Digital Marketing Interview Preparation Guide
1. 210+ Technical Interview Questions & Answers
- Introduction to Digital Marketing: 5 questions
- Website Development & Management: 10 questions
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): 30 questions
- Content Marketing: 10 questions
- Social Media Marketing: 15 questions
- Paid Advertising (PPC & SEM): 20 questions
- Email Marketing: 15 questions
- Google Analytics: 15 questions
- YouTube Marketing: 10 questions
- Affiliate Marketing: 10 questions
- Freelancing in Digital Marketing: 10 questions
- Marketing Automation & Tools: 10 questions
- Conversion Rate Optimization: 10 questions
- Mobile Marketing: 10 questions
- Analytics & Reporting: 10 questions
- E-commerce Marketing: 10 questions
- Additional Important Concepts: 10 questions
🎓 Turn Theory into Real-World Skills — Learn with Experts!
🚀 Join the Digital Marketing Course →
Introduction to Digital Marketing
Q1. What do you understand by digital marketing?
Digital marketing means promoting products or services using the internet and electronic devices. It includes things like websites, social media, emails, search engines, and mobile apps. Think of it as reaching customers where they spend most of their time today—online.
Q2. How is digital marketing different from traditional marketing?
Traditional marketing uses newspapers, TV, radio, and billboards. Digital marketing uses websites, social media, and online ads. The big difference is that digital marketing lets you talk directly to your audience, measure results instantly, and change strategies quickly. It’s also cheaper and reaches people worldwide.
Q3. Why should businesses invest in digital marketing?
Most people today search online before buying anything. Businesses need to be visible where their customers are looking. Digital marketing helps companies reach the right people at the right time, build relationships, and grow sales without spending huge amounts of money.
Q4. What are the main types of digital marketing?
The main types include SEO, social media marketing, content marketing, email marketing, paid advertising, affiliate marketing, and influencer marketing. Each type serves a different purpose but works best when used together.
Q5. Can you explain what a digital marketing strategy is?
A digital marketing strategy is your plan for achieving business goals through online channels. It includes understanding your audience, choosing the right platforms, creating valuable content, setting budgets, and measuring success. It’s basically your roadmap for online success.
💡 Plan Your Digital Marketing Career the Smart Way!
🧭 Explore Digital Marketing Roadmap →
Website Development & Management

Q6. Why is having a website important for digital marketing?
A website is your online home base. It’s where people learn about your business, see your products, and contact you. Without a website, you lose credibility and miss out on customers searching online. It’s the foundation of all your digital marketing efforts.
Q7. What’s the difference between a domain and hosting?
A domain is your website’s address, like www.yourcompany.com. Hosting is the space where your website files are stored so people can access them online. Think of the domain as your home address and hosting as the actual building.
Q8. What does CMS stand for and why is it useful?
CMS means Content Management System. It’s software that helps you create and manage website content without knowing coding. WordPress is the most popular CMS because it’s free, flexible, and beginner-friendly.
Q9. What’s the difference between WordPress.com and WordPress.org?
WordPress.com is a hosted platform where everything is managed for you, but you have limited control. WordPress.org is self-hosted, giving you complete freedom to customize everything, but you need to handle your own hosting and maintenance.
Q10. What is cPanel and what is it used for?
cPanel is a control panel that helps you manage your web hosting. You can create email accounts, install WordPress, manage files, check website statistics, and handle domain settings—all from one easy dashboard.
Q11. What are the different types of hosting?
Shared hosting means multiple websites share one server—it’s cheap but slower. VPS hosting gives you dedicated resources on a shared server—better performance. Cloud hosting uses multiple servers for reliability. Dedicated hosting means you rent an entire server—most expensive but fastest.
Q12. What is a landing page?
A landing page is a standalone web page created specifically for a marketing campaign. When someone clicks your ad or email link, they land here. It’s designed with one goal—to get visitors to take action like signing up, downloading something, or making a purchase.
Q13. What makes a good landing page?
A good landing page has a clear headline, compelling copy, attractive visuals, one strong call-to-action, mobile-friendly design, fast loading speed, and minimal distractions. Every element should guide visitors toward completing the desired action.
Q14. What is responsive web design?
Responsive design means your website automatically adjusts to look good on any device—desktop, tablet, or phone. Since most people browse on mobile devices, responsive design is essential for user experience and search engine rankings.
Q15. Why is website loading speed important?
People are impatient online. If your website takes more than 3 seconds to load, visitors leave. Slow websites also rank lower in search results. Fast loading improves user experience, reduces bounce rates, and increases conversions.
🌐 Build and Manage WordPress Sites Like a Pro !
🧠 Read Step-by-Step How-to Guides
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)

Q16. What is SEO in simple terms?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. It’s the practice of improving your website so it appears higher in search results when people look for products or services you offer. Higher rankings mean more visitors and potential customers.
Q17. How do search engines work?
Search engines like Google use crawlers to scan websites, index the information, and then rank pages based on relevance and quality when someone searches. They consider hundreds of factors to decide which pages deserve the top spots.
Q18. What’s the difference between on-page and off-page SEO?
On-page SEO is what you do on your website—optimizing content, titles, images, and page structure. Off-page SEO is what happens outside your website—mainly building backlinks from other sites and building your online reputation.
Q19. What is keyword research and why is it important?
Keyword research means finding the actual words and phrases people type into search engines. It’s important because you need to know what your audience is searching for so you can create content that answers their questions and appears in their search results.
Q20. What are long-tail keywords?
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific search phrases like “best digital marketing course in Hyderabad” instead of just “digital marketing.” They have less competition and attract people who are closer to making a decision or purchase.
Q21. What is a meta title and meta description?
The meta title is the clickable headline that appears in search results. The meta description is the short summary below it. Both should be compelling and include relevant keywords to encourage people to click through to your website.
Q22. What is keyword density and does it still matter?
Keyword density is how often a keyword appears in your content compared to total words. It used to matter a lot, but now search engines focus more on natural, helpful content. Using keywords naturally without stuffing is the right approach.
Q23. What are header tags (H1, H2, H3)?
Header tags organize your content into sections. H1 is the main title, H2s are major sections, H3s are subsections, and so on. They help readers scan content quickly and help search engines understand your page structure and main topics.
Q24. What is a backlink?
A backlink is when another website links to your website. Search engines see backlinks as votes of confidence. Quality backlinks from trusted sites significantly improve your search rankings and bring referral traffic.
Q25. What’s the difference between dofollow and nofollow links?
Dofollow links pass SEO value from one site to another, helping your rankings. Nofollow links have a tag telling search engines not to pass SEO value. Both types are normal and natural in a healthy link profile.
Q26. What is anchor text?
Anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink. Using descriptive anchor text helps both users and search engines understand what the linked page is about. Varied, natural anchor text is best for SEO.
Q27. What is image optimization in SEO?
Image optimization means making images load faster and helping search engines understand them. This includes compressing file sizes, using descriptive file names, adding alt text, and choosing the right image format.
Q28. What is alt text for images?
Alt text is a description of an image that appears if the image doesn’t load and helps visually impaired users understand the content. It also helps search engines understand what the image shows, improving your image search rankings.
Q29. What is internal linking?
Internal linking means linking to other pages on your own website. It helps visitors navigate your site, keeps them engaged longer, and helps search engines discover and understand the relationship between your pages.
Q30. What is a sitemap?
A sitemap is a file that lists all important pages on your website. It helps search engines discover and crawl your pages more efficiently. XML sitemaps are for search engines, while HTML sitemaps help human visitors navigate.
Q31. What is robots.txt?
The robots.txt file tells search engine crawlers which pages they can or cannot access on your website. It’s useful for blocking search engines from crawling unimportant pages like admin areas or duplicate content.
Q32. What is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console is a free tool from Google that helps you monitor how your website appears in search results. You can submit sitemaps, check indexing status, see which keywords bring traffic, and fix technical issues.
Q33. What are rich snippets?
Rich snippets are enhanced search results that show extra information like star ratings, prices, images, or recipe details. They make your listing stand out in search results and can increase click-through rates significantly.
Q34. What is schema markup?
Schema markup is code you add to your website to help search engines understand your content better. It enables rich snippets and helps search engines provide more informative results to users.
Q35. What is local SEO?
Local SEO optimizes your online presence to attract customers from specific geographic locations. It includes claiming your Google Business Profile, getting local citations, gathering reviews, and targeting location-based keywords.
Q36. What is Google My Business (now Google Business Profile)?
It’s a free tool that lets businesses manage how they appear in Google Search and Maps. You can add your address, hours, photos, and respond to reviews. It’s crucial for local businesses wanting to be found online.
Q37. What is technical SEO?
Technical SEO focuses on website infrastructure—making sure search engines can crawl, understand, and index your site properly. It includes site speed, mobile-friendliness, security, site architecture, and structured data.
Q38. What is a canonical URL?
A canonical URL tells search engines which version of a page is the main one when you have duplicate or similar content. It prevents duplicate content issues and consolidates SEO value to one preferred URL.
Q39. What is a 301 redirect?
A 301 redirect permanently sends visitors and search engines from one URL to another. It’s used when you move pages, change URLs, or delete content. It passes most of the original page’s SEO value to the new URL.
Q40. What’s the difference between white hat, black hat, and grey hat SEO?
White hat SEO follows search engine guidelines and focuses on providing value to users. Black hat SEO uses manipulative tactics that violate guidelines and risk penalties. Grey hat SEO falls somewhere in between—not clearly wrong but potentially risky.
Q41. What is keyword cannibalization?
Keyword cannibalization happens when multiple pages on your site target the same keyword, causing them to compete with each other. This confuses search engines and can hurt your rankings. Each page should target unique keywords.
Q42. What is bounce rate and why does it matter?
Bounce rate is the percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate might indicate that your content isn’t relevant, your site is slow, or the user experience is poor.
Q43. What is crawl budget?
Crawl budget is the number of pages a search engine will crawl on your website within a given timeframe. For large sites, optimizing crawl budget ensures important pages get crawled and indexed regularly.
Q44. What are SERP features?
SERP stands for Search Engine Results Page. SERP features are special results like featured snippets, knowledge panels, image packs, video carousels, and local packs that appear alongside regular search listings.
Q45. What is a featured snippet?
A featured snippet is the boxed information that appears at the top of some search results, often called “position zero.” It directly answers the user’s question and provides huge visibility, even above the first organic result.
📚 Need more interview prep guides?
📘 Browse All Interview Resources →
Content Marketing
Q46. What is content marketing?
Content marketing is creating and sharing valuable content to attract and engage your target audience. Instead of directly promoting products, you provide helpful information that builds trust and positions you as an expert in your field.
Q47. What types of content can you create for marketing?
You can create blog posts, videos, infographics, podcasts, ebooks, case studies, webinars, social media posts, email newsletters, whitepapers, templates, and interactive tools. Different formats appeal to different audiences.
Q48. What makes content valuable to an audience?
Valuable content solves problems, answers questions, educates, entertains, or inspires your audience. It should be relevant to their needs, easy to understand, well-researched, and presented in an engaging format.
Q49. What is a content calendar?
A content calendar is a schedule that plans what content you’ll publish and when. It helps you stay organized, maintain consistency, align content with campaigns or seasons, and ensure you cover all important topics.
Q50. What is evergreen content?
Evergreen content remains relevant and valuable over time, unlike news or trending topics. Examples include how-to guides, tutorials, tips articles, and FAQs. Evergreen content continues attracting traffic months or years after publication.
Q51. How do you measure content marketing success?
Success metrics include website traffic, engagement rates, time on page, social shares, comments, lead generation, conversion rates, and SEO rankings. The specific metrics depend on your goals—awareness, engagement, or conversions.
Q52. What is a content pillar?
A content pillar is a comprehensive piece covering a broad topic in-depth. It serves as the foundation, with smaller related pieces linking back to it. This structure helps SEO and establishes authority on key topics.
Q53. What is user-generated content?
User-generated content is created by customers rather than brands—reviews, testimonials, social media posts, photos, or videos featuring your products. It’s authentic, builds trust, and provides free marketing.
Q54. What is storytelling in content marketing?
Storytelling makes your content more engaging by sharing real experiences, challenges, and solutions in a narrative format. Stories create emotional connections, make information memorable, and humanize your brand.
Q55. What is content repurposing?
Content repurposing means taking existing content and transforming it into different formats. For example, turning a blog post into a video, infographic, podcast episode, or social media posts. It maximizes your content investment.
✍️ Download Free Content Marketing Templates & Case Studies
📘 Access All Resources →
Social Media Marketing (SMM)

Q56. What is social media marketing?
Social media marketing uses platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter to promote your business, engage with audiences, and drive website traffic or sales. It combines organic posts with paid advertising.
Q57. Which social media platform should a business use?
It depends on your target audience. LinkedIn works for B2B and professionals. Instagram and Facebook suit visual brands and B2C. Twitter works for news and conversations. YouTube is best for video content. Research where your customers spend time.
Q58. What’s the difference between a social media page and profile?
A profile is for individuals with a focus on personal connections. A page (or business account) is for companies and public figures, offering business features like analytics, advertising options, and the ability to have multiple administrators.
Q59. What is social media engagement?
Engagement includes likes, comments, shares, saves, and clicks on your social media posts. High engagement shows your content resonates with your audience and increases your reach as platforms show engaging content to more people.
Q60. What is organic reach versus paid reach on social media?
