desperately seeking professionals who can automate their business processes and build intelligent workflows. Whether you’re a fresh graduate or an experienced professional looking to upskill, this roadmap will take you from complete beginner to job-ready Pega developer in just three months.
💡 New to Pega?
Learn the fundamentals step-by-step with our beginner How-to Guides.
1. Why Choose Pega Development in 2025 ?
Before diving into the daily learning plan, understand what makes Pega special. Unlike traditional coding that requires years of experience, Pega is a low-code platform that lets you build enterprise applications faster. You’ll learn to create business workflows, automate processes, design user interfaces, and integrate systems—all skills that make you invaluable to any organization. With over 207 Pega job openings in India right now and companies actively hiring developers with just 1-2 years of experience, the timing couldn’t be better.
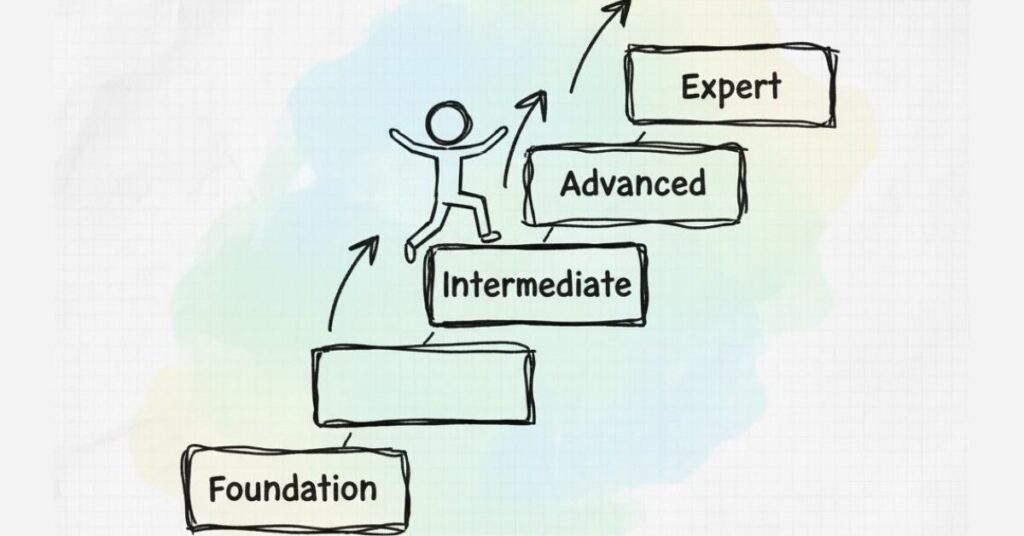
Course Structure: 90 Days to Master Pega
This roadmap is divided into four major phases: Foundation (Days 1-25), Intermediate Skills (Days 26-50), Advanced Concepts (Days 51-75), and Real-World Implementation (Days 76-90). Each day includes specific topics, hands-on practice, and daily assignments to ensure you’re not just learning theory but actually building applications.

2. Foundation Building (Days 1-25)
📘 Download practice assignments, rules examples & beginner templates from our Resource Library.
Week 1: Getting Started with Pega (Days 1-7)
Day 1: Introduction to Pega BPM and Platform Overview
Today marks the beginning of your transformation. You’ll explore what Pega BPM (Business Process Management) really means and why companies worldwide trust it for their critical business operations. Start with understanding the PRPC (Pega Rules Process Commander) IDE—the environment where all magic happens. Get familiar with operators and logins, which are your entry points into the Pega universe.
Daily Assignment: Install Pega Personal Edition on your system and successfully log in as an operator. Document your first impressions.
Day 2: Creating Your First Pega Application
Nothing beats the excitement of creating your first application. Using the Application Wizard, you’ll build a simple application from scratch. Don’t worry about complexity—focus on understanding the process flow. Learn what makes Pega applications different from traditional programming—the rule-based architecture that makes changes faster and deployment easier.
Daily Assignment: Create a basic “Employee Leave Request” application using the wizard. Name it, configure it, and save it successfully.
Day 3: Understanding Class Groups and Predefined Classes
Think of class groups as organizing folders that keep your application structured. Today you’ll understand why organization matters in Pega and how class groups prevent chaos in large projects. Explore the predefined classes that Pega provides out-of-the-box—these are templates that save you hours of work.
Daily Assignment: Create three custom classes within your application and document their purpose and relationships.
Day 4: Mastering Inheritance in Pega
Inheritance is what makes Pega powerful. Instead of rebuilding everything from scratch, you inherit properties and behaviors from parent classes. Learn about Direct Inheritance (straightforward parent-child relationships) and Pattern Inheritance (flexible, dynamic inheritance). This concept will save you countless hours throughout your career.
Daily Assignment: Build a class structure showing inheritance relationships. Create Work-MyApp-Employee and Work-MyApp-Manager classes with proper inheritance.
Day 5: Web Page Creation and Flow Execution
Time to make things visible! Create your first web page and understand how it connects to flows. A web page without a flow is like a car without an engine—it looks good but doesn’t work. Today you’ll connect both and see your first working screen.
Daily Assignment: Design a simple data entry web page with five fields and connect it to a flow that navigates between screens.
Day 6: Properties and Property Rules
Properties are the building blocks of data in Pega. Learn about different property types—text, integer, date, true/false—and when to use each. Understanding the property rule form helps you create fields that validate data correctly and store information efficiently.
Daily Assignment: Create ten different properties with various data types for an employee profile. Include validation rules for at least three properties.
Day 7: User Interface Design with Sections
Sections are reusable UI components that make your life easier. Instead of designing the same form twenty times, create it once as a section and reuse it everywhere. Today you’ll master the art of creating clean, professional-looking user interfaces using sections.
Daily Assignment: Build three sections—header, form, and footer—and combine them into a complete page layout. Make it visually appealing.
Week 2: Working with Flows and Actions (Days 8-14)
Day 8: Flow Actions Fundamentals
Flow Actions are buttons that users click to move processes forward—Submit, Approve, Reject, Cancel. Each action can trigger different behaviors and navigate to different screens. Understanding Flow Actions is crucial because they control the entire user experience.
Daily Assignment: Create five different flow actions with custom labels and icons. Configure each to perform different navigation patterns.
Day 9: Understanding PRPC Process Flows
Process flows are visual representations of your business logic. Think of them as flowcharts that actually execute. Today you’ll learn to drag and drop shapes—assignments, decisions, integrations—and connect them to create working business processes.
Daily Assignment: Build a complete approval process flow with three levels—submission, manager review, and final approval. Include reject and resubmit paths.
Day 10: Creating and Managing Work Objects
Work Objects represent tasks, cases, or requests that move through your system. An insurance claim, a loan application, a support ticket—all are work objects. Learn how they’re created, tracked, and completed.
Daily Assignment: Create a work object manually and through automation. Track it through different statuses and observe the lifecycle.
Day 11: Changing Work Object Status with Assignments
Assignments are stages where work pauses and waits for user action. Learn to change work object status using assignment shapes in your flow. Each status change triggers different behaviors and notifications.
Daily Assignment: Build a flow that changes status five times—New, Pending-Review, Pending-Approval, Approved, Completed. Test the entire journey.
Day 12: Clipboard and Data Management
The Clipboard is Pega’s temporary memory where all data lives during processing. Understanding it is like looking under the hood of a car—you see exactly what’s happening. Master the “Where Am I?” tool to navigate clipboard pages and properties.
Daily Assignment: Run a process, open the Clipboard, and document the entire data structure. Identify system-created pages and your custom data.
Day 13: Understanding pyWorkPage
pyWorkPage is the heart of every work object—the main page that holds all your business data. Pega creates it automatically, but understanding how it works gives you superpowers. Learn what properties exist on it and how to use them effectively.
Daily Assignment: Explore pyWorkPage for your work objects. Create a document mapping all standard properties and their purposes.
Day 14: Advanced Layouts – Multi, Dynamic, and Free Form
Professional applications need professional layouts. Move beyond basic forms to create multi-column layouts, dynamic sections that appear conditionally, and free-form designs that match your creativity. Good UI design separates amateur developers from professionals.
Daily Assignment: Create one page using all three layout types. Make dynamic sections that show/hide based on user selections. Focus on visual appeal.
Week 3: Business Logic and Conditions (Days 15-21)
Day 15: When Conditions – The Power of Dynamic Logic
When conditions are if-then statements that control visibility, enable/disable fields, and make decisions. Instead of hardcoding logic, you create reusable When rules that make your application intelligent and adaptive.
Daily Assignment: Create five When conditions checking different scenarios—field values, user roles, dates, numerical comparisons. Test each thoroughly.
Day 16: Applying When Rules to Layouts and Properties
Now apply yesterday’s When rules to actually control your UI. Make sections appear only for managers, hide fields until certain conditions are met, enable buttons only when data is complete. This is where applications become smart.
Daily Assignment: Build a form where fields appear dynamically based on selections. Create a cascading reveal effect where each choice unlocks new options.
Day 17: Introduction to Activities – Business Logic Layer
Activities are step-by-step instructions that manipulate data, call other rules, and execute business logic. Think of them as recipes—precise steps that achieve specific outcomes. Today marks your entry into programmatic thinking within Pega.
Daily Assignment: Create your first activity with five steps that create a page, set properties, display messages, and remove the page.
Day 18: Working with User Pages and Basic Methods
User pages are temporary containers for data manipulation. Learn essential methods: Page-New (creates pages), Property-Set (assigns values), Page-Remove (cleans up), and Show-Page (displays data for debugging). These are your everyday tools.
Daily Assignment: Build an activity that creates three user pages, populates them with data from your work object, performs calculations, and displays results.
Day 19: Mastering the Tracer – Your Debugging Best Friend
The Tracer is like X-ray vision for your application. It shows every rule execution, every decision made, every property set—in real-time. Learning to read Tracer output separates struggling developers from efficient problem-solvers.
Daily Assignment: Run a complex flow with the Tracer on. Identify exactly where data changes, which rules execute, and how long each step takes. Find and fix one issue using Tracer.
Day 20: Call vs Branch – Activity Flow Control
When one activity needs to execute another, you use Call or Branch instructions. Call waits for completion and returns; Branch transfers control completely. Understanding when to use which prevents many bugs and performance issues.
Daily Assignment: Create three activities that call each other using both Call and Branch. Document the differences in execution and use cases.
Day 21: Exit-Activity vs End-Activity Methods
These methods control how activities conclude. Exit-Activity stops immediately and returns to the caller; End-Activity completes the current activity’s remaining steps first. Small difference, huge implications for your application’s behavior.
Daily Assignment: Build scenarios demonstrating both methods. Create situations where using the wrong one causes errors or unexpected behavior.
Week 4: Data Storage and Database Integration (Days 22-25)
Day 22: Calling Flows from Activities
Sometimes automated processes need to start user workflows. Learn to invoke flows from activities, passing data between automated logic and human interaction. This technique is essential for complex applications that blend automation and manual steps.
Daily Assignment: Create an activity that processes data, validates it, then launches a flow for human review. Pass parameters between both.
Day 23: Activity Parameters – Data Communication
Parameters let activities communicate—sending and receiving data like functions in programming. Master parameter definition, passing values between activities, and viewing parameters in Tracer. This skill is crucial for modular, reusable code.
Daily Assignment: Build a calculator using three activities with parameters—one for input, one for calculation, one for display. Pass values through all three.
Day 24: Data Storage Rules and Data Tables
Move beyond temporary clipboard data to permanent storage. Data Tables store reference data—country lists, product catalogs, configuration settings. Learn what “Does not belong to Class Group” means and why it matters for data organization.
Daily Assignment: Create three data tables—Countries, Departments, and Products. Populate each with at least ten records. Set up proper keys and searchable columns.
Day 25: Understanding Data Layer vs Work Layer
Pega separates reference data (Data Layer) from transactional work (Work Layer). This architecture improves performance and maintainability. Learn about the Data- predefined class, why it’s special, and how it organizes your application structure.
Daily Assignment: Document the entire class structure of your application, clearly identifying Data Layer classes versus Work Layer classes. Explain the purpose of each.
🎓 Become job-ready faster—join our complete Pega Developer Course with real projects.
🎯 Progress Check: You're 28% Complete!
Congratulations! You’ve mastered the fundamentals. You can now create applications, design interfaces, write business logic, and store data. Take a moment to review your work from the past 25 days. Build a mini-project combining everything you’ve learned—perhaps a simple help desk system or expense tracker. This consolidation is crucial before moving to intermediate concepts.
3. Intermediate Skills Development (Days 26-50)
Week 5: Database Operations and Advanced Data Handling (Days 26-32)
Day 26: Physical Database Tables and Class Mapping
Every Pega class maps to a physical database table. Understanding this connection is crucial for performance optimization and troubleshooting. Learn about pzInsKey (the unique identifier for every database record) and how to test database connections through the Class rule form.
Daily Assignment: Map your application’s class structure to physical database tables. Document table names, primary keys, and connection properties for each class.
Day 27: Obj-Methods for Data Operations
Obj-Methods are your tools for interacting with the database. Unlike manual SQL, these methods follow Pega’s security and business rules automatically. Today you’ll work with fundamental methods that form the backbone of data operations.
Daily Assignment: Create an activity using five different Obj-Methods to demonstrate CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) on your work objects.
Day 28: Obj-Browse – Searching and Retrieving Data
Obj-Browse retrieves multiple records from the database based on search criteria. It’s like writing SELECT queries without actual SQL. Learn to fetch filtered data, sort results, and limit record counts for performance.
Daily Assignment: Build a search functionality that lets users find work items by status, date range, and assigned operator. Display results in a clean table format.
Day 29: Dropdown Controls and Data Population
Dropdown menus make applications user-friendly. Learn to implement pxDropDown controls and populate values from Data Storage Rules instead of hardcoding options. When reference data changes, your dropdowns update automatically.
Daily Assignment: Create five cascading dropdowns where each selection filters the next—Country → State → City → Department → Team. Populate all from data tables.