Organic reach is how many people see your posts naturally without paying. Paid reach is how many people see your content through advertisements. Organic reach has declined on most platforms, making paid promotion increasingly important.
Q61. What is a social media content strategy?
A content strategy plans what, when, and how often you post on social media. It defines your brand voice, content themes, posting schedule, and goals. A good strategy balances promotional, educational, and entertaining content.
Q62. What is the 80-20 rule in social media marketing?
The 80-20 rule suggests that 80% of your social content should educate, entertain, or provide value, while only 20% should directly promote your products. This keeps your audience engaged without feeling overwhelmed by sales pitches.
Q63. What are hashtags and how do you use them effectively?
Hashtags are keywords preceded by # that categorize content and make it discoverable. Use relevant, specific hashtags mixing popular and niche ones. Research which hashtags your target audience follows. Don’t overuse them—quality over quantity.
Q64. What is social listening?
Social listening means monitoring social media for mentions of your brand, competitors, products, or relevant keywords. It helps you understand customer sentiment, identify trends, respond to concerns, and discover opportunities.
Q65. What is influencer marketing?
Influencer marketing partners with people who have engaged followings on social media. They promote your products to their audience, providing authentic recommendations that feel more trustworthy than traditional advertising.
Q66. How do you measure social media ROI?
Track metrics aligned with your goals—engagement rates, follower growth, website traffic from social, leads generated, and sales conversions. Compare the value gained against time and money invested in social media activities.
Q67. What is a social media audit?
A social media audit reviews all your social profiles to assess performance, identify what’s working, check brand consistency, remove outdated information, and discover opportunities for improvement. It’s a health check for your social presence.
Q68. What are social media algorithms?
Algorithms determine which content appears in users’ feeds and in what order. They prioritize content based on relevance, engagement, relationships, and timeliness. Understanding algorithms helps you create content that reaches more people.
Q69. What is a call-to-action (CTA) in social media?
A CTA tells your audience what to do next—”Click the link,” “Share your thoughts,” “Tag a friend,” “Shop now.” Clear CTAs increase engagement and conversions by giving people a specific action to take.
Q70. What is community management on social media?
Community management involves responding to comments, messages, and mentions, fostering discussions, addressing complaints, and building relationships with your audience. It humanizes your brand and builds loyal customers.
📱 Create Viral Campaigns Like a Pro!
🧠 Explore Social Media How-to Guides →
Paid Advertising (PPC & SEM)

Q71. What is PPC advertising?
PPC stands for Pay-Per-Click. It’s online advertising where you pay each time someone clicks your ad. Google Ads and Facebook Ads are common PPC platforms. You set budgets and bid for ad placement.
Q72. What is SEM?
SEM means Search Engine Marketing—using paid advertising to appear in search engine results. It includes PPC campaigns on platforms like Google Ads and Bing Ads. SEM provides immediate visibility while SEO builds long-term organic presence.
Q73. What’s the difference between SEO and SEM?
SEO is organic—you don’t pay for clicks but invest time in optimization. SEM is paid—you pay for each click. SEO takes longer but provides sustainable traffic. SEM delivers immediate results but requires ongoing budget.
Q74. What is Google Ads?
Google Ads is Google’s advertising platform where businesses bid to display ads in search results, on YouTube, and across Google’s partner websites. It’s the largest online advertising platform globally.
Q75. What are the different types of Google Ads campaigns?
Main types include Search Ads (text ads in search results), Display Ads (visual ads on websites), Video Ads (YouTube), Shopping Ads (product listings), App Ads (promote apps), and Performance Max (automated across channels).
Q76. What is Quality Score in Google Ads?
Quality Score is Google’s rating of your ad’s relevance and quality on a scale of 1-10. It considers expected click-through rate, ad relevance, and landing page experience. Higher scores mean lower costs and better ad positions.
Q77. What is Ad Rank?
Ad Rank determines your ad position in search results. It’s calculated using your bid amount, Quality Score, and expected impact of ad extensions and formats. Higher Ad Rank means better placement without necessarily paying more.
Q78. What is a landing page in the context of paid advertising?
A landing page is where visitors arrive after clicking your ad. It should match the ad’s message, have a clear goal, remove distractions, and make it easy to complete the desired action. Relevant landing pages improve conversion rates.
Q79. What is retargeting or remarketing?
Retargeting shows ads to people who previously visited your website but didn’t convert. It reminds them of your products and encourages them to return and complete a purchase. It’s highly effective because you’re targeting warm leads.
Q80. What is conversion tracking?
Conversion tracking monitors what happens after someone clicks your ad—whether they made a purchase, filled a form, called your business, or completed another valuable action. It measures campaign effectiveness and ROI.
Q81. What is Cost Per Click (CPC)?
CPC is the amount you pay each time someone clicks your ad. It varies based on competition, Quality Score, and your maximum bid. Lower CPCs mean more clicks for your budget.
Q82. What is Cost Per Acquisition (CPA)?
CPA is the cost to acquire one customer or conversion. It’s calculated by dividing total ad spend by number of conversions. CPA helps you understand whether your advertising is profitable.
Q83. What is Click-Through Rate (CTR)?
CTR is the percentage of people who click your ad after seeing it. It’s calculated by dividing clicks by impressions. Higher CTR indicates your ad is relevant and compelling to your target audience.
Q84. What are ad extensions?
Ad extensions add extra information to your ads—phone numbers, location, additional links, prices, or promotions. They make ads more useful, increase visibility, and often improve click-through rates at no extra cost.
Q85. What is A/B testing in advertising?
A/B testing compares two versions of an ad to see which performs better. You might test different headlines, images, CTAs, or landing pages. Testing helps optimize campaigns by showing what resonates with your audience.
Q86. What is impression share?
Impression share is the percentage of times your ad appeared compared to total possible appearances. Low impression share might mean limited budget or low Ad Rank. It helps identify missed opportunities.
Q87. What is negative keywords?
Negative keywords prevent your ads from showing for irrelevant searches. For example, if you sell premium furniture, you might add “cheap” or “free” as negative keywords to avoid wasting budget on unqualified clicks.
Q88. What is Facebook Ads Manager?
Facebook Ads Manager is the platform for creating and managing ads on Facebook and Instagram. It offers detailed targeting options, various ad formats, budget control, and comprehensive analytics.
Q89. What targeting options are available in Facebook Ads?
You can target by demographics (age, gender, location), interests, behaviors, connections, custom audiences (your customer lists), and lookalike audiences (people similar to your customers). The targeting is very precise.
Q90. What is a lookalike audience?
A lookalike audience finds new people similar to your existing customers. Facebook analyzes characteristics of your customer list and finds users with similar profiles, helping you reach qualified prospects who haven’t heard of you yet.
💰 Master Google Ads & Meta Ads — Get Certified in Digital Marketing!
→ 🚀 Join the Course
Email Marketing

Q91. What is email marketing?
Email marketing sends targeted messages to a list of subscribers. It nurtures leads, promotes products, shares news, builds relationships, and drives sales. It’s one of the most cost-effective digital marketing channels with high ROI.
Q92. Why is email marketing still relevant?
Email provides direct access to people’s inboxes. You own your email list, unlike social media followers. It offers personalization, automation, measurable results, and reaches people already interested in your business.
Q93. What is an email service provider (ESP)?
An ESP is software that helps you send marketing emails to large lists. Popular ESPs include Mailchimp, Constant Contact, and SendGrid. They provide templates, automation, list management, and analytics.
Q94. What is an email subject line and why is it important?
The subject line is the first thing recipients see. It determines whether they open your email. A good subject line is concise, relevant, creates curiosity or urgency, and accurately represents the email content.
Q95. What is preheader text?
Preheader text appears next to or below the subject line in the inbox preview. It’s additional text that entices people to open. Use it to complement your subject line and provide more context.
Q96. What is email segmentation?
Segmentation divides your email list into smaller groups based on characteristics like purchase history, interests, location, or engagement level. Segmented emails are more relevant, leading to higher open and conversion rates.
Q97. What is email personalization?
Personalization customizes emails for individual recipients—using their name, recommending products based on past purchases, or sending birthday offers. Personalized emails perform significantly better than generic ones.
Q98. What is email automation?
Email automation sends messages triggered by specific actions or timing—welcome emails for new subscribers, abandoned cart reminders, birthday messages, or re-engagement campaigns for inactive subscribers. It saves time while maintaining engagement.
Q99. What is a drip campaign?
A drip campaign is a series of automated emails sent on a schedule. For example, a 5-email course delivered weekly, or a welcome series for new customers. Drip campaigns nurture leads through the customer journey.
Q100. What is an email open rate?
Open rate is the percentage of recipients who opened your email. It’s calculated by dividing opens by delivered emails. Industry average is 15-25%. Open rates indicate how compelling your subject lines are.
Q101. What is click-through rate in email marketing?
Email CTR measures the percentage of recipients who clicked a link in your email. It shows how engaging your content is and how effective your call-to-action is. Average email CTR is around 2-5%.
Q102. What is email deliverability?
Deliverability is your ability to successfully land in recipients’ inboxes rather than spam folders. It depends on sender reputation, authentication, list quality, content, and engagement rates. Good deliverability is crucial for email success.
Q103. What are spam filters and how do you avoid them?
Spam filters analyze emails for characteristics of spam—suspicious words, excessive caps, misleading subject lines, or poor sender reputation. Avoid spam triggers by using permission-based lists, authentic content, and proper authentication.
Q104. What is double opt-in?
Double opt-in requires subscribers to confirm their email address by clicking a link sent to them. It ensures list quality, proves consent, reduces spam complaints, and improves deliverability, though it may lower initial subscription numbers.
Q105. What is email list hygiene?
List hygiene means regularly cleaning your email list by removing inactive subscribers, invalid addresses, and bounces. It improves deliverability, engagement rates, and sender reputation while reducing costs.
✉️ Map Your Journey from Email Marketer to Automation Expert!
→ 🧭 View Full Career Roadmap
Google Analytics
Q106. What is Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is a free tool that tracks website traffic and user behavior. It shows how many people visit, where they come from, what they do on your site, and whether they convert. It’s essential for data-driven marketing decisions.
Q107. What is the difference between Google Analytics and Google Search Console?
Google Analytics tracks all website traffic and user behavior. Google Search Console focuses specifically on how your site performs in Google search results, including rankings, impressions, and technical issues.
Q108. What are sessions in Google Analytics?
A session is a group of interactions one user has with your website within a given timeframe. It includes page views, events, and transactions. Sessions end after 30 minutes of inactivity or at midnight.
Q109. What is bounce rate in Analytics?
Bounce rate is the percentage of visitors who leave after viewing only one page without any interaction. High bounce rates might indicate irrelevant traffic, poor content, slow loading, or bad user experience.
Q110. What are goals in Google Analytics?
Goals track specific actions you want visitors to complete—purchases, form submissions, newsletter signups, or video views. Setting up goals helps measure conversions and understand how well your site achieves its objectives.
Q111. What is the difference between pageviews and unique pageviews?
Pageviews count every time a page loads, including if the same person views it multiple times. Unique pageviews count the number of sessions during which a page was viewed at least once.
Q112. What is conversion rate?
Conversion rate is the percentage of visitors who complete a desired action. It’s calculated by dividing conversions by total visitors. For example, if 100 people visit and 5 buy, your conversion rate is 5%.
Q113. What are traffic sources in Analytics?
Traffic sources show how visitors found your website—organic search, paid ads, social media, direct (typing URL), referral (links from other sites), or email. Understanding sources helps optimize marketing efforts.
Q114. What is the difference between direct and organic traffic?
Direct traffic is visitors who type your URL directly or use bookmarks. Organic traffic comes from unpaid search engine results. Direct often includes brand awareness or returning visitors, while organic indicates search visibility.
Q115. What are UTM parameters?
UTM parameters are tags added to URLs to track campaign performance in Analytics. They identify the source, medium, campaign name, content, and keywords. This helps you see exactly which marketing efforts drive traffic.
Q116. What is event tracking in Google Analytics?
Event tracking monitors specific interactions that don’t load a new page—button clicks, video plays, file downloads, or scroll depth. Events help understand user engagement beyond just page views.
Q117. What is Google Analytics 4 (GA4)?
GA4 is the latest version of Google Analytics with a focus on user-centric measurement across websites and apps. It uses events rather than pageviews, offers better privacy controls, and provides predictive metrics using machine learning.
Q118. What is the difference between acquisition, behavior, and conversion reports?
Acquisition reports show how people find your site. Behavior reports reveal what they do once there. Conversion reports track whether they completed goals. Together, they provide a complete picture of user journey.
Q119. What is user flow in Analytics?
User flow visualizes the path visitors take through your site—which pages they visit, where they drop off, and how they navigate. It helps identify popular paths and bottlenecks in the user journey.
Q120. What is a segment in Google Analytics?
A segment isolates and analyzes a subset of your data—for example, mobile users, visitors from a specific country, or people who made purchases. Segments help you understand different audience behaviors.
📊 Learn Google Analytics & Tag Manager with Practical Guides!
🧠 Read Analytics How-to Guides →
YouTube Marketing
Q121. Why is YouTube important for digital marketing?
YouTube is the second-largest search engine after Google. Video content is highly engaging, builds trust faster, and people retain information better from videos. YouTube offers organic reach and advertising options for businesses.
Q122. What is YouTube SEO?
YouTube SEO optimizes your videos to rank higher in YouTube search and suggested videos. It includes keyword research, optimizing titles, descriptions, tags, thumbnails, engagement metrics, and watch time.
Q123. What makes a good YouTube thumbnail?
A good thumbnail is eye-catching, clear at small sizes, uses high-contrast colors, includes readable text, shows faces with emotions, and accurately represents the video content. Thumbnails significantly impact click-through rates.
Q124. What is watch time on YouTube?
Watch time is the total minutes viewers spend watching your videos. YouTube prioritizes videos with high watch time because it indicates quality content that keeps people on the platform. It’s crucial for rankings and recommendations.
Q125. What are YouTube tags and how do you use them?
Tags are keywords describing your video’s content. They help YouTube understand your video topic and show it in related searches. Use specific tags first, then broader ones, including common misspellings and variations.
Q126. What is a YouTube end screen?
An end screen appears in the last 5-20 seconds of your video. It can promote other videos, playlists, your channel, or external websites. End screens keep viewers watching more content and increase channel engagement.
Q127. What are YouTube cards?
Cards are interactive elements that appear during your video, promoting other videos, playlists, channels, polls, or links. They appear as small teasers that viewers can click, helping increase engagement and views.
Q128. What is the YouTube Partner Program?
The YouTube Partner Program allows creators to monetize their content through ads, channel memberships, merchandise, and Super Chat. Requirements include 1,000 subscribers and 4,000 watch hours in the past 12 months.
Q129. What are YouTube Shorts?
YouTube Shorts are vertical videos up to 60 seconds long, similar to TikTok or Instagram Reels. They’re designed for mobile viewing and have a dedicated section with high discovery potential for new audiences.
Q130. How do you grow a YouTube channel?
Consistent posting schedule, quality content, eye-catching thumbnails, SEO optimization, engaging titles, strong hooks in first 10 seconds, audience interaction, collaboration with other creators, promotion on other platforms, and analyzing what works.
Affiliate Marketing
Q131. What is affiliate marketing?
Affiliate marketing is performance-based marketing where you earn commissions by promoting other companies’ products. You share special tracking links, and when someone buys through your link, you get paid a percentage.
Q132. How do affiliate links work?
Affiliate links contain unique tracking codes that identify you as the referrer. When someone clicks your link and makes a purchase within a specific timeframe, the system credits you with the sale and pays your commission.
Q133. What is an affiliate network?
An affiliate network connects merchants with affiliates. Popular networks like Amazon Associates, ShareASale, and CJ Affiliate offer thousands of products to promote, handle tracking, and manage payments. They simplify finding products to promote.
Q134. What is cookie duration in affiliate marketing?
Cookie duration is how long the tracking cookie lasts after someone clicks your affiliate link. If they buy within this period, you earn commission. Durations vary from 24 hours to 90 days depending on the program.
Q135. What makes a good affiliate product to promote?
Good affiliate products match your audience’s interests, solve real problems, offer fair commissions, come from reputable companies, have quality marketing materials, provide reasonable cookie duration, and have positive reviews.
Q136. What is the difference between CPA, CPC, and CPM in affiliate marketing?
CPA (Cost Per Action) pays when someone completes an action like a sale or signup. CPC (Cost Per Click) pays for each click on your affiliate link. CPM (Cost Per Mille) pays per 1,000 impressions or views.
Q137. What disclosure requirements exist for affiliate marketing?
You must clearly disclose affiliate relationships to your audience. It’s legally required and builds trust. Use clear statements like “This post contains affiliate links” prominently near links or at the beginning of content.
Q138. How do you promote affiliate products ethically?
Only recommend products you genuinely believe in, be honest about pros and cons, disclose affiliate relationships clearly, prioritize audience value over commissions, and provide helpful context rather than just pushing links.
Q139. What is an affiliate conversion rate?
Affiliate conversion rate is the percentage of people who click your affiliate link and then complete a purchase. If 100 people click and 3 buy, that’s a 3% conversion rate. Higher rates indicate better-targeted promotions.
Q140. What metrics should affiliates track?
Track clicks, conversion rates, earnings per click (EPC), top-performing products, traffic sources, content performance, commission amounts, and customer lifetime value. These metrics help optimize your strategy.
Freelancing in Digital Marketing

Q141. What is freelancing in digital marketing?
Freelancing means working independently for multiple clients rather than being employed by one company. You offer digital marketing services like SEO, social media management, content writing, or advertising on a project or contract basis.
Q142. What services can digital marketers offer as freelancers?
SEO services, content writing, social media management, PPC campaign management, email marketing, web design, graphic design, video editing, marketing strategy consulting, analytics reporting, and conversion optimization.
Q143. What are the best freelancing platforms?
Popular platforms include Upwork, Fiverr, Freelancer, PeoplePerHour, and Toptal. LinkedIn is also effective for finding freelance opportunities. Different platforms suit different skill levels and service types.
Q144. How do you set freelance rates?
Consider your skills, experience, market rates, project complexity, time required, and overhead costs. Research what others charge. You can charge hourly, per project, or on retainer. Start competitively and increase rates as you build reputation.
Q145. How do you build a freelance portfolio when starting?
Create sample projects, offer discounted services to first clients, do pro bono work for nonprofits, document personal projects, showcase certifications, write case studies, and gradually build real client examples.
Q146. What is the difference between freelancing and consulting?
Freelancers typically execute tasks as directed by clients—managing social accounts or writing content. Consultants provide strategic advice and expertise, guiding clients on what to do rather than doing it themselves. Consulting commands higher rates.
Q147. How do you handle difficult freelance clients?
Set clear expectations upfront, use contracts, communicate regularly, document everything, stay professional, listen to concerns, offer solutions, know when to compromise, and recognize when to end relationships that aren’t working.
Q148. What should a freelance contract include?
Scope of work, deliverables, timelines, payment terms, revision policies, cancellation clauses, confidentiality agreements, intellectual property rights, and communication expectations. Contracts protect both parties.
Q149. How do you find freelance clients?
Use freelance platforms, network on LinkedIn, attend industry events, ask for referrals, showcase your work on social media, create a professional website, join relevant online communities, and reach out to potential clients directly.
Q150. What skills do successful freelancers need beyond technical skills?
Time management, communication, self-discipline, business management, negotiation, problem-solving, adaptability, client relations, marketing yourself, financial management, and continuous learning to stay current.
💼 Access Freelancer Tools, Templates & Pitch Decks! 📘 Explore All Free Resources →
Marketing Automation & Tools
Q151. What is marketing automation?
Marketing automation uses software to automate repetitive marketing tasks like email campaigns, social media posting, lead nurturing, and customer segmentation. It saves time, personalizes communication at scale, and improves efficiency.
Q152. What is a marketing automation workflow?
A workflow is a series of automated actions triggered by specific conditions—for example, when someone subscribes, they receive a welcome email, then three days later an educational email, then a week later a promotional offer.
Q153. What are popular marketing automation tools?
HubSpot, Marketo, Mailchimp, ActiveCampaign, Pardot, Drip, and ConvertKit are popular options. Tool choice depends on business size, budget, required features, and technical complexity. Many offer free tiers for beginners.
Q154. What is lead scoring?
Lead scoring assigns numerical values to leads based on their behavior and characteristics—website visits, email opens, job title, company size. Higher scores indicate more qualified leads, helping prioritize sales follow-up.
Q155. What is a trigger in marketing automation?
A trigger is an event that starts an automated workflow—form submission, email click, website visit, purchase, date/time, or milestone reached. Triggers ensure timely, relevant communication based on user actions.
Q156. What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager manages website tags (tracking codes) without editing code directly. You can add, update, and deploy analytics, conversion tracking, and marketing pixels through one interface. It simplifies tracking implementation.
Q157. What is a webhook?
A webhook sends real-time data from one application to another when specific events occur. For example, when someone fills a form, a webhook can instantly send that data to your CRM or trigger email automation.
Q158. What tools help with social media scheduling?
Buffer, Hootsuite, Later, Sprout Social, and Meta Business Suite allow scheduling posts across multiple platforms in advance. They provide analytics, content calendars, and team collaboration features.
Q159. What is ChatGPT and how can marketers use it?
ChatGPT is an AI language model that generates human-like text. Marketers use it for content ideas, writing assistance, email templates, social media captions, SEO keyword research, ad copy, and customer service chatbot responses.
Q160. What AI tools are useful for digital marketing?
Content creation: ChatGPT, Jasper, Copy.ai. Design: Canva AI, Midjourney, DALL-E. Video: Synthesia, Pictory. SEO: Surfer SEO, Clearscope. Analytics: Google Analytics, Tableau. Email: Phrasee. Social: Lately, Predis.ai.
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)
Q161. What is conversion rate optimization?
CRO improves the percentage of website visitors who complete desired actions—purchases, signups, downloads. Instead of getting more traffic, you make existing traffic more valuable through testing, design improvements, and psychology.
Q162. What elements affect conversion rates?
Headlines, call-to-action buttons, page loading speed, mobile responsiveness, trust signals (reviews, guarantees), form length, navigation clarity, visual hierarchy, color schemes, social proof, and content relevance all impact conversions.
Q163. What is A/B testing?
A/B testing shows two versions of a page to different visitors to see which performs better. You might test different headlines, button colors, images, or layouts. The version with more conversions wins and becomes the default.
Q164. What is multivariate testing?
Multivariate testing tests multiple elements simultaneously to find the best combination. Unlike A/B testing which tests one change, multivariate testing might test headlines, images, and buttons together. It requires more traffic.
Q165. What is a call-to-action (CTA)?
A CTA tells visitors what to do next—”Buy Now,” “Sign Up,” “Download Free Guide.” Effective CTAs are clear, action-oriented, visible, create urgency, and explain benefits. CTA placement and design significantly affect conversions.
Q166. What is social proof in marketing?
Social proof uses evidence that others trust you—customer reviews, testimonials, case studies, client logos, social media followers, or “X people bought this today” messages. People are more likely to act when they see others doing the same.
Q167. What is FOMO in marketing?
FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out) creates urgency by highlighting limited availability or time-sensitive offers—”Only 3 left in stock,” “Sale ends tonight,” or “Join 10,000 happy customers.” It motivates faster decision-making.
Q168. What is the inverted pyramid structure for landing pages?
The inverted pyramid puts most important information first—attention-grabbing headline, key benefits, supporting details, then less critical information lower. People often don’t scroll much, so critical elements should be “above the fold.”
Q169. What is the fold in web design?
The fold is the bottom of the visible screen before scrolling. Content “above the fold” is immediately visible. Important elements like headlines, value propositions, and primary CTAs should appear above the fold.
Q170. What is friction in the context of conversions?
Friction is anything that makes completing an action difficult or annoying—complicated forms, slow loading, confusing navigation, lack of trust signals, or too many steps. Reducing friction improves conversion rates.
Mobile Marketing

Q171. Why is mobile marketing important?
Over 60% of web traffic comes from mobile devices. People use phones for searching, shopping, and social media. If your marketing isn’t mobile-friendly, you’re losing most of your audience. Mobile-first design is now essential.
Q172. What is responsive design?
Responsive design automatically adapts website layout and content to different screen sizes. Text remains readable, buttons stay clickable, and images resize properly on phones, tablets, and desktops. Google prioritizes mobile-responsive sites.
Q173. What is mobile-first indexing?
Mobile-first indexing means Google primarily uses the mobile version of your website for ranking and indexing. If your mobile site is poor, your rankings suffer. Mobile optimization is no longer optional—it’s critical for SEO.
Q174. What is AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages)?
AMP is an open-source framework that creates ultra-fast mobile pages by stripping unnecessary code. AMP pages load almost instantly, improving user experience and potentially boosting search rankings, especially for news and blog content.
Q175. What is SMS marketing?
SMS marketing sends promotional messages via text. It has extremely high open rates (over 90%) and immediate delivery. Used for flash sales, appointment reminders, shipping updates, or exclusive offers to subscribers who opted in.
Q176. What is WhatsApp Business?
WhatsApp Business lets companies communicate with customers through WhatsApp. Features include business profiles, automated messages, product catalogs, and message labels. It’s popular in regions where WhatsApp is the primary communication tool.
Q177. What are in-app advertisements?
In-app ads appear within mobile applications—banner ads, video ads, native ads, or rewarded ads. They target users based on app context and user data. Mobile gaming apps commonly monetize through in-app advertising.
Q178. What is mobile app marketing?
App marketing promotes mobile applications to increase downloads and user engagement. Strategies include App Store Optimization (ASO), app ads, influencer partnerships, content marketing, and encouraging reviews to improve visibility.
Q179. What is App Store Optimization (ASO)?
ASO optimizes your app listing to rank higher in app store search results. It includes keyword optimization in title and description, compelling screenshots, positive reviews, download velocity, and engagement metrics.
Q180. What is a progressive web app (PWA)?
A PWA is a website that functions like a mobile app—works offline, sends push notifications, and can be added to home screens. PWAs combine web’s reach with app-like experience without requiring downloads from app stores.
Analytics & Reporting

Q181. What are KPIs in digital marketing?
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are measurable values showing how effectively you achieve objectives. Examples include website traffic, conversion rate, cost per lead, ROI, engagement rate, and customer acquisition cost. KPIs vary by goals.
Q182. What is ROI in marketing?
ROI (Return on Investment) measures profit generated compared to marketing costs. It’s calculated as: (Revenue from marketing – Marketing cost) / Marketing cost x 100. Positive ROI means your marketing is profitable.
Q183. What is attribution modeling?