Day 30: Expression Builder Mastery
The Expression Builder creates dynamic formulas and calculations. Generate primary keys, calculate totals, format dates, concatenate strings—all without writing code. This tool makes your applications intelligent and reduces manual data entry.
Daily Assignment: Build ten expressions: automatic ID generation, age calculation from birthdate, full name from first/last names, discount calculations, and date formatting.
Day 31: Obj-Save with Write Now and Commit
Saving data seems simple until you understand transaction management. Learn the difference between Write Now (immediate database commit) and Commit methods (batch transaction). Wrong choices cause data loss or performance issues.
Daily Assignment: Create scenarios demonstrating both approaches. Build an activity that saves multiple records and observe transactional behavior with database failures.
Day 32: Obj-Open Methods – Primary Key vs Handle
Two methods retrieve single records: Obj-Open (using your defined primary key) and Obj-Open-By-Handle (using pzInsKey). Understanding when to use each prevents errors and improves efficiency. pzInsKey is unique across all tables; your key might not be.
Daily Assignment: Retrieve the same record using both methods. Document the differences in parameters, performance, and appropriate use cases for each approach.
Week 6: Advanced Business Logic (Days 33-39)
Day 33: Working with Operator Data
Operators (users) have their own database table with login credentials, preferences, and permissions. Learn to access operator information using the OperatorID page and Data-Admin-DB-Operator class. This knowledge is essential for personalization and audit trails.
Daily Assignment: Build a dashboard showing current user’s information: full name, email, work group, access roles, and last login time. Add a user directory search feature.
Day 34: Rule Data Form and pzInsKey Retrieval
Every rule in Pega has a database record with a pzInsKey. The Rule Data form lets you examine rule storage and retrieve keys for any rule. This is advanced knowledge that helps with rule manipulation and custom utilities.
Daily Assignment: Create a utility that lists all flow rules in your application with their pzInsKeys, versions, and last modified dates. Make it searchable.
Day 35: Reports – Fetching Work Objects by Status
Reports extract business intelligence from your work items. Learn to create reports that filter by status, date ranges, assigned users, and custom properties. Reports power dashboards and management visibility.
Daily Assignment: Build three reports: pending items by age, completed items by user, and monthly volume trends. Add visual formatting to highlight urgent items.
Day 36: Report Joins – Class and Index Joins
Simple reports pull from one table; real business questions need data from multiple sources. Class Joins relate work objects to associated data based on relationships. Index Joins use database indexes for optimal performance.
Daily Assignment: Create reports using both join types: work items with customer details (class join) and aged case analysis with user information (index join).
Day 37: Introduction to Data Transforms
Data Transforms (DTF) map data between pages or set default values efficiently. They’re like activities but optimized for data manipulation without procedural logic. Learning when to use DTF versus activities is a mark of experienced developers.
Daily Assignment: Create five data transforms: copy customer data to work page, set default values for new cases, transform data formats, aggregate calculations, and conditional mapping.
Day 38: Customizing pyDefault Data Transform
pyDefault runs automatically when creating work objects, setting initial values. Customizing it ensures every case starts with correct data—user information, timestamps, sequence numbers, calculated fields.
Daily Assignment: Customize pyDefault for your application to auto-populate creator name, creation timestamp, auto-generated case number, and default priority based on case type.
Day 39: Activity vs Data Transform Decision Making
This is where experience shows. Activities offer full procedural control with branching, looping, and method calls. Data Transforms excel at simple mappings and run faster. Learn the decision criteria professionals use.
Daily Assignment: Convert three activities to data transforms where appropriate. Document scenarios where activities are mandatory: database operations, flow invocations, complex branching.
Week 7: Declare Rules – Automated Intelligence (Days 40-46)
Day 40: Understanding Declare Expressions
Declare Expressions calculate values automatically whenever inputs change. Unlike activities you call manually, these run automatically in the background. Understand Forward Chaining (calculates immediately) versus Backward Chaining (calculates on-demand when needed).
Daily Assignment: Create five declare expressions: order total from line items, age from birthdate, days until deadline, status message based on conditions, and dynamic pricing.
Day 41: Declare Constraints – Data Validation
Declare Constraints enforce business rules automatically. They validate data and prevent invalid records from saving. Unlike When conditions that control visibility, constraints block incorrect data entry entirely.
Daily Assignment: Implement constraints for your application: email format validation, date range checks, required field enforcement, numerical limits, and cross-field validation rules.
Day 42: Declare OnChange – Reactive Logic
Declare OnChange triggers activities when specific property values change. It’s like event-driven programming—when status changes to “Approved,” automatically send emails and update related records. This automation reduces manual steps and ensures consistency.
Daily Assignment: Create OnChange rules for status transitions: send notifications, update timestamps, cascade changes to child cases, log audit entries, and trigger external integrations.
Day 43: Declare Trigger – Database Event Monitoring
Declare Triggers watch database tables for changes from any source—Pega or external systems. When records are inserted, updated, or deleted, triggers execute specified activities. This enables real-time integration with other enterprise systems.
Daily Assignment: Set up a trigger monitoring your work table. When new high-priority cases arrive, automatically assign them to specific users and send escalation alerts.
Day 44: Declare Pages – Cached Data for Performance
Declare Pages load data once and cache it for reuse, dramatically improving performance. Instead of querying the database repeatedly for country lists or product catalogs, declare pages load them once at startup.
Daily Assignment: Create declare pages for reference data: countries, product categories, organizational hierarchy, and configuration settings. Measure performance improvement in your reports.
Day 45: Declare Index – Optimized Search
Declare Index creates database indexes automatically based on report usage patterns. Proper indexing transforms slow reports running in minutes to subsecond queries. Understanding indexing is crucial for enterprise-scale applications.
Daily Assignment: Analyze your slowest reports using the Database Trace tool. Create declare indexes for commonly searched properties and remeasure performance.
Day 46: Integration Review and Mini-Project
Today consolidates Week 7 learning. Declare rules are powerful automation tools that separate good developers from great ones. They make applications intelligent and self-maintaining.
Daily Assignment: Build a mini-project using all declare rules: an order management system with automatic totals, validation, status-based notifications, external system monitoring, cached product data, and optimized search.
Week 8: Versioning and Rule Management (Days 47-50)
Day 47: Rules, RuleSets, and Versioning Fundamentals
Every piece of configuration in Pega is a rule. RuleSets organize rules into deployable packages. Versioning enables you to enhance applications without breaking production systems. Understanding this architecture is essential for enterprise development.
Daily Assignment: Document your application’s ruleset structure. Create a new ruleset version following naming conventions. Understand major and minor version differences.
Day 48: Rule Versioning and Bulk Operations
Learn to create new rule versions for enhancements, perform bulk check-ins of related rules, and lock ruleset versions to prevent changes after deployment. These practices ensure controlled, auditable development.
Daily Assignment: Create version 2 of your application. Copy and modify ten rules in the new version. Perform bulk operations to check in all changes and lock the previous version.