Attribution modeling determines which marketing touchpoints receive credit for conversions. Did the customer buy because of an ad, email, or social post? Different models assign credit differently—first-click, last-click, or multi-touch attribution.
Q184. What is the difference between vanity metrics and actionable metrics?
Vanity metrics look good but don’t drive decisions—total page views or follower count. Actionable metrics directly inform business decisions—conversion rate, customer lifetime value, or cost per acquisition. Focus on actionable metrics.
Q185. What is customer acquisition cost (CAC)?
CAC is the total cost to acquire one new customer, including all marketing and sales expenses. It’s calculated by dividing total acquisition costs by number of new customers. Lower CAC means more efficient marketing.
Q186. What is customer lifetime value (CLV or LTV)?
CLV is the total revenue you expect from a customer throughout their relationship with your business. If your CLV is higher than CAC, your business model is sustainable. Increasing CLV is often easier than reducing CAC.
Q187. What is churn rate?
Churn rate is the percentage of customers who stop using your product or service during a specific period. High churn indicates dissatisfaction or competition. Reducing churn is crucial for subscription businesses and long-term growth.
Q188. What is cohort analysis?
Cohort analysis groups users who share common characteristics or experiences within a defined time period, then tracks their behavior over time. It reveals patterns like which acquisition channels produce the most valuable long-term customers.
Q189. What is a marketing dashboard?
A marketing dashboard visualizes key metrics in one place—traffic, conversions, costs, ROI. Dashboards provide real-time performance overview, helping identify trends, problems, and opportunities quickly. Tools like Google Data Studio create custom dashboards.
Q190. What is data-driven marketing?
Data-driven marketing makes decisions based on data analysis rather than intuition. It involves collecting customer data, analyzing patterns, testing hypotheses, measuring results, and continuously optimizing based on what the numbers show.
E-commerce Marketing
Q191. What is e-commerce marketing?
E-commerce marketing promotes online stores to drive traffic, convert visitors into customers, and encourage repeat purchases. It includes SEO, PPC, email marketing, social commerce, content marketing, and conversion optimization specifically for online selling.
Q192. What are product listing ads (PLAs)?
PLAs are shopping ads showing product images, prices, and store names directly in search results. Also called Google Shopping ads, they appear when people search for products. They drive high-intent traffic since searchers see products before clicking.
Q193. What is cart abandonment rate?
Cart abandonment rate is the percentage of shoppers who add items to cart but leave without purchasing. Average rate is around 70%. Common reasons include unexpected costs, complicated checkout, or just browsing. Abandoned cart emails can recover sales.
Q194. How do you reduce cart abandonment?
Show total costs upfront, simplify checkout, offer guest checkout, provide multiple payment options, display trust badges, optimize for mobile, save carts for later, send abandonment emails, and eliminate surprise fees.
Q195. What is dynamic product advertising?
Dynamic ads automatically show relevant products to people based on their browsing behavior. If someone viewed running shoes on your site, they see ads for those specific shoes on Facebook or other sites. It’s highly personalized retargeting.
Q196. What is upselling and cross-selling?
Upselling encourages customers to buy a premium version of what they’re considering—”Upgrade to Pro for $10 more.” Cross-selling suggests related products—”Customers also bought these accessories.” Both increase average order value.
Q197. What is an abandoned cart email?
An automated email sent when someone adds products to cart but doesn’t complete purchase. It reminds them about forgotten items, addresses concerns, and often includes incentives like discounts or free shipping. These emails have high conversion rates.
Q198. What is customer retention marketing?
Retention marketing focuses on keeping existing customers buying again rather than only acquiring new ones. Strategies include loyalty programs, email marketing, personalized recommendations, exclusive offers, and exceptional customer service.
Q199. What is a referral program?
A referral program rewards customers for recommending your business to others. Both referrer and new customer typically receive discounts or benefits. It’s cost-effective marketing since you only pay for successful acquisitions.
Q200. What is average order value (AOV)?
AOV is the average amount customers spend per transaction, calculated by dividing total revenue by number of orders. Increasing AOV through upselling, cross-selling, and bundling is often easier than acquiring new customers.
Additional Important Concepts
Q201. What is brand awareness?
Brand awareness measures how familiar people are with your brand. High awareness means more people recognize your name, logo, and what you offer. Building awareness is often the first marketing goal before driving conversions.
Q202. What is a buyer persona?
A buyer persona is a detailed profile of your ideal customer including demographics, goals, challenges, behavior patterns, and preferences. Creating personas helps target marketing, create relevant content, and understand customer needs.
Q203. What is the marketing funnel?
The marketing funnel represents the customer journey from awareness to purchase: Awareness → Interest → Consideration → Conversion → Loyalty. Different marketing tactics work at different funnel stages. Not everyone who enters reaches the bottom.
Q204. What is omnichannel marketing?
Omnichannel marketing provides seamless customer experience across all channels—website, email, social media, physical store, mobile app. Customers can start on one channel and continue on another without disruption. It requires integrated systems.
Q205. What is growth hacking?
Growth hacking finds creative, low-cost strategies to acquire and retain customers rapidly. It emphasizes experimentation, data, and viral mechanics over traditional marketing. Common in startups with limited budgets but growth ambitions.
Q206. What is viral marketing?
Viral marketing creates content so compelling that people eagerly share it, causing exponential reach. It leverages social networks and word-of-mouth. Successful viral campaigns generate massive exposure at minimal cost but are difficult to plan.
Q207. What is remarketing vs retargeting?
The terms are often used interchangeably, but technically retargeting uses cookies to display ads to people who visited your site. Remarketing refers more broadly to re-engaging people who interacted with your brand, including email remarketing.
Q208. What is GDPR and why does it matter for marketing?
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is European law protecting personal data. It requires explicit consent for data collection, allows users to request data deletion, and imposes strict penalties for violations. Marketers must ensure compliance globally.
Q209. What is the difference between hard bounce and soft bounce in email?
A hard bounce is permanent—invalid email address or domain doesn’t exist. A soft bounce is temporary—full inbox or server problem. Remove hard bounces immediately. Soft bounces can be retried, but repeated soft bounces become hard bounces.
Q210. What makes a marketing campaign successful?
Clear objectives, well-defined target audience, compelling message, appropriate channels, consistent branding, strong call-to-action, proper timing, sufficient budget, measurement plan, and ability to optimize based on data. Success ultimately means achieving your specific goals.
💼 Access Freelancer Tools, Templates & Pitch Decks! 📘 Explore All Free Resources →
2. 50 Self-Preparation Prompts Using ChatGPT
How to Use These Prompts
Copy and paste these prompts directly into ChatGPT or any AI assistant to practice, learn, and prepare for your digital marketing interviews. These prompts will help you understand concepts deeper, create practice scenarios, and build confidence. Feel free to modify them based on your specific needs.
Understanding Core Concepts
Prompt 1: Explain Like I’m Five
“Explain the concept of SEO in the simplest way possible, as if you’re teaching a 10-year-old child. Use everyday examples that anyone can understand.”
Prompt 2: Real-World Examples
“Give me 5 real-world examples of successful digital marketing campaigns from Indian companies. Explain what made each campaign successful and what lessons I can learn from them.”
Prompt 3: Compare and Contrast
“Create a detailed comparison table between SEO and SEM. Include differences in cost, time to results, sustainability, targeting, and when to use each approach.”
Prompt 4: Industry Trends
“What are the top 10 digital marketing trends in 2025? Explain each trend in simple terms and tell me how a fresher can prepare to work with these trends.”
Prompt 5: Terminology Deep Dive
“I’m preparing for a digital marketing interview. Explain these terms with examples: CTR, CPC, CPA, CPM, ROAS, and conversion rate. Make it easy to remember.”
SEO Practice Prompts
Prompt 6: Keyword Research Practice
“I need to do keyword research for a digital marketing training institute in Hyderabad. Walk me through the complete process step-by-step, including what tools to use and how to choose the best keywords.”
Prompt 7: On-Page SEO Checklist
“Create a comprehensive on-page SEO checklist for optimizing a blog post. Present it as a step-by-step checklist that I can follow for any article I write.”
Prompt 8: Technical SEO Audit
“Explain how to conduct a basic technical SEO audit of a website. What should I check, what tools should I use, and what common issues should I look for?”
Prompt 9: Backlink Strategy
“I need to build quality backlinks for a new e-commerce website. Give me 10 ethical white-hat strategies to get backlinks, explaining how each strategy works.”
Prompt 10: Local SEO Setup
“Walk me through setting up local SEO for a restaurant in Bangalore. Cover everything from Google Business Profile to local citations and review management.”
Prompt 11: SEO Case Study Analysis
“Create a sample SEO case study showing how you increased organic traffic for a fictional company. Include before/after metrics, strategies used, and timeline.”
Prompt 12: Algorithm Updates
“Explain the major Google algorithm updates (Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird, BERT, Core Updates) in simple language. What did each update target and how should websites adapt?”
Content Marketing Prompts
Prompt 13: Content Calendar Creation
“Help me create a 30-day content calendar for a digital marketing agency’s blog. Include topic ideas, keywords to target, content types, and publishing schedule.”
Prompt 14: Writing Better Headlines
“I want to improve my headline writing skills. Give me 20 headline formulas that work for digital marketing content, with examples for each formula.”
Prompt 15: Content Distribution Strategy
“I’ve written a great blog post about social media marketing. Now what? Create a complete distribution plan to promote this content across different channels.”
Prompt 16: Storytelling Practice
“Help me write a compelling brand story for a fictional digital marketing training institute. Show me how to make it emotional and memorable.”
Prompt 17: Repurposing Content
“I have a 2000-word blog post about email marketing. Show me how to repurpose this into 10 different content pieces for various platforms.”
Prompt 18: Content Gap Analysis
“Explain how to perform a content gap analysis to find topics my competitors are ranking for but I’m not. Walk me through the process step-by-step.”
Social Media Marketing Prompts
Prompt 19: Platform-Specific Strategies
“Explain the unique content strategy for each major platform: Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Twitter, and YouTube. What works best on each platform and why?”
Prompt 20: Social Media Post Templates
“Create 15 social media post templates for a digital marketing agency. Include different types: tips, quotes, questions, behind-the-scenes, testimonials, etc.”
Prompt 21: Hashtag Research
“Teach me how to research and choose the right hashtags for Instagram posts about digital marketing courses. How many should I use and how do I find them?”
Prompt 22: Crisis Management
“Create a social media crisis management plan. What should I do if a post goes viral for the wrong reasons or if customers complain publicly?”
Prompt 23: Engagement Strategies
“Give me 20 creative ways to increase engagement on social media posts without spending money on ads. Explain why each strategy works.”
Prompt 24: Influencer Collaboration
“How do I find and approach micro-influencers for collaboration? Create an outreach message template and explain the negotiation process.”
Prompt 25: Social Media Audit
“Create a template for auditing social media accounts. What metrics should I track, what should I analyze, and how do I present findings?”
Paid Advertising Prompts
Prompt 26: Google Ads Campaign Setup
“Walk me through setting up my first Google Search Ads campaign for a digital marketing course. Cover keyword selection, ad copy, bidding, and budget allocation.”
Prompt 27: Facebook Ads Practice
“I have a budget of ₹10,000 for Facebook Ads to promote a digital marketing webinar. Create a complete campaign strategy including targeting, ad creative ideas, and budget breakdown.”
Prompt 28: Ad Copy Writing
“Write 10 different Google Ads headlines and 5 descriptions for a digital marketing training institute. Explain what makes each one effective.”
Prompt 29: Retargeting Strategy
“Explain retargeting campaigns in detail. How do I set up retargeting pixels, create audiences, and design effective retargeting ads?”
Prompt 30: A/B Testing Plan
“Create an A/B testing plan for Facebook Ads. What elements should I test, how long should I run tests, and how do I analyze results?”
Prompt 31: Ad Performance Analysis
“I’m running Google Ads but not getting good results. Give me a troubleshooting checklist to identify and fix common problems affecting campaign performance.”
Email Marketing Prompts
Prompt 32: Email Sequence Creation
“Create a 5-email welcome sequence for new subscribers to a digital marketing blog. Include subject lines, email body structure, and timing between emails.”
Prompt 33: Newsletter Ideas
“Give me 30 newsletter topic ideas for a digital marketing audience. Make them interesting, valuable, and likely to get high open rates.”
Prompt 34: Subject Line Formulas
“Teach me the psychology of email subject lines. Give me 15 proven subject line formulas with examples that increase open rates.”
Prompt 35: Email Design Best Practices
“Explain email design best practices. What makes an email visually appealing, mobile-friendly, and likely to drive clicks?”
Prompt 36: List Segmentation Strategy
“I have 5,000 email subscribers. Show me how to segment this list into meaningful groups and create targeted campaigns for each segment.”
Prompt 37: Abandoned Cart Email
“Write a 3-email abandoned cart sequence for an e-commerce store. Make it persuasive but not pushy, including subject lines and email copy.”
Analytics & Reporting Prompts
Prompt 38: Google Analytics Setup
“I just installed Google Analytics on my website. Walk me through the essential setup steps and explain which reports I should check regularly.”
Prompt 39: Creating Marketing Reports
“Create a monthly digital marketing report template. What metrics should I include, how should I visualize data, and what insights should I highlight?”
Prompt 40: UTM Parameter Guide
“Explain UTM parameters in detail. Show me how to create them, what each parameter means, and how to use them for campaign tracking.”
Prompt 41: Conversion Tracking Setup
“How do I set up conversion tracking for a website? Explain the process for Google Analytics, Google Ads, and Facebook Pixel.”
Prompt 42: Interpreting Analytics Data
“My website has high traffic but low conversions. Help me analyze possible reasons and create an action plan to improve conversion rates.”
Email Marketing Prompts
Prompt 43: Mock Interview Questions
“Act as an interviewer for a digital marketing position. Ask me 10 challenging interview questions and then evaluate my answers, providing feedback on how to improve.”
Prompt 44: Case Study Practice
“Give me a digital marketing case study scenario to solve. Present a business problem and ask me how I would approach it, then critique my solution.”
Prompt 45: Portfolio Project Ideas
“I’m a fresher without work experience. Suggest 5 digital marketing projects I can do on my own to build a portfolio that impresses employers.”
Prompt 46: Answering Tough Questions
“Prepare me for tough interview questions like ‘What’s your biggest weakness?’, ‘Why should we hire you?’, and ‘Where do you see yourself in 5 years?’ Give me frameworks for answering.”
Prompt 47: Salary Negotiation
“I’m a fresher interviewing for a digital marketing role. Help me understand typical salary ranges and teach me how to negotiate confidently without underselling myself.”
Advanced Concept Prompts
Prompt 48: Marketing Funnel Strategy
“Explain the complete marketing funnel (awareness, consideration, conversion, loyalty). For each stage, tell me what content to create, which channels to use, and how to measure success.”
Prompt 49: Competitor Analysis
“Teach me how to conduct a comprehensive digital marketing competitor analysis. What tools should I use, what should I analyze, and how do I present findings?”
Prompt 50: Personal Branding
“I want to build my personal brand as a digital marketing professional on LinkedIn. Create a 90-day action plan including content strategy, networking tips, and profile optimization.”
Bonus: Combined Learning Prompts
Prompt 51: Daily Learning Plan
“Create a 30-day digital marketing learning plan for me. Break down what I should study each day, which topics to prioritize, and how to practice what I learn.”
Prompt 52: Certification Guidance
“Which digital marketing certifications should I pursue as a fresher? List the most valuable certifications, explain what each covers, and tell me which are free.”
Prompt 53: Industry Vocabulary
“Create flashcards for 50 essential digital marketing terms. Format it as: Term | Definition | Example | How to use it in a sentence.”
Prompt 54: Mistake Prevention
“What are the most common mistakes beginners make in digital marketing? For each mistake, explain why it’s wrong and what to do instead.”
Prompt 55: Tool Recommendations
“I’m starting as a digital marketer. Recommend free tools for SEO, social media, email marketing, design, and analytics. Explain what each tool does and how to use it.”
How to Maximize Learning with These Prompts
Daily Practice Routine
Week 1: Use Prompts 1-10 (Core Concepts and SEO)
- Spend 30 minutes each day on 2 prompts
- Take notes on key learnings
- Try to explain concepts in your own words
Week 2: Use Prompts 11-25 (Content and Social Media)
- Create actual content based on what you learn
- Practice writing posts and captions
- Build a sample portfolio
Week 3: Use Prompts 26-37 (Paid Ads and Email Marketing)
- Focus on campaign planning
- Create mock campaigns
- Understand budget management
Week 4: Use Prompts 38-50 (Analytics and Interview Prep)
- Practice data interpretation
- Do mock interviews with friends
- Prepare your interview stories
Week 5: Review and Advanced Learning (Prompts 51-55)
- Fill knowledge gaps
- Get certifications
- Build confidence
Pro Tips for Using ChatGPT Effectively
Ask Follow-Up Questions
Don’t stop at the first answer. Ask “Can you explain that differently?” or “Give me more examples” or “How would this work in a real scenario?”
Request Specific Formats
Ask for checklists, templates, tables, or step-by-step guides. Specific formats help you understand and remember better.
Apply to Real Projects
Take what you learn and immediately apply it to a personal blog, social media account, or practice website. Learning by doing is most effective.
Simulate Interview Conditions
When using interview prompts, set a timer and answer without looking anything up first. This builds confidence for real interviews.
Create Your Own Prompts
As you learn, create custom prompts for areas where you feel weak. Personalized learning is powerful.
Combine Multiple Concepts
Try prompts like “How would I use SEO, content marketing, and email marketing together to launch a new product?” This builds strategic thinking.
Track Your Progress
Keep a learning journal noting which prompts you’ve completed, key takeaways, and questions that come up. Review weekly.
Special Career-Focused Prompts
Prompt 56: Resume Building
“Help me create a strong digital marketing resume as a fresher. What sections should I include, how do I highlight my course training, and what keywords should I use?”
Prompt 57: Cover Letter Template
“Write a compelling cover letter template for applying to digital marketing positions. Show me how to customize it for different companies.”
Prompt 58: LinkedIn Profile Optimization
“Audit my LinkedIn profile for a digital marketing career. What should my headline be, how do I write a strong summary, and what skills should I add?”
Prompt 59: Job Search Strategy
“Create a job search strategy for finding my first digital marketing job. Which job boards should I use, how should I network, and what’s the best way to apply?”
Prompt 60: First 90 Days Plan
“If I get hired as a junior digital marketer, what should my first 90 days look like? Create a learning and contribution plan to make a strong impression.”
🤖 Use AI to Boost Your Digital Marketing Prep!
📚 Try All AI Learning Prompts →
3. Communication Skills and Behavioural Interview Preparation
Section A: Essential Communication Skills for Digital Marketers
Why Communication Matters in Digital Marketing
Digital marketing is not just about tools and technical knowledge. You need to explain strategies to clients, write compelling content, present reports to managers, collaborate with teams, and convince people to take action. Strong communication separates average marketers from exceptional ones.
Verbal Communication Skills
Speaking Clearly and Confidently
Why It Matters
In interviews and at work, you’ll need to explain complex marketing concepts to people who may not understand technical terms. Clear communication shows confidence and expertise.
How to Improve
Practice the 3-Second Rule
Before answering any question, take a 3-second pause to organize your thoughts. This prevents rambling and makes you sound more thoughtful.
Use the PREP Framework
- Point: State your main idea first
- Reason: Explain why it’s important
- Example: Give a real example
- Point: Summarize your main idea again
Example in Action:
Question: Why is SEO important?
Answer using PREP:
“SEO is essential for business growth (Point). It helps websites appear when potential customers search for products or services, bringing in qualified traffic without paying for every click (Reason). For instance, a local bakery that optimizes for ‘best birthday cakes in Bangalore’ can attract customers actively looking to buy, rather than hoping random people see their ad (Example). That’s why investing in SEO creates long-term sustainable growth (Point).”
Avoid Filler Words
Common fillers like “um,” “like,” “actually,” “basically,” and “you know” make you sound uncertain. Record yourself answering questions and notice your filler words. Replace them with brief pauses instead.
Practice Exercise:
Set a timer for 2 minutes and explain a digital marketing concept without using any filler words. Do this daily with different topics until it becomes natural.
Active Listening Skills
Why It Matters
Many candidates lose interviews not because they don’t know answers, but because they don’t listen carefully to questions. Active listening helps you understand what’s really being asked.
How to Practice Active Listening
Listen for Keywords
When an interviewer asks a question, identify the key words. If they ask “Tell me about a time you handled a difficult situation,” the keywords are “time,” “handled,” and “difficult situation.” This means they want a specific story, not a general answer.
Paraphrase Before Answering
For complex questions, repeat what you understood: “So you’re asking how I would approach creating a social media strategy for a new brand, correct?” This shows you’re engaged and ensures you’re answering the right question.
Don’t Interrupt
Let the interviewer finish completely before you start answering. Interrupting shows impatience and disrespect, even if you’re excited to answer.
Take Notes
In longer interviews or client meetings, jot down key points. This shows professionalism and helps you address every point raised.
Watch for Non-Verbal Cues
If the interviewer looks confused or disinterested, pause and ask “Would you like me to clarify or provide more details?” This shows awareness and adaptability.
Professional Email Communication
Why It Matters
As a digital marketer, you’ll write countless emails to clients, team members, and stakeholders. Professional email communication reflects your attention to detail and respect for others’ time.
Email Structure That Works
Subject Line:
- Be specific and clear
- Include action items when relevant
- Keep it under 50 characters
Good Examples:
- “Meeting Request: Q4 Marketing Strategy Discussion”
- “Question About Facebook Campaign Budget”
- “Monthly SEO Report – October 2025”
Bad Examples:
- “Hi”
- “Important!!!”
- “Question”
Opening:
Use appropriate greetings based on formality level:
- First time: “Dear Mr. Sharma” or “Hello Ms. Reddy”
- Established relationship: “Hi Rajesh” or “Hello Priya”
- Team emails: “Hi team” or “Hello everyone”
Body:
- Start with the purpose: “I’m writing to discuss…”
- Use short paragraphs (2-3 sentences maximum)
- Use bullet points for multiple items
- Be direct but polite
- Include all necessary information
Closing:
- “Best regards” – Professional and warm
- “Thank you” – When requesting something
- “Looking forward to hearing from you” – Expecting a response
- “Please let me know if you have questions” – Offering help
Signature:
Include your full name, position, company, and contact information.
Email Example:
Subject: Request for Meeting – Social Media Strategy Review
Hi Karthik,
I hope you’re doing well.
I’m reaching out to schedule a 30-minute meeting to review our current social media strategy and discuss optimization opportunities.
I’ve noticed some interesting trends in our recent Instagram engagement data that I’d love to share with you. Would any of these times work for you?
– Thursday, October 17 at 2:00 PM
– Friday, October 18 at 11:00 AM
– Monday, October 21 at 3:00 PM
Please let me know which works best, or suggest an alternative time.
Best regards,
Priya Sharma
Digital Marketing Executive
Frontlines Edutech
Presentation Skills
Why It Matters
You’ll frequently present campaign results, strategy proposals, or monthly reports. Strong presentation skills help you influence decisions and demonstrate your value.
The Golden Rules of Presentations
Structure Your Presentation
- Opening: Hook their attention with a surprising stat or question
- Context: Explain the background or problem
- Main Content: Present your findings or strategy (3-5 key points maximum)
- Action Items: What should happen next?
- Closing: Memorable summary or call-to-action
Simplify Complex Data
Don’t show spreadsheets with 50 rows of data. Extract the 3 most important insights and present them visually with charts or graphs.
Tell Stories with Data
Instead of: “Website traffic increased by 45%”
Say: “Three months ago, our website had 10,000 monthly visitors. Today, we’re welcoming 14,500 potential customers every month—that’s 4,500 more opportunities to convert leads into sales.”
Handle Questions Confidently
- If you know: Answer directly and concisely
- If you’re unsure: “That’s a great question. Let me verify the exact details and get back to you by tomorrow.”
- If it’s outside your scope: “That’s outside my area of expertise, but I can connect you with our technical team who can help.”
Practice Exercise:
Create a 5-minute presentation explaining a recent digital marketing trend. Record yourself, watch it, and note areas for improvement. Repeat until you feel confident.
Section B: Behavioral Interview Questions & STAR Method
Understanding Behavioral Interviews
Behavioral questions ask about past experiences to predict future performance. They usually start with:
- “Tell me about a time when…”
- “Give me an example of…”
- “Describe a situation where…”
- “How did you handle…”
These questions test your problem-solving, teamwork, leadership, adaptability, and work ethic.
The STAR Method
STAR is a framework for answering behavioral questions effectively:
S – Situation: Set the context (When? Where? What was happening?)
T – Task: Explain your responsibility (What needed to be done?)
A – Action: Describe what YOU did (Be specific about your actions)
R – Result: Share the outcome (Use numbers when possible)
50 Common Behavioural Questions with STAR Answers
Category 1: Problem-Solving & Critical Thinking
Q1. Tell me about a time when you faced a difficult problem and how you solved it.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During my digital marketing internship, our client’s Facebook ad campaign had a high click-through rate but zero conversions after two weeks.
Task: My manager asked me to investigate why people were clicking but not buying.
Action: I analyzed the entire customer journey. I discovered that the ad promised “50% off all products” but the landing page showed regular prices. I created a new landing page specifically for ad traffic, clearly showing the discount, and implemented conversion tracking to monitor results.
Result: Within one week, we got our first 15 conversions. The conversion rate improved from 0% to 3.2%, and the client was extremely happy. I learned that message consistency between ads and landing pages is crucial.
Q2. Describe a situation where you had to learn something new quickly.
STAR Answer:
Situation: Three days before an important client presentation, my manager asked me to include Google Analytics data, a tool I had never used before.
Task: I needed to understand Google Analytics basics and extract meaningful insights within 72 hours.
Action: I spent the first evening watching YouTube tutorials on Google Analytics fundamentals. The next day, I accessed the client’s account and explored the interface, focusing on reports most relevant to our presentation. I made notes on key metrics and identified three important trends. On the third day, I created clear visualizations and prepared simple explanations.
Result: The presentation went smoothly. The client appreciated the data-driven approach, and my manager praised my initiative. This experience taught me that I can quickly learn new tools when needed.
Q3. Give me an example of how you used data to make a decision.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During a college project, we were running a social media campaign for a local business but weren’t sure which platform to prioritize.
Task: We needed to decide where to invest our limited time and resources.
Action: I analyzed their existing social media presence across Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn. I looked at engagement rates, follower demographics, and post performance. The data showed that Instagram had 3x higher engagement despite having fewer followers than Facebook. I recommended focusing 60% of our efforts on Instagram.