Day 49: RuleSet Prerequisites and Dependencies
Applications often depend on multiple rulesets—your custom application, shared frameworks, and Pega system rules. Prerequisites define which rulesets are available and their version ranges. Misconfigured prerequisites cause mysterious errors.
Daily Assignment: Map your application’s complete ruleset dependency tree. Document all prerequisites, their versions, and the rationale for each dependency. Test with intentionally wrong versions to understand error messages.
Day 50: Enhancement Workflow – Real Development Practice
From this day forward, all development follows real-world practices: create new versions, develop enhancements, test thoroughly, version your changes, and prepare for deployment. This workflow matches professional environments.
Daily Assignment: Choose a feature from your application and enhance it using proper versioning. Document the complete process: requirement, design, development in new version, testing, and check-in.

🧭 Plan your long-term Pega career—explore the next certifications & growth interview Guide
🎯 Progress Check: You're 56% Complete!
Outstanding progress! You’ve moved from basics to intermediate mastery. You can now handle complex data operations, automate business logic with declare rules, and manage application versions professionally. Your skills match those expected of developers with 6-12 months of experience.
4. Advanced Development Concepts (Days 51-75)
🎨 Improve your UI/UX skills with ready-to-use templates, section guides & design resources.
Week 9: Advanced Flow Design (Days 51-57)
Day 51: Types of Flows – Process, Sub, and Screen Flows
Pega offers three flow types for different purposes. Process Flows model complex business processes with branching and decision-making. Sub Flows are reusable flow components. Screen Flows guide users through connected screens without business process context.
Daily Assignment: Build one of each flow type: a loan approval process flow, a reusable document collection sub-flow, and a multi-step registration screen flow. Understand when to use each.
Day 52: Screen Flows Deep Dive
Screen Flows excel at wizards and multi-step forms. Learn the “Save on Last Step” option that prevents saving incomplete data. Understand when screen flows are better than process flows—simple, sequential user interactions without complex business logic.
Daily Assignment: Create a comprehensive onboarding screen flow: personal info, employment details, document upload, preferences, review, and submit. Implement validation at each step.
Day 53: Sub-Process Shape and Flow Reusability
The Sub-Process shape invokes sub-flows or screen flows from process flows. This modular approach promotes reusability and maintains cleaner flow diagrams. Large flows become manageable when decomposed into logical sub-flows.
Daily Assignment: Refactor your most complex flow by extracting repeated logic into sub-flows. Invoke them using sub-process shapes. Document how reusability improves maintenance.
Day 54: Spin-Off – Parallel Work Creation
Spin-Off creates new work objects from existing ones—child cases from parents or parallel processing paths. When a loan application needs separate credit checks, income verification, and collateral assessment simultaneously, Spin-Off creates each as an independent case.
Daily Assignment: Implement a purchase order approval system that spins off separate approval tasks to finance, operations, and legal teams. Parent case completes only when all children finish.
Day 55: Decision Shapes – Activity vs Declare Expression
Decision shapes route flows based on conditions. You can use activities (programmatic decisions) or declare expressions (declarative logic). The choice affects performance, maintainability, and rule reuse.
Daily Assignment: Create five different decision scenarios using both approaches. Compare execution speed using Tracer. Identify patterns for when each approach is optimal.
Day 56: Decision Tables and Decision Trees
Decision Tables evaluate conditions in tabular format—perfect for pricing rules, eligibility checks, and risk scoring. Decision Trees handle hierarchical decisions with branching logic. Learn when each structure fits your business rules better.
Daily Assignment: Build insurance premium calculation using a decision table (age, coverage, region) and a loan eligibility decision tree (income, credit score, employment). Compare usability.
Day 57: Map Value and Fork in Decisions
Map Value rules translate codes to descriptions without complex when rules or decision tables. Fork allows parallel execution from decision points. These advanced techniques handle specialized scenarios elegantly.
Daily Assignment: Create map value rules for status codes, error messages, and user role descriptions. Implement a forked decision where multiple teams review cases simultaneously.
Week 10: User Experience and Actions (Days 58-64)
Day 58: Flow Action Types and Configurations
Flow Actions are more than simple buttons. Learn different action types: Connector Actions (move flow forward), Local Actions (side tasks without flow advancement), and their various configurations. Each serves specific user experience needs.
Daily Assignment: Create ten different flow actions with various configurations: standard submit, approve/reject pair, cancel with confirmation, save draft, print, email, delegate, and custom actions.
Day 59: Local Actions and Popups
Local Actions perform side tasks without advancing the flow—adding comments, uploading documents, viewing history. Learn to implement them as popups for better UX or as flow-wide actions available throughout the process.
Daily Assignment: Add five local actions to your application: add notes (popup), attach documents, view case history, print summary, and email case details. Test their availability across different flow stages.
Day 60: Attachments and Document Management
Professional applications manage documents—contracts, invoices, identification. Learn about attachment tables, work object attachment classes, and predefined sections for upload/display. Security and version control are crucial here.
Daily Assignment: Implement comprehensive document management: upload with category classification, preview attachments, download, delete with permissions, and version history. Support multiple file types.
Day 61: Harness Types – New, Perform, Confirm, Review
Harnesses are templates that frame your user interface. New Harness displays new case creation screens. Perform Harness shows active assignments. Confirm Harness displays read-only summaries. Each serves distinct user interactions.
Daily Assignment: Customize all four harness types for your application. Brand them with logos, adjust layouts for mobile responsiveness, and ensure consistent navigation across all harness types.
Day 62: Customizing OOTB Sections
Pega provides out-of-the-box (OOTB) sections like pyActionArea and pzActionAreaButtons that control action buttons and navigation. Customizing these gives you fine-grained control over user experience.
Daily Assignment: Customize action area sections to: hide default buttons, add custom actions with icons, reorder buttons based on priority, and implement conditional visibility for different user roles.
Day 63: Dynamic System Settings (DSS)
Dynamic System Settings store configuration values accessible application-wide without code changes. Environment-specific settings, feature toggles, timeout values, and thresholds become configurable without redeployment.
Daily Assignment: Create DSS for: email timeout values, retry counts for integrations, feature flags for A/B testing, approval thresholds by region, and notification preferences. Use them in expression builder.
Day 64: User Experience Polish and Testing
Consolidate all UX learning. Professional applications feel intuitive and responsive. Every button placement, label text, color choice, and loading indicator affects user perception and adoption.
Daily Assignment: Conduct UX review of your entire application. Document improvements needed. Implement: loading indicators for slow operations, confirmation dialogs for destructive actions, helpful error messages, and consistent styling.
Week 11: Email Integration and Communication (Days 65-71)
Day 65: Outbound Email Integration Fundamentals
Business applications must communicate. Email integration notifies users of assignments, sends confirmations, and delivers reports. Learn SMTP configuration, email accounts, and security considerations.
Daily Assignment: Configure email account settings in Pega. Test connectivity. Send a simple test email from an activity using the standard email activity. Document configuration parameters and troubleshooting steps.
Day 66: Correspondence Rules and Types
Correspondence rules are email templates that merge dynamic data into formatted messages. Different types serve different purposes—notifications, confirmations, alerts, reports. Parameter configuration using DSS enables environment-specific customization.
Daily Assignment: Create five correspondence templates: case assignment notification with deadline, approval request with case summary, rejection notification with reasons, completion confirmation, and weekly pending items report.
Day 67: OOTB Email Activities and Correspondence Smart Shape
Pega provides pre-built email activities and a Correspondence smart shape for flows. Learn when to use each approach. Smart shapes integrate seamlessly into process flows; activities offer more control for complex scenarios.
Daily Assignment: Implement email notifications using both methods. Add correspondence shapes to your flows for automatic notifications. Create custom email activities for scenarios needing special logic or attachments.
Day 68: Email Templates with Attachments and HTML Formatting
Professional emails use HTML formatting, embedded images, and attachments. Learn to create visually appealing correspondence that represents your organization professionally. Include case documents as attachments dynamically.
Daily Assignment: Design branded email templates with HTML: company logo, formatted tables for case details, conditional sections, call-to-action buttons, and automatic PDF generation of case summaries attached to emails.
Day 69: Operator Management and Custom Operators
Understanding operators deeply enables security implementation, team management, and personalization. Learn to create operators, configure their profiles, set passwords, and manage access.
Daily Assignment: Create five operators representing different roles: developer, tester, manager, business user, and administrator. Configure appropriate access for each. Test your application with each operator to verify permissions.
Day 70: Operator, Access Group, and Application Relationships
This is crucial security architecture. Operators belong to Access Groups. Access Groups reference Applications and RuleSets. Understanding these relationships prevents security holes and access issues.
Daily Assignment: Document complete security architecture for your application. Create a diagram showing operators, access groups, applications, and rulesets. Create test scenarios verifying appropriate access restrictions.
Day 71: Multiple Access Groups and Dynamic Access
Operators can have multiple access groups for different contexts—a developer might access both development and testing environments differently. Learn dynamic access group assignment based on context.
Daily Assignment: Configure operators with multiple access groups. Create scenarios where access changes based on: application being accessed, time of day, user location, or case type. Test thoroughly.
Week 12: Routing and Assignment Distribution (Days 72-75)
Day 72: Routing Fundamentals and Types
Routing determines who works on assignments. Learn different routing types: Worklist (specific user), Workbasket (team queue), skill-based routing, load-balanced routing. Each strategy suits different business scenarios.
Daily Assignment: Document routing requirements for five business scenarios: personal tasks, team queues, urgent escalations, specialized skills, and balanced distribution. Design routing strategies for each.
Day 73: Worklist Routing and Work Groups
Understand the relationship between Operators, Work Groups, and Worklists. Work Groups organize users into logical teams. Worklist routing assigns tasks to specific users within those groups.
Daily Assignment: Create organizational structure: three departments, each with two work groups. Configure operators as members. Implement routing that assigns cases to specific users based on case properties and user availability.
Day 74: Workbasket Routing and Team Queues
Workbaskets (Work Queues) are team pools where any team member can claim assignments. Learn to create workbaskets, configure access, and implement get-next-work logic that prioritizes urgent items.
Daily Assignment: Create workbaskets for customer service, approvals, and escalations. Implement routing rules assigning cases to appropriate queues based on type, priority, and SLA. Configure workbasket access in user portals.
Day 75: Conditional Routing Based on Status and Properties
Real applications need intelligent routing. Route simple requests to junior staff, complex ones to experts. Route based on status transitions—new cases to reviewers, rejected cases back to originators, approved cases to fulfillment.
Daily Assignment: Implement sophisticated routing logic using decision rules. Create scenarios where routing changes based on: case complexity score, customer tier, monetary value, SLA urgency, and previous assignment history.
📘 Master routing with structured How-to Guide for real business scenarios.
🎯 Progress Check: You're 83% Complete!
Exceptional achievement! You’ve mastered advanced development concepts that position you as a strong mid-level Pega developer. Your knowledge now spans user experience design, integration, security, and assignment management. These skills typically require 12-18 months of professional experience.
5 .Enterprise Features and Real-World Implementation (Days 76-90)
🤖 Understand enterprise automation with our AI-based learning resources.
Week 13: Service Level Agreements and Agents (Days 76-82)
Day 76: Service Level Agreement (SLA) Fundamentals
SLAs ensure work completes on time by setting deadlines and escalations. Every assignment can have goals, deadlines, and passed-deadline urgency adjustments. Understanding SLAs is critical for meeting business commitments and maintaining customer satisfaction.
Daily Assignment: Design SLA structure for five different case types: urgent support tickets (2-hour goal, 4-hour deadline), standard approvals (1-day goal, 3-day deadline), complex reviews (3-day goal, 7-day deadline). Define escalation actions for each.
Day 77: SLA Types and Configuration
Learn different SLA types: assignment-level (individual tasks), case-level (entire process), and service-level (organizational metrics). Configure how urgency increases over time and understand the pySLAName property in pyDefault activity.
Daily Assignment: Implement all three SLA types in your application. Create a dashboard showing cases approaching deadline, past deadline, and requiring escalation. Color-code by urgency level.
Day 78: Escalation Activities and Urgency Management
When deadlines approach or pass, escalation activities execute automatically—reassigning work, notifying managers, or triggering emergency processes. Combine SLAs with escalation activities to ensure critical work never falls through cracks.
Daily Assignment: Create escalation activities that: send manager notifications at 75% of deadline, reassign to senior staff at deadline, and notify executives for cases 24 hours past deadline. Test the complete flow.
Day 79: Agents – Background Processing Automation
Agents are background processes that run scheduled tasks without user intervention—sending nightly reports, processing batch updates, monitoring queues. Understanding agent types, modes, and intervals is essential for enterprise applications.
Daily Assignment: Document agent architecture: standard agents, advanced agents, recurring schedules, agent queue processing. Create a plan for five automated tasks your application needs.
Day 80: Standard vs Advanced Agents
Standard agents run activities on schedule—simple, straightforward automation. Advanced agents query for work items and process them in batches. Learn when to use each mode and how agent queues manage workload distribution.
Daily Assignment: Create both agent types: a standard agent sending daily summary emails at 6 PM, and an advanced agent processing pending notifications every 15 minutes. Monitor their execution through agent logs.
Day 81: Agent Queue and Queue-For-Agent Method
Agent queues hold items waiting for agent processing. The Queue-For-Agent method adds items programmatically. This pattern enables asynchronous processing—users don’t wait for long operations to complete.
Daily Assignment: Implement a document generation system: when users request reports, queue them for agent processing. Users receive email when generation completes. Handle failures with retry logic.
Day 82: Agent Access Groups and Configuration
Agents run under specific access groups determining their permissions. Misconfigured agent access causes mysterious failures. Learn to configure agent access groups properly and troubleshoot common agent issues.
Daily Assignment: Create dedicated access groups for your agents with minimal necessary permissions. Test agents under different access groups to understand security implications. Document best practices.
Week 14: Advanced Integration (Days 83-89)
Day 83: Job Scheduler Configuration
Job Schedulers trigger agents and activities at specific times or intervals. More powerful than simple agent schedules, job schedulers handle complex timing requirements and dependencies between automated tasks.