Result: After implementing this strategy, our engagement increased by 85% in one month, and the business gained 200 new followers. The owner received several customer inquiries directly from Instagram. This taught me the importance of data-driven decision-making.
Q4. Tell me about a time you made a mistake and how you handled it.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During my internship, I scheduled social media posts for a Diwali campaign but accidentally posted them a day early because I didn’t account for time zone differences.
Task: I needed to address this error immediately and minimize damage.
Action: I immediately informed my supervisor about the mistake before anyone else noticed. I explained what happened and took full responsibility. Together, we quickly adjusted the remaining campaign schedule and created additional content to fill the gap. I also set up timezone reminders in our scheduling tool to prevent future errors.
Result: My supervisor appreciated my honesty and quick action. The campaign still performed well, and I learned to always double-check scheduling settings. More importantly, I learned that admitting mistakes early shows integrity and maturity.
Q5. Describe a time when you had to work with incomplete information.
STAR Answer:
Situation: For a class project, we needed to create a digital marketing strategy for a fictional company, but our professor provided minimal background information about the target audience.
Task: I needed to develop a comprehensive strategy despite having limited data.
Action: I made reasonable assumptions based on industry standards and clearly documented them. I researched similar companies to understand typical customer demographics. I created multiple strategy versions for different audience segments. I presented all versions to my professor, explaining the logic behind each approach.
Result: My professor appreciated the thorough research and logical thinking. My team received the highest grade in class. I learned that when information is incomplete, you should make educated guesses, document your assumptions, and be prepared to adapt.
Category 2: Teamwork & Collaboration
Q6. Tell me about a time you worked successfully in a team.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During my final semester, our group was assigned a comprehensive digital marketing project covering SEO, social media, and content marketing.
Task: We had to coordinate four team members with different skill levels and create a cohesive strategy in three weeks.
Action: I suggested we start with a kickoff meeting to assign roles based on everyone’s strengths. I volunteered to handle SEO since that was my strongest area. We set up a shared Google Drive for collaboration and scheduled weekly check-ins. When one team member struggled with content writing, I spent extra time helping them improve without making them feel bad.
Result: We submitted the project two days early and received an A grade. Our professor specifically praised our teamwork and how well-integrated our different sections were. I learned that clear communication and supporting each other leads to better outcomes.
Q7. Describe a situation where you had conflict with a team member.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During a group project, one team member consistently missed deadlines, which affected everyone’s progress.
Task: I needed to address this issue without creating more conflict or making them defensive.
Action: Instead of confronting them publicly, I had a private, friendly conversation. I asked if they were facing any challenges and if there was anything preventing them from completing tasks on time. They shared that they were struggling with a personal issue and felt overwhelmed. Together, we broke their tasks into smaller, more manageable pieces and adjusted some deadlines.
Result: They started meeting deadlines regularly. Our team completed the project successfully, and they thanked me for understanding their situation. I learned that most conflicts can be resolved through empathy and open communication.
Q8. Give an example of when you helped a struggling colleague.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During my internship, a new intern joined who was struggling with basic Excel functions needed for marketing reports.
Task: While not officially my responsibility, I wanted to help because their delays were affecting team deadlines.
Action: I offered to spend 30 minutes daily after work teaching them essential Excel skills—creating tables, using formulas, and making charts. I created a simple cheat sheet with the most common functions we used. I was patient and encouraged them to practice with sample data.
Result: Within a week, they could create basic reports independently. They completed their work on time, which helped the entire team’s workflow. My manager noticed my initiative and mentioned it in my performance review. I learned that helping others succeed creates a better work environment for everyone.
Category 3: Leadership & Initiative
Q9. Tell me about a time you took initiative without being asked.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During my internship, I noticed our social media content calendar was disorganized, with different team members posting inconsistently.
Task: Nobody had assigned me to fix this, but I saw an opportunity to add value.
Action: I created a simple social media content calendar template in Google Sheets with columns for date, platform, content type, caption, and posting time. I shared it with the team and offered a quick 15-minute tutorial on how to use it. I also suggested a color-coding system for different content types.
Result: The team adopted the calendar immediately. Our posting became more consistent, and we avoided duplicate content. My manager was impressed with my proactive approach and asked me to document the process for future interns. I learned that taking initiative, even on small improvements, demonstrates leadership potential.
Q10. Describe a time when you led a project or team.
STAR Answer:
Situation: For our college’s annual fest, I was chosen to lead the social media promotion team of five students.
Task: We needed to create buzz and drive registrations for 15 different events across one month.
Action: I started by having a planning meeting where we set clear goals—5000 social media impressions and 500 registrations. I divided responsibilities based on each person’s strengths—content creation, graphic design, posting, and engagement monitoring. I created a shared calendar with deadlines and set up weekly check-ins to track progress. When we hit roadblocks, I helped brainstorm solutions rather than just assigning more work.
Result: We exceeded our goal with 7,200 impressions and 620 registrations. Three events were sold out partly due to our social media efforts. The organizing committee thanked our team publicly. I learned that good leadership means empowering others, not just directing them.
Q11. Tell me about a time you motivated others.
STAR Answer:
Situation: Midway through a semester project, my team members were losing motivation because we received discouraging feedback on our first draft.
Task: I needed to boost morale and refocus the team on improvement.
Action: I organized a team meeting where we first acknowledged that the feedback was tough but then analyzed it constructively. I broke down each criticism and showed how we could address it step by step. I reminded everyone of the good points the professor mentioned that we shouldn’t overlook. I suggested we celebrate small wins—after fixing each issue, we’d take a short break together.
Result: The team’s energy returned. We worked through the feedback methodically and resubmitted a significantly improved project. We received a B+ grade (up from the initial C-), and everyone felt proud of our comeback. I learned that motivation comes from showing people a clear path forward.
Category 4: Time Management & Organization
Q12. Tell me about a time you had to manage multiple deadlines.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During exam week, I also had to submit a major digital marketing project and complete my internship deliverables.
Task: I needed to balance three important priorities without compromising quality on any of them.
Action: I created a detailed schedule using Google Calendar, blocking specific hours for each task. I tackled the most urgent deadline first—my internship report—by working on it immediately after classes. I studied for exams during morning hours when my concentration was best. I worked on the project in the evenings and reserved one full day on the weekend for final reviews. I also communicated with my professor and internship supervisor about my workload to manage expectations.
Result: I submitted all deliverables on time, scored 85% on my exams, received positive feedback on my internship report, and got an A on the project. I learned that proper planning and honest communication can help manage even the most stressful periods.
Q13. Describe a situation where you had to prioritize tasks.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During my internship, my manager gave me three tasks on Monday morning—create social media content for the week, analyze last month’s website traffic, and update the email newsletter template. All had Friday deadlines.
Task: I needed to determine which task to complete first to maximize impact.
Action: I assessed each task based on urgency and importance. The social media content affected daily posting, so delays would be immediately visible. The traffic analysis could inform strategy decisions but wasn’t time-critical. The newsletter template was important but not urgent since the newsletter wouldn’t be sent until next week. I completed social media content first, then the template, and finished the analysis last.
Result: All three tasks were completed by Thursday. My manager appreciated that I prioritized the customer-facing content. The early completion also gave me time to add extra insights to the traffic analysis. I learned to evaluate tasks based on impact and urgency, not just deadlines.
Q14. Give an example of when you missed a deadline and what you learned.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During a group project, I was responsible for creating presentation slides and underestimated how long it would take.
Task: I had committed to sharing the slides three days before the presentation but realized I wouldn’t finish on time.
Action: Two days before the deadline, I realized I was behind schedule. I immediately informed my team rather than waiting until the last minute. I explained the situation honestly, apologized, and proposed a solution—I would share a rough draft by the original deadline and complete the final version 24 hours later. I worked extra hours to minimize the delay.
Result: My team appreciated the advance notice, which gave them time to adjust their review schedules. We still delivered a successful presentation. However, I learned a valuable lesson about realistic time estimation and the importance of communicating potential delays early. Now I always add buffer time to my schedules.
Category 5: Adaptability & Flexibility
Q15. Tell me about a time when you had to adapt to a significant change.
STAR Answer:
Situation: Halfway through my digital marketing course, the institute switched from offline to online classes due to local restrictions.
Task: I needed to adapt to online learning while maintaining my performance and engagement.
Action: I set up a dedicated study space at home to minimize distractions. I adjusted my schedule to match the new class timings and made sure to test my internet connection before each session. I participated actively in online discussions to stay engaged and formed a WhatsApp study group with classmates to maintain connection and support. When I faced technical issues, I recorded sessions and reviewed them later.
Result: My grades actually improved during online learning because I could re-watch complex topics. I also developed better self-discipline and time management skills. I learned that change can be an opportunity for growth if you approach it with the right mindset.
Q16. Describe a time when you had to learn from criticism.
STAR Answer:
Situation: After presenting my first marketing campaign proposal during my internship, my supervisor pointed out that I focused too much on creative ideas but didn’t include budget considerations or ROI projections.
Task: I needed to accept the feedback constructively and improve my future proposals.
Action: Instead of getting defensive, I thanked my supervisor for the feedback and asked for specific examples of what a complete proposal should include. I requested sample proposals from previous campaigns to study. I took notes on budget planning and ROI calculation methods. For my next proposal, I included a detailed budget breakdown and realistic ROI expectations based on industry benchmarks.
Result: My second proposal was approved with only minor adjustments. My supervisor noted significant improvement and started giving me more responsibility. I learned that criticism is valuable feedback that helps you grow professionally, not a personal attack.
Q17. Tell me about a time when your plans changed unexpectedly.
STAR Answer:
Situation: I planned a weekend to complete a major assignment, but my grandmother fell ill on Friday evening, and I had to travel home immediately to help family.
Task: I still needed to submit the assignment by Monday morning while managing family responsibilities.
Action: During the train journey, I worked on the research portion using my phone and laptop. Once at home, I woke up early each morning to work for two hours before others needed help. I broke the assignment into smaller tasks and completed them in short bursts whenever I had free time. I also reached out to a classmate to verify that I hadn’t missed any last-minute instructions from our professor.
Result: I submitted the assignment on time despite the disruption. My grandmother recovered, and I was there to support my family. My professor later praised the quality of my work. I learned that flexibility and breaking large tasks into smaller ones helps navigate unexpected situations.
Category 6: Customer Focus & Client Handling
Q18. Tell me about a time you dealt with a difficult customer or client.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During my internship, a client was unhappy because their social media engagement hadn’t increased as quickly as they expected, even though we had only been working together for two weeks.
Task: I needed to address their concerns while managing expectations about realistic timelines.
Action: I scheduled a call to listen to their concerns without interrupting. I acknowledged their frustration and explained that organic social media growth typically takes 4-6 weeks to show significant results. I showed them the small improvements we had already achieved—15% increase in profile visits and better quality content engagement. I created a detailed roadmap showing what they could expect week by week and suggested a paid promotion to accelerate results.
Result: The client appreciated the transparency and agreed to continue with our plan. By week six, engagement had increased by 40%. They later became one of our best clients and referred two others. I learned that managing expectations and maintaining clear communication prevents misunderstandings.
Q19. Describe a time when you went above and beyond for a customer.
STAR Answer:
Situation: A small business owner who was our client mentioned they were struggling to understand their Google Analytics reports.
Task: While teaching analytics wasn’t part of my job, I saw an opportunity to add value and strengthen the relationship.
Action: I offered to create a simplified one-page guide explaining the most important metrics for their business. I spent my personal time over a weekend creating visual examples and simple explanations without jargon. I also recorded a 10-minute video walkthrough they could refer to anytime. I sent it to them with a note saying there was no charge—it was just to help them make better decisions.
Result: The client was extremely grateful and shared positive feedback with my manager. They signed up for additional services because they felt we genuinely cared about their success, not just their money. My manager recognized my initiative in the next team meeting. I learned that small gestures that show you care can create loyal, long-term relationships.
Q20. Give an example of when you had to say no to a customer request.
STAR Answer:
Situation: A client asked us to guarantee them the number one ranking on Google for a highly competitive keyword within one month.
Task: I needed to decline their unrealistic request while maintaining a positive relationship and offering an alternative solution.
Action: I explained politely that ethical SEO agencies cannot guarantee specific rankings because Google’s algorithm considers hundreds of factors outside our control. I educated them about white hat versus black hat SEO practices and the risks of promises that sound too good to be true. Instead, I proposed realistic goals—improving rankings for less competitive long-tail keywords, increasing organic traffic by 30%, and tracking conversions rather than just rankings.
Result: The client appreciated the honesty and education. They agreed to the alternative approach and were happy when we achieved a 35% traffic increase in three months. They later told us they had almost hired a company that made false guarantees. I learned that saying no with education and alternatives is better than agreeing to impossible promises.
Category 7: Creativity & Innovation
Q21. Tell me about a time you came up with a creative solution to a problem.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During a college project, we needed to promote an event but had zero budget for paid advertising.
Task: I needed to generate awareness and registrations without spending money.
Action: I proposed a creative user-generated content campaign. We asked people to share their expectations from the event using a unique hashtag and tag three friends. The best posts would win free passes. We also collaborated with student influencers who agreed to promote the event in exchange for VIP access. I created shareable content templates that made it easy for people to participate.
Result: The hashtag trended locally with over 500 posts. We got 300 registrations without spending a rupee on ads. The event was fully booked, and the organizers asked us to handle promotion for future events. I learned that creativity and strategic partnerships can achieve results that money alone cannot.
Q22. Describe a time when you improved a process or system.