Daily Assignment: Configure job scheduler for end-of-month reporting: aggregation agent runs at midnight on last day, report generation agent runs when aggregation completes, distribution agent sends reports to stakeholders.
Day 84: Queue Processors for System Integration
Queue Processors monitor message queues (JMS, KAFKA) for incoming integration requests. They enable real-time integration with external systems, processing messages as they arrive rather than polling on schedules.
Daily Assignment: Research queue processor configuration. Document how queue processors differ from agents and file listeners. Create a theoretical integration design using queue processors for order processing.
Day 85: External Database Integration
Enterprise applications integrate with external databases—legacy systems, data warehouses, third-party applications. Learn to create external database connections, use Connect SQL rules, and work with RDB-methods (RDB-List, RDB-Open, RDB-Save, RDB-Delete).
Daily Assignment: Configure external database connection. Create Connect SQL rules querying external data. Build screens displaying external data alongside Pega data. Understand when to use RDB-methods versus Obj-methods.
Day 86: SOAP Web Service Integration
SOAP protocol enables complex enterprise integration. Learn to consume external SOAP services from Pega using XML Stream and Parse XML rules. Understand the Apply-Parse-XML method for handling responses.
Daily Assignment: Integrate with a public SOAP web service (weather, currency conversion, or postal codes). Create screens displaying integrated data. Implement error handling for service failures using pySOAPError, pyStatusMessage, and pyStatus properties.
Day 87: Creating Pega Services for External Consumption
Your Pega application can expose services for other systems to consume. Learn to create service packages, configure service rules, and publish SOAP services. This makes Pega applications integration hubs.
Daily Assignment: Create three services exposing your application’s functionality: case creation service, status inquiry service, and update service. Test them using SOAP testing tools. Document the service contract.
Day 88: File Listener Integration
File Listeners monitor directories for incoming files and process them automatically. Common for batch integration—receiving nightly customer updates, processing bulk orders, or importing data feeds.
Daily Assignment: Implement file listener monitoring an input directory. When CSV files arrive, parse them, validate data, create or update cases automatically, move processed files to archive directory, and send completion notifications.
Day 89: Error Handling and Exception Management
Professional applications handle errors gracefully. Learn error handler flows for SOAP and Connect SQL rules, exception handling in activity steps using transitions, and OOTB when rules (Step Status Fail, Step Status Good, Step Status Warn).
Daily Assignment: Review your entire application adding comprehensive error handling. Implement error handler flows for all integrations, transition-based exception handling in critical activities, and user-friendly error messages.
Day 90: Real-World Project Implementation and Production Readiness
Final Day: Enterprise Application Architecture
Today consolidates everything into enterprise-level understanding. Learn about dev, integration, UAT, and production servers. Understand LDAP, SSO, authentication services, and deployment processes used in real organizations.
Daily Assignment: Document complete production deployment plan for your application: environment architecture, authentication configuration, deployment steps, rollback procedures, monitoring strategy, and support processes.
📚 Download integration samples, API structures & database files for hands-on practice.
🎯 You Did It! 90 Days Complete - You're Job-Ready!
Congratulations on completing this intensive journey! You’ve transformed from a complete beginner to a competent Pega developer ready for the marketplace. Your knowledge now spans the entire Pega platform—from basic application creation to advanced enterprise integration.
6. CAREER ACCELERATION Profile Optimization & Job Hunting Strategy
LinkedIn Profile Optimization for Pega Developers
Your technical skills mean nothing if recruiters can’t find you. LinkedIn is where hiring managers search for Pega talent, and your profile needs optimization to appear in their searches. Here’s how to stand out in the competitive Pega job market.
Headline Optimization: Don’t just write “Pega Developer.” Use keyword-rich headlines like “Certified Pega System Architect | BPM Solutions | Case Management | 90-Day Intensive Training Graduate.” This helps you appear in recruiter searches for multiple terms .
About Section Strategy: Tell your transformation story. Mention your 90-day intensive training, projects completed, technologies mastered, and career goals. Include phrases like “Pega PRPC,” “Business Process Management,” “Low-Code Development,” “Workflow Automation,” and “Enterprise Application Development” naturally throughout. Recruiters search for these terms.
Skills Section Priority: List Pega-specific skills first: Pega Platform 8.x, Pega Case Management, Pega UI/UX, Data Modeling, Integration (REST/SOAP), Decision Rules, SLA Configuration, and Agent Development. Get endorsements from classmates and instructors. Skills with more endorsements rank higher in searches.
Projects Showcase: Add your 90-day training projects to your profile with descriptions: “Developed loan approval application with multi-stage workflow, integration with external credit bureau, SLA-based escalation, and comprehensive reporting.” Each project description should include technologies used and problems solved.
Certifications Section: Once you earn Pega Certified System Architect (CSA) certification, display it prominently. Certifications dramatically increase recruiter interest and often qualify you for positions requiring “Pega certification mandatory”.
Want a professionally optimized LinkedIn profile that attracts recruiters? Frontlines Edutech includes LinkedIn profile building as part of the comprehensive training program, ensuring you present yourself as a polished professional from day one.
Top Job Platforms for Pega Developers in India
The Indian job market is hungry for Pega developers. With over 207 active Pega positions currently available and companies hiring candidates with just 1-2 years of experience, your timing is perfect. Here’s where to focus your job search efforts:
Naukri.com: India’s largest job portal consistently lists 150+ Pega developer positions. Set up job alerts for “Pega Developer,” “Pega CSA,” “Pega Consultant,” and “BPM Developer.” Upload your Pega-optimized resume and update it weekly to appear in recent searches.
LinkedIn Jobs: Currently showing 85+ Pega positions in Hyderabad alone and hundreds across India. Enable “Open to Work” feature with targeted preferences. LinkedIn’s algorithm recommends you to hiring managers based on profile strength—another reason for optimization.
Indeed India: Lists 25+ Pega developer positions in major cities with salary ranges visible. Create a comprehensive Indeed profile and apply directly through the platform. Many companies use Indeed for quick hiring.
Foundit (Monster India): Specializes in IT positions with dedicated Pega developer section. Good for finding positions in MNCs and large enterprises that use Pega extensively.
Company Career Pages Direct: Major Pega employers like Accenture, TCS, Cognizant, Wipro, Infosys, Capgemini, and HCL Technologies maintain career portals. Apply directly for higher visibility.
Pega Partner Network: Companies that are official Pega partners are always hiring. Research Pega’s partner directory and target these organizations specifically.
Consulting Firms: Pega implementation consulting firms like Tech Mahindra, Deloitte Digital, and PWC Digital Services hire Pega developers regularly for client projects.
Salary Expectations: Entry-level Pega developers in India earn ₹4-8 lakhs annually. With 1-2 years of experience, salaries jump to ₹8-15 lakhs. Mid-level developers (3-5 years) command ₹15-25 lakhs, and senior professionals earn ₹25-78 lakhs based on skills and certifications.
Application Strategy: Don’t just apply randomly. Tailor your resume for each position, highlighting relevant projects from your training. Apply to 5-10 carefully selected positions daily rather than 50 generic applications. Quality beats quantity in Pega hiring.
🎓 Become a certified Pega developer—join the complete Pega Course with projects & interview prep.
Interview Preparation: Standing Out in Pega Interviews
Pega interviews follow a unique pattern different from traditional coding interviews. Expect a mix of conceptual questions, practical scenarios, and live platform demonstrations. Here’s how to prepare systematically:
Technical Round Preparation:
Interviewers will ask about your hands-on experience with key concepts: case management, flow design, data modeling, integration patterns, and SLA configuration. Be ready to explain not just “what” but “why”—why you chose a particular approach over alternatives.
Common technical questions include:
- Explain the difference between activities and data transforms and when to use each
- How does rule resolution work in Pega?
- What are the different types of flows and their use cases?
- Explain the inheritance hierarchy in your application
- How do you optimize Pega application performance?
- Describe your experience with integrations and which protocols you’ve used
- What are declare rules and how do they improve applications?
Live Platform Demonstration:
Many interviews include live exercises where you build something simple in Pega Personal Edition during a screen share. Practice these scenarios:
- Create a simple approval flow with three stages
- Design a form with validation rules
- Implement a decision table for business rules
- Configure an SLA with escalation
- Build a report with filtering options
Scenario-Based Questions:
Interviewers present business scenarios asking how you’d implement them in Pega. Practice thinking through complete solutions:
- “Design a customer complaint management system with priority-based routing”
- “Implement a multi-level approval process with conditional routing”
- “How would you integrate with an external payment gateway?”
- “Design data architecture for a loan origination application”
Project Discussion:
Be prepared to discuss your 90-day training projects in detail. Interviewers will probe your decision-making: Why did you design it that way? What challenges did you face? How did you handle errors? What would you do differently now?
Behavioral Round:
Don’t overlook soft skills. Pega developers work closely with business stakeholders translating requirements into technical solutions. Expect questions about:
- How do you handle unclear requirements?
- Describe a challenging technical problem you solved
- How do you prioritize when multiple stakeholders want different features?
- Tell me about a time you learned a new technology quickly
Certification Questions:
If you’ve earned Pega CSA certification, expect detailed questions about exam topics. If not, be honest but emphasize your practical training and readiness to certify.
Want comprehensive interview preparation with 200+ real Pega interview questions, mock interviews, and expert guidance? Frontlines Edutech provides dedicated interview preparation sessions as part of the training program, ensuring you confidently face any interview scenario. For our complete Pega Interview Preparation Guide with technical questions, live demo scenarios, and salary negotiation strategies, visit www.frontlinesedutech.com/interview-prep
📄 Download resume templates, project summaries & ATS-optimized formats.
Resume Building for Pega Positions
Your resume is your first impression. Here’s how to craft a Pega-specific resume that gets interviews:
Contact Section: Include LinkedIn URL, GitHub profile (if you’ve shared code samples), and Pega Academy profile if active.
Professional Summary: Write 3-4 lines emphasizing: “Pega Certified System Architect with comprehensive training in enterprise application development. Proficient in case management, workflow automation, integration, and UI/UX design. Completed 90-day intensive Pega training program with hands-on projects. Seeking entry-level Pega developer position to contribute to digital transformation initiatives.”
Technical Skills Section: Organize by category:
- Pega Platform: Pega PRPC 8.x, Case Management, Flow Design, UI/UX Development, Decision Rules
- Integration: REST APIs, SOAP Web Services, Connect SQL, File Listeners, Queue Processors
- Other: SQL, HTML, CSS, JavaScript basics, Agile/Scrum methodology
- Tools: Pega Tracer, Clipboard Tool, Database Trace, Deployment Manager
Projects Section: Detail 3-4 major projects from training:
Project: Customer Service Management System
- Designed and developed end-to-end customer complaint handling application
- Implemented priority-based routing with SLA escalation for urgent issues
- Created comprehensive reporting dashboard for management visibility
- Integrated email notifications for status updates and escalations
- Technologies: Pega 8.x, Data Modeling, Flow Design, SLA Configuration, SMTP Integration
Education: List your degree, then immediately follow with:
Professional Training:
Pega Developer Certification Program – Frontlines Edutech (2025)
- 90-day intensive training covering Pega Platform development
- Hands-on projects in case management, integration, and workflow automation
- Daily assignments, live project experience, and interview preparation
Certifications: List Pega CSA when earned. Include “In Progress” if currently preparing.
Resume Keywords: Ensure these appear naturally: Pega Platform, PRPC, Case Management, BPM, Workflow Automation, Low-Code Development, Rule Resolution, Data Modeling, Integration, SLA, Decision Rules, Declare Rules, Agent Configuration.
Frontlines Edutech provides professional resume building services specifically for Pega developers, ensuring your resume passes applicant tracking systems (ATS) and impresses hiring managers.
BONUS MODULES: Advanced Topics for Career Acceleration
Understanding Case Management Framework
Case Management is Pega’s core strength—the ability to model complex business processes as cases with stages and steps. Advanced case management includes parent-child case relationships, data propagation between related cases, case instantiation patterns, and locking mechanisms (default and optimistic).
Real-world applications use sophisticated case designs: a mortgage application (parent) might create credit check, appraisal, and income verification as child cases. Understanding properties like pxCoveredInsKeys and pxCoveredCount enables you to work with case families effectively.
Data Pages: Modern Data Management
Data Pages represent Pega’s modern approach to data handling. Understanding data page sources (database, REST, data transform), scope (thread, requestor, node), read-only versus editable pages, refresh strategies, and UI references is crucial for performant applications.
Data pages eliminate redundant database calls by caching reference data intelligently. They’re central to Pega 8.x development and frequently appear in interviews.
Circumstancing and Dynamic Rule Behavior
Circumstancing creates rule variants for different scenarios without copying rules. A single “Calculate Tax” decision table might have circumstances for different states or customer types, with Pega automatically selecting the correct variant at runtime.
Admin Studio and Requestor Management
Understanding different requestor types, managing system resources, monitoring application health, and troubleshooting production issues separates developers from developer-administrators. Admin Studio skills make you more valuable to employers.
Email Listener Configuration
Email Listeners process incoming emails automatically—creating cases from customer emails, parsing attachments, extracting data from email body text. This advanced integration pattern enables email-driven workflows.