STAR Answer:
Situation: At my internship, the team manually tracked social media performance by checking each platform individually and copying data into Excel every week—a process that took 2-3 hours.
Task: While not asked to improve this, I saw an inefficient process that wasted valuable time.
Action: I researched free social media management tools and found one that could connect multiple accounts and generate automated reports. I created a test report to show the team how it worked and demonstrated that we could get the same information in 10 minutes instead of 3 hours. I prepared a simple guide for team members to access these reports anytime.
Result: The team adopted the tool immediately. We saved approximately 10 hours per month, which we redirected toward strategy and content creation. My manager appreciated the initiative and asked me to look for other process improvements. I learned that questioning “the way we’ve always done it” can lead to significant improvements.
Category 8: Work Ethic & Professionalism
Q23. Tell me about a time you worked under pressure.
STAR Answer:
Situation: Two days before a major client presentation, a team member fell sick, leaving their portion of the work incomplete.
Task: I needed to complete both my work and understand their portion well enough to present it convincingly.
Action: I stayed late both evenings to review their research and integrate it with my section. I reached out to the sick colleague via message to clarify a few points without burdening them. I practiced the entire presentation multiple times and prepared for potential questions about both sections. I also prepared backup slides in case I needed extra time on complex topics.
Result: The presentation went smoothly. The client approved our proposal, and my manager praised my dedication and professionalism. The sick colleague thanked me for covering for them. I learned that stepping up during critical moments demonstrates reliability and team commitment.
Q24. Describe a time when you showed integrity.
STAR Answer:
Situation: During a project, I discovered that data I had included in a report was incorrect due to a tracking error.
Task: I could have hoped nobody noticed, or I could be honest about the mistake even though the report had already been shared.
Action: I immediately informed my supervisor about the error, explained how it happened, and provided the corrected data. I took responsibility without making excuses. I also implemented a double-check process to prevent similar errors in the future.
Result: My supervisor appreciated my honesty and said that catching the error before major decisions were made was valuable. My credibility actually increased because I prioritized accuracy over protecting my image. I learned that integrity means doing the right thing even when it’s uncomfortable.
Q25. Give an example of when you received positive feedback.
STAR Answer:
Situation: After completing a three-month internship, I had a final evaluation with my supervisor.
Task: I was nervous about the feedback since it was my first professional experience.
Action: Throughout the internship, I had focused on being proactive, meeting deadlines, asking good questions, accepting feedback positively, and maintaining professional communication.
Result: My supervisor gave excellent feedback, particularly praising my willingness to learn, attention to detail, and positive attitude. They offered me a recommendation letter without me asking and said they’d be happy to have me back for future opportunities. I realized that consistent small efforts—punctuality, quality work, positive attitude—make a bigger impression than occasional big gestures.
Section C: Common HR Interview Questions
Questions About You
Q26. Tell me about yourself.
The Formula:
Present + Past + Future (Keep it under 2 minutes)
Sample Answer:
“I recently completed my digital marketing course from Frontlines Edutech where I learned SEO, social media marketing, content strategy, and Google Ads (Present). Before that, I completed my graduation in Commerce, where I developed analytical skills and worked on several team projects. During my studies, I realized I enjoyed the creative and strategic aspects of marketing, which led me to pursue specialized training in digital marketing (Past). Now I’m looking for an opportunity where I can apply my skills in a practical setting, continue learning from experienced professionals, and contribute to growing a brand’s online presence (Future).”
Q27. What are your strengths?
How to Answer:
Choose 2-3 strengths relevant to digital marketing and provide brief examples.
Sample Answer:
“My biggest strength is analytical thinking. During my course projects, I enjoyed analyzing campaign data to identify what worked and what didn’t, then using those insights to improve performance. For example, in a practice campaign, I noticed that posts with questions had 3x higher engagement, so I adjusted our strategy accordingly.
Another strength is adaptability. Digital marketing changes constantly with algorithm updates and new features. I stay updated by following industry blogs and testing new features like Instagram Reels and YouTube Shorts as soon as they launch. I enjoy learning new tools and techniques.”
Q28. What are your weaknesses?
How to Answer:
Choose a real weakness but show how you’re working to improve it. Avoid clichés like “I’m a perfectionist.”
Sample Answer:
“I sometimes struggle with public speaking and presenting in front of large groups. I get nervous, which can affect my delivery. However, I’m actively working on this by volunteering to present in smaller group settings and taking online courses on presentation skills. During my course, I pushed myself to present our final project to the class, and while I was nervous, the experience helped me improve. I believe that with continued practice and exposure, I’ll become more confident in this area.”
Q29. Why should we hire you?
How to Answer:
Connect your skills and qualities to what they need. Research the company first.
Sample Answer:
“You should hire me because I bring a combination of updated digital marketing knowledge, genuine enthusiasm for the field, and a strong willingness to learn. I recently completed comprehensive training covering SEO, social media, content marketing, and paid advertising. I understand that this role requires someone who can create engaging content and analyze performance data—both areas where I’ve practiced extensively during my course projects.
More importantly, I’m someone who takes initiative and stays updated with industry changes. I follow leading digital marketing blogs, experiment with new features, and genuinely enjoy this work. As a fresher, I’m eager to learn from your experienced team and contribute fresh ideas and perspectives.”
Q30. Where do you see yourself in 5 years?
How to Answer:
Show ambition but also loyalty. Avoid saying you’ll leave or start your own business.
Sample Answer:
“In five years, I see myself as an experienced digital marketing specialist with deep expertise in at least two areas—perhaps SEO and content strategy. I’d like to have progressed to a senior role where I’m leading campaigns, mentoring junior team members, and contributing to strategic decisions.
I’m particularly interested in understanding how different marketing channels work together and how to create integrated campaigns. I believe this company offers the learning opportunities and growth potential to help me achieve these goals while contributing significantly to the team’s success.”
Q31. Why do you want to work in digital marketing?
Sample Answer:
“I’m drawn to digital marketing because it perfectly combines creativity, strategy, and data. I love that you can be creative in developing content and campaigns, but then use data to see exactly what works. There’s immediate feedback, which means continuous learning and improvement.
I also appreciate that digital marketing is accessible to all business sizes—a small local shop can compete with bigger brands through smart strategies. The field is constantly evolving with new platforms and features, which keeps it exciting. Plus, seeing a campaign you created actually drive results—whether it’s increased website traffic, more followers, or actual sales—is incredibly satisfying.”
Q32. What do you know about our company?
How to Prepare:
Research the company before the interview. Visit their website, social media, and recent news.
Sample Answer:
“I’ve researched your company extensively. I see that you specialize in digital marketing for healthcare clients, which is a unique niche. I’ve looked at your website case studies and was particularly impressed by how you helped XYZ Clinic increase patient appointments by 60% through local SEO and Google Ads.
I also follow your LinkedIn page and noticed you recently shared insights about healthcare marketing regulations—it’s clear you’re not just doing generic marketing but really understand the specific challenges and compliance requirements in healthcare. That specialization is one reason I’m excited about this opportunity. I’d love to develop expertise in a specific industry rather than doing general marketing.”
Q33. What are your salary expectations?
How to Answer:
Research typical salaries for the role and location. Provide a range rather than a fixed number.
Sample Answer:
“Based on my research of digital marketing roles for freshers in this area, I understand the typical range is between ₹15,000 to ₹25,000 per month. Given my completed training and practical project experience, I’m looking for something in the range of ₹18,000 to ₹22,000. However, I’m flexible and more focused on finding the right opportunity to learn and grow. If the role offers strong learning opportunities and career development, I’m open to discussing compensation.”
Important: If you’re truly unsure, you can say: “I’m still learning about market rates for this role. Could you share the budgeted range for this position? That would help me provide a more informed response.”
Q34. Why did you choose digital marketing as a career?
Sample Answer:
“After completing my graduation, I was exploring different career paths and realized I wanted something that combined creativity with measurable results. I’ve always enjoyed writing and creating content, but I also like understanding what works and why.
I started learning about digital marketing through free online resources and was fascinated by how businesses can reach specific audiences, measure every aspect of their campaigns, and continuously improve based on data. I enrolled in a comprehensive course at Frontlines Edutech to get structured learning and hands-on practice. The more I learned, the more certain I became that this is the right career path for me. The field offers constant learning, creativity, strategy, and tangible results—everything I was looking for.”
Q35. Do you have any questions for us?
Always ask questions. It shows interest and helps you evaluate if the role is right for you.
Good Questions to Ask:
- “What does success look like in this role during the first six months?”
- “What digital marketing tools and platforms does your team currently use?”
- “How is the marketing team structured, and who would I be working with most closely?”
- “What opportunities are there for learning and professional development?”
- “What are the biggest marketing challenges the company is currently facing?”
- “Can you describe the typical projects I’d work on in this role?”
- “What’s the team culture like, and what qualities do successful people here share?”
Questions to Avoid:
- Don’t ask about salary and benefits in the first interview unless they bring it up
- Don’t ask questions clearly answered on their website
- Don’t ask “What does your company do?” (Research this beforehand)
Section D: Body Language & Interview Etiquette
he Silent Communication
Body language communicates confidence, interest, and professionalism before you even speak. Studies show that 55% of communication is through body language, 38% through tone of voice, and only 7% through actual words.
Essential Body Language Tips
The Entrance
- Walk in confidently with good posture
- Smile genuinely as you enter
- Make eye contact with everyone in the room
- Wait to be offered a seat before sitting
Handshake (if offered)
- Firm but not crushing grip
- 2-3 shakes, then release
- Maintain eye contact during the handshake
- If culturally appropriate for your region
Sitting Position
- Sit upright but not rigid
- Both feet on the floor or one ankle crossed
- Lean slightly forward to show engagement
- Don’t slouch, cross arms, or fidget
Eye Contact
- Maintain eye contact 60-70% of the time
- Look away occasionally to avoid staring
- If multiple interviewers, distribute eye contact
- Looking away briefly when thinking is natural
Hand Gestures
- Use natural hand movements when explaining points
- Keep hands visible (not in pockets or under table)
- Avoid touching your face, hair, or fidgeting with objects
- Open palms suggest honesty and confidence
Facial Expressions
- Smile naturally, especially when greeting and saying goodbye
- Show interest through your expressions
- Nod occasionally to show understanding
- Match the tone—if discussing serious topics, look appropriately serious
Voice and Speech
- Speak clearly at a moderate pace
- Don’t speak too softly (shows lack of confidence) or too loudly (seems aggressive)
- Pause between thoughts rather than using “um” or “uh”
- Vary your tone to maintain interest—avoid monotone
What to Avoid
- Checking your phone or watch repeatedly
- Playing with pen, hair, or jewelry
- Crossing arms (appears defensive)
- Tapping feet or bouncing knees
- Looking at the ceiling or floor when answering
- Covering your mouth while speaking
- Yawning (even if nervous)
Virtual Interview Etiquette
Technical Setup
- Test your internet connection beforehand
- Use a laptop or desktop, not a phone if possible
- Charge your device fully
- Close unnecessary tabs and programs
- Join the call 2-3 minutes early, not late
Environment
- Choose a quiet space with minimal background noise
- Ensure good lighting (face the light source, don’t have it behind you)
- Use a plain, professional background (not your bed)
- Sit against a wall if possible to avoid distractions behind you
Camera Position
- Position camera at eye level (not looking down or up)
- Sit at arm’s length from the camera
- Look at the camera when speaking, not at your own image
- Test your video beforehand to check framing
During the Interview
- Dress professionally from head to toe (in case you need to stand)
- Maintain “eye contact” by looking at the camera
- Smile and nod to show engagement
- Mute when not speaking if there’s background noise
- Don’t multitask or read notes obviously
If Technical Issues Occur
- Stay calm and professional
- Have the interviewer’s phone number as backup
- Communicate immediately if you lose connection
- Apologize briefly but don’t dwell on technical problems
Professional Appearance
For Men:
- Formal shirt (solid colors or subtle patterns)
- Trousers (avoid jeans unless company culture is very casual)
- Closed shoes (not sandals or sneakers)
- Clean, well-groomed hair
- Clean-shaven or well-maintained beard
- Minimal cologne
- Remove visible piercings (except small ear studs)
For Women:
- Professional kurti and trousers or churidar
- Salwar suit (simple, not heavily embellished)
- Business casual Western wear (avoid overly casual)
- Modest necklines and appropriate length
- Closed or semi-formal footwear
- Minimal jewelry
- Subtle makeup (if worn)
- Neat, professional hairstyle
- Light perfume
General Grooming:
- Clean, trimmed nails
- Fresh breath (avoid strong-smelling foods before interview)
- Clean, ironed clothes
- Polished or clean shoes
- Avoid excessive accessories or strong fragrances
Interview Day Checklist
The Night Before:
- Confirm interview time and location/link
- Prepare outfit and keep it ready
- Print multiple copies of your resume
- Charge phone and laptop fully
- Research the company one final time
- Review your prepared answers
- Get good sleep
Morning Of:
- Eat a proper meal
- Leave early (arrive 10-15 minutes before time)
- Bring resume copies, notepad, and working pen
- Turn off phone or put on silent
- Visit restroom before entering
- Take a few deep breaths to calm nerves
What to Bring:
- 3-4 copies of your resume
- Notepad and pen
- Certificates (if relevant)
- Portfolio or work samples (if applicable)
- List of references
- Your questions for them
- Photo ID
- Folder or bag to carry everything
🗣️ Ace HR & Behavioral Rounds with Confidence!