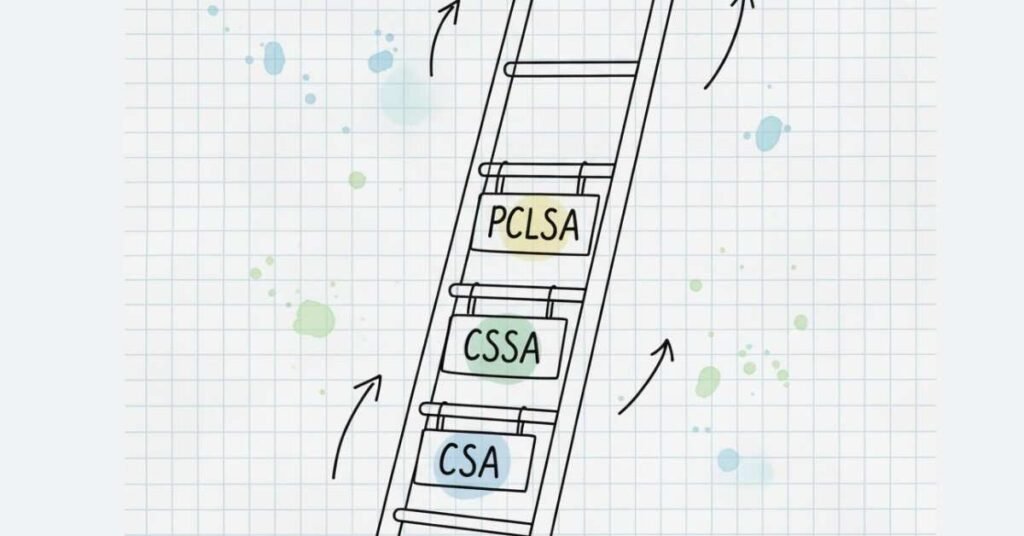
CERTIFICATION ROADMAP: Your Path to Higher Earnings
Pega Certified System Architect (CSA): Your first certification, typically achieved within 3-6 months of starting Pega. This certification validates foundational knowledge and is mandatory for many positions. Salary impact: ₹2-4 lakhs increase.
Pega Certified Senior System Architect (CSSA): Requires 1-2 years of experience. Covers advanced topics like performance optimization, complex integrations, and architectural patterns. Salary impact: ₹4-6 lakhs increase.
Pega Certified Lead System Architect (PCLSA): Senior certification requiring 3-5 years of experience. Demonstrates ability to architect entire enterprise solutions. Opens doors to architect and lead developer positions with ₹25-40 lakh salaries.
Specialized Certifications: Pega also offers certifications in Customer Service, Marketing, Decisioning, and RPA. Specialization increases demand and compensation for niche roles.
7. Your Next Steps
Week 1 Post-Training: Complete your resume, optimize LinkedIn, and set up job alerts on all platforms. Apply to 10 carefully selected entry-level positions. Schedule your Pega CSA certification exam.
Week 2-3: Apply to 5-10 positions daily. Practice interview questions for 2 hours daily. Build one additional personal project showcasing a unique use case. Network with Pega professionals on LinkedIn—comment on their posts, join Pega groups.
Week 4-6: Attend interviews actively. After each interview, note questions you struggled with and review those topics. Update your LinkedIn with new projects and skills. Consider contributing to Pega community forums to build reputation.
Week 7-8: If not placed yet, reassess your strategy. Are you applying to appropriate positions? Is your resume getting past ATS systems? Do you need more hands-on practice? Seek feedback from recruiters and training instructors.
Month 3: Take your CSA certification exam. Certification dramatically increases interview callbacks. Continue applying, practicing, and networking. Persistence pays off—the average job search for entry-level Pega positions takes 2-3 months.
MARKET REALITY: What Employers Actually Want
Based on current market analysis, entry-level Pega positions seek candidates who can:
- Independently build simple applications: Given requirements, you should create flows, UIs, and data models without constant supervision
- Debug using Pega tools: Tracer, Clipboard, and logs should be your diagnostic toolkit
- Understand integration basics: You don’t need deep expertise, but should explain REST/SOAP concepts
- Communicate effectively: Translate technical concepts for business users and vice versa
- Learn quickly: Pega evolves constantly; demonstrated learning ability matters more than current knowledge depth
- Work in Agile teams: Understand sprints, standups, and iterative development
- Follow Pega Guardrails: Build applications the “Pega way” ensuring maintainability and performance
Your 90-day training covers all these expectations. Now you need to demonstrate these abilities confidently in interviews.
FINAL MOTIVATION: Your Career Transformation Awaits
Ninety days ago, you started this journey. Today, you possess skills that companies desperately need and pay premium salaries for. The Business Process Management market is exploding—$21.51 billion in 2025 growing to $70.93 billion by 2032. Every bank, insurance company, healthcare provider, and large enterprise needs Pega developers to digitize their operations.
You’re not just learning a technology; you’re securing your financial future. Entry-level Pega salaries start at ₹4-8 lakhs, but with certification and 1-2 years of experience, you’ll command ₹15-25 lakhs. Senior Pega professionals earn ₹40-78 lakhs annually—life-changing income in India.
The demand is real. Over 207 positions are open right now across India, with companies actively seeking candidates with just 1-2 years of experience—exactly where you’ll be after your first project. Major cities like Hyderabad alone have 85+ openings. The opportunity is here, today, waiting for qualified candidates like you.
Your competition isn’t other candidates—it’s your own consistency. Those who apply daily, practice regularly, and persist through rejections get hired. Those who give up after a few rejections don’t. Which will you be?
ENROLL IN FRONTLINES EDUTECH'S PEGA DEVELOPER PROGRAM TODAY
This roadmap gives you the complete 90-day plan. But self-learning has limits. You need:
✅ Expert Instructors from top industries who’ve built real Pega applications for Fortune 500 companies
✅ Daily Assignments with feedback ensuring you’re actually learning, not just watching videos
✅ Live Project Experience working on actual business scenarios, not toy examples
✅ LinkedIn Profile Optimization making you visible to recruiters searching for Pega talent
✅ Professional Resume Building that passes ATS systems and impresses hiring managers
✅ Interview Preparation with 200+ real questions, mock interviews, and expert coaching
✅ Certification Guidance preparing you for Pega CSA exam success on first attempt
✅ Placement Support with dedicated placement team connecting you to hiring companies
✅ Downloadable Resources including course content, project templates, and reference guides
✅ Q&A Sessions getting expert answers to your specific questions
✅ Certification of Completion from an ISO 21001:2018 certified institution
✅ On-Demand Video Access letting you learn at your pace while maintaining structure
Frontlines Edutech Private Limited is an ISO 21001:2018 certified educational institution trusted by thousands of learners across India. They’ve successfully trained and placed students in Pega roles at top companies.
Investment in your future: The complete Pega Developer program costs a fraction of your first year’s salary increase. Most students recover their investment within 2-3 months of placement.
Ready to Transform Your Career?
📞 Call Now: +91-83330 77727
🌐 Visit: www.frontlinesedutech.com
📧 Email: media.frontlines@gmail.com
Follow on Social Media:
- Instagram: @frontlines_edutech
- YouTube: FrontLinesMedia
- LinkedIn: Frontlines Edutech Private Limited
Don’t let another day pass watching others succeed while you wait. The Pega developer shortage means companies are hiring NOW. Your 90-day transformation starts the moment you decide to invest in yourself.
Enroll today. Three months from now, you’ll thank yourself.
This complete 90-day Pega Developer Roadmap is designed based on the official Frontlines Edutech Pega course syllabus, current market demands, and proven learning methodologies. Every day counts. Every assignment builds skills. Every week moves you closer to your ₹15-25 lakh career. Your future is waiting—claim it.