💡 Check Interview How-to Guides →
4. ADDITIONAL PREPARATION ELEMENTS
Section A: Building Your Digital Marketing Resume

Resume Fundamentals for Digital Marketers
Your resume is your marketing document. Just like you’d optimize a landing page for conversions, optimize your resume to get interview calls. Most recruiters spend only 6-10 seconds on the first scan, so every word matters.
Resume Structure That Works
Contact Information
Place this at the top, clearly visible:
- Full Name (larger font, bold)
- Phone Number (with country code)
- Professional Email (firstname.lastname@gmail.com, not coolboy123@)
- LinkedIn Profile URL (customized, not default numbers)
- Portfolio Website or Blog (if you have one)
- City and State (no need for complete address)
Professional Summary (3-4 Lines)
Write a compelling snapshot of who you are professionally. This isn’t the place to be modest.
Example for Freshers:
“Results-oriented Digital Marketing professional with comprehensive training in SEO, SEM, Social Media Marketing, and Content Strategy from Frontlines Edutech. Hands-on experience managing practice campaigns with measurable improvements in engagement and traffic. Passionate about data-driven marketing and staying updated with industry trends. Eager to contribute fresh ideas and dedication to a dynamic marketing team.”
Example for Those with Internship:
“Digital Marketing Specialist with 6 months of internship experience executing multi-channel campaigns. Successfully increased client social media engagement by 45% and reduced cost-per-click by 20% through campaign optimization. Skilled in Google Analytics, Facebook Ads Manager, SEO tools, and content creation. Proven ability to analyze data and translate insights into actionable strategies.”
Skills Section
Divide into categories for easy scanning:
Technical Skills:
- SEO & SEM
- Google Analytics & Google Ads
- Facebook Ads Manager
- Email Marketing (Mailchimp)
- Content Management Systems (WordPress)
- Social Media Marketing
- Keyword Research & Analysis
- A/B Testing & Conversion Optimization
Tools & Platforms:
- Google Analytics 4
- Google Search Console
- SEMrush / Ahrefs (if you’ve used them)
- Canva / Adobe Creative Suite
- Microsoft Excel
- Google Tag Manager
- Hootsuite / Buffer
Soft Skills:
- Data Analysis
- Content Writing
- Project Management
- Team Collaboration
- Client Communication
- Creative Problem-Solving
Education
List in reverse chronological order (most recent first):
Digital Marketing Course
Frontlines Edutech, Hyderabad
Duration: [Month Year] – [Month Year]
- Comprehensive 360-degree digital marketing training
- Completed projects in SEO, social media marketing, Google Ads, and email campaigns
- Achieved [specific accomplishment if any, like top project grade]
Bachelor’s Degree
[Your Degree Name], [College/University Name]
Graduation Year: [Year]
Percentage/CGPA: [Your score]
Professional Experience (or Projects for Freshers)
If you have internship experience, format it like this:
Digital Marketing Intern
[Company Name], [City]
[Month Year] – [Month Year]
Use bullet points starting with action verbs. Include numbers wherever possible:
- Managed social media accounts across Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn, growing follower base by 35% in 3 months
- Created and scheduled 60+ social media posts monthly using content calendar and scheduling tools
- Conducted keyword research and implemented on-page SEO improvements, resulting in 25% increase in organic traffic
- Assisted in managing Google Ads campaigns with monthly budget of ₹50,000, achieving 15% reduction in CPC
- Analyzed campaign performance using Google Analytics and prepared weekly reports for management
- Collaborated with design team to create engaging visual content for campaigns
If you’re a fresher without work experience, create a “Projects” section:
Projects
SEO Website Optimization Project
[Month Year]
- Conducted comprehensive SEO audit for practice website using SEMrush
- Implemented on-page optimization including meta tags, header structure, and internal linking
- Created content strategy based on keyword research targeting 20+ relevant keywords
- Improved website loading speed by 40% through image optimization and caching
- Result: Increased organic traffic by 55% over 8 weeks
Social Media Marketing Campaign
[Month Year]
- Designed and executed 30-day Instagram marketing campaign for fictional brand
- Created content calendar with mix of educational, entertaining, and promotional content
- Implemented hashtag strategy combining trending and niche hashtags
- Engaged with target audience through comments, stories, and direct messaging
- Result: Achieved 200+ new followers and 300% increase in engagement rate
Google Ads Campaign Management
[Month Year]
- Created search ads campaign for local business practice project
- Performed keyword research identifying 50+ relevant keywords with optimal search volume
- Wrote compelling ad copy with clear call-to-action and relevant ad extensions
- Set up conversion tracking and monitored performance metrics daily
- Result: Achieved 4.5% CTR and 12% conversion rate within simulated budget
Certifications
List relevant certifications that add credibility:
- Google Analytics Individual Qualification (GAIQ)
- Google Ads Search Certification
- Facebook Blueprint Certification
- HubSpot Content Marketing Certification
- SEMrush SEO Toolkit Course
- Google Digital Garage Certification
Awards and Achievements (Optional)
Only include if genuinely impressive:
- Best Digital Marketing Project Award, Frontlines Edutech 2025
- 1st Place in College Marketing Competition
- Published article on digital marketing trends in [Publication Name]
Resume Writing Best Practices
Use Action Verbs
Start every bullet point with strong action verbs:
- Managed, Created, Developed, Implemented, Optimized, Analyzed
- Increased, Improved, Achieved, Generated, Launched, Coordinated
- Conducted, Designed, Executed, Monitored, Collaborated, Presented
Quantify Everything
Numbers catch attention and prove impact:
- Instead of: “Improved social media presence”
- Write: “Increased Instagram followers by 300 (from 500 to 800) in 2 months”
- Instead of: “Managed Google Ads campaigns”
- Write: “Managed 5 Google Ads campaigns with combined monthly budget of ₹75,000, achieving average CTR of 3.8%”
Avoid Common Mistakes
- Spelling and grammar errors (use Grammarly to check)
- Using fancy fonts or colors (stick to professional fonts)
- Making it longer than 2 pages (1 page is ideal for freshers)
- Including irrelevant information (your hobbies unless relevant)
- Using personal pronouns (I, me, my)
- Listing responsibilities without results
- Having gaps in dates without explanation
- Using passive voice
ATS Optimization
Many companies use Applicant Tracking Systems that scan resumes before humans see them:
- Use standard section headings (Experience, Education, Skills)
- Avoid tables, text boxes, headers, and footers
- Use standard fonts (Arial, Calibri, Times New Roman)
- Save as .docx or PDF (check job posting for preference)
- Include keywords from job description naturally
- Don’t use images or graphics
- Spell out acronyms at least once (SEO – Search Engine Optimization)
Formatting Guidelines
- Use consistent formatting throughout
- Font size: 10-12 for body text, 14-16 for name
- Margins: 0.5 to 1 inch on all sides
- Line spacing: 1.0 to 1.15
- Use bold for headings and company names
- Use bullet points, not paragraphs
- Leave white space for easy reading
Cover Letter Essentials
While not always required, a good cover letter can differentiate you from other candidates with similar qualifications.
Structure:
Opening Paragraph:
State the position you’re applying for and where you found it. Add one compelling reason why you’re interested.
Example:
“I am writing to express my strong interest in the Digital Marketing Executive position at [Company Name] advertised on LinkedIn. As a recent digital marketing graduate from Frontlines Edutech with hands-on experience in SEO and social media campaigns, I am excited about the opportunity to contribute to your team’s innovative marketing initiatives.”
Body Paragraphs (1-2):
Connect your skills and experiences to their needs. Show you’ve researched the company.
Example:
“During my comprehensive digital marketing training, I developed expertise in multi-channel marketing strategies. I successfully managed a practice social media campaign that increased engagement by 65% through strategic content planning and community management. I am particularly drawn to [Company Name]’s data-driven approach to marketing, as I believe combining creativity with analytics produces the most effective campaigns.
Your recent campaign for [specific campaign if you know] demonstrated innovative use of video content and user engagement strategies. I would love to bring my skills in content creation, analytics interpretation, and social media management to support similar initiatives and help achieve your marketing objectives.”
Closing Paragraph:
Thank them and express interest in discussing further.
Example:
“I am enthusiastic about the possibility of contributing to [Company Name]’s marketing success and would welcome the opportunity to discuss how my skills and passion align with your team’s needs. Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to hearing from you.”
Keep It:
- Under one page
- Personalized for each company (avoid generic letters)
- Professional but showing personality
- Free of errors
- Focused on what you can do for them, not what they can do for you
Section B: LinkedIn Profile Optimization
LinkedIn is your online professional identity. Recruiters actively search LinkedIn for candidates, so an optimized profile increases your visibility and opportunities.
Profile Photo
Your photo is the first thing people notice:
- Use a professional headshot (not a group photo or casual selfie)
- Dress professionally as you would for an interview
- Smile naturally and make eye contact with camera
- Use a clean, neutral background
- Ensure good lighting (face well-lit, no harsh shadows)
- Photo should be recent and actually look like you
- High resolution (at least 400×400 pixels)
Background Banner:
Don’t leave it as default blue. Use a custom banner that reflects your profession:
- Canva has free LinkedIn banner templates
- Include keywords like “Digital Marketing Professional”
- Keep it professional and not too busy
- Make sure any text is readable on mobile devices
Headline (120 Characters)
Your headline appears below your name everywhere on LinkedIn. Make it compelling and keyword-rich.
Weak Examples:
- “Looking for opportunities”
- “Digital Marketing Student”
- “Fresher”
Strong Examples:
- “Digital Marketing Specialist | SEO | Social Media Marketing | Content Strategy | Helping Brands Grow Online”
- “Performance Marketing Professional | Google Ads | Facebook Ads | Data-Driven Growth | Open to Opportunities”
- “Digital Marketing Graduate | Certified in Google Analytics & Ads | Passionate About Brand Growth Through Strategic Campaigns”
Tips:
- Include relevant keywords recruiters search for
- Show your specialization
- Add certification if impressive
- Use vertical bars (|) to separate elements
- Update when you gain new skills or certifications
About Section (2600 Characters Max)
This is your elevator pitch in written form. Write in first person and show personality while remaining professional.
Structure:
Opening Hook (2-3 sentences):
Grab attention with your passion or a compelling statement.
“I believe data and creativity are not opposites—they’re partners. As a digital marketing professional, I combine analytical thinking with creative storytelling to help brands connect with their audiences and achieve measurable growth.”
Your Background (3-4 sentences):
Briefly explain your journey and training.
“I recently completed comprehensive digital marketing training at Frontlines Edutech, where I gained hands-on experience in SEO, SEM, social media marketing, email campaigns, and analytics. Through real-world projects, I learned to not just execute campaigns but understand the ‘why’ behind every strategy.”
Your Skills and Value (4-5 bullet points):
What can you do? Be specific.
“My expertise includes:
- Search Engine Optimization (On-page, Off-page, and Technical SEO)
- Paid Advertising (Google Ads and Facebook Ads campaign management)
- Social Media Strategy and Community Management
- Content Creation and Marketing
- Web Analytics and Data-Driven Decision Making”
Achievements or Projects:
Include 1-2 specific examples with numbers.
“In one of my projects, I optimized a website’s SEO which resulted in 55% increase in organic traffic over 8 weeks. I also managed a simulated Google Ads campaign achieving 4.2% CTR and 15% conversion rate.”
Call to Action:
End with how people can connect with you.
“I’m actively seeking opportunities to begin my career in digital marketing where I can contribute to meaningful campaigns and continue learning. Let’s connect if you’re looking for a dedicated, curious, and results-oriented marketing professional.”
Tips:
- Use keywords naturally throughout
- Break into short paragraphs for easy reading
- Show personality while remaining professional
- Update as you gain experience
- Proofread carefully
Experience Section
Add your internships, projects, or volunteer work:
For Each Position:
- Use the same bullet points as your resume
- Include rich media (attach presentations, documents, links to campaigns)
- Add numbers and results
- Use keywords relevant to digital marketing
Even Without Formal Experience:
- Add course projects as “experience”
- Include freelance work (even if unpaid)
- List volunteer marketing work
- Add any content creation (blog, YouTube channel if relevant)
Skills & Endorsements
Add up to 50 skills, but prioritize the most important ones in top positions:
Top Priority Skills (Position 1-5):
- Digital Marketing
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- Social Media Marketing
- Google Analytics
- Content Marketing
Other Important Skills:
- Google Ads
- Facebook Advertising
- Email Marketing
- Marketing Strategy
- Content Writing
- Data Analysis
- WordPress
- Copywriting
- Market Research
- Campaign Management
Get Endorsements:
- Endorse your classmates’ skills (many will reciprocate)
- Ask mentors or instructors to endorse you
- Endorse colleagues from internships
- Quality matters more than quantity
Recommendations
Recommendations are powerful social proof. Aim for 2-3 quality recommendations.
Who to Ask:
- Instructors from your course
- Internship supervisors
- Team leaders from projects
- Clients if you did any freelance work
- Professors who know your work
How to Ask:
Send a polite, personalized message:
“Hi [Name],
I hope you’re doing well. I’m currently updating my LinkedIn profile as I search for digital marketing opportunities. Would you be willing to write a brief recommendation about the work we did together on [specific project/internship]?
I particularly valued your feedback on [specific aspect], and I think a recommendation highlighting [specific skill or quality] would be helpful to potential employers.
I’d be happy to return the favor or provide any specific points you’d like me to include if you’d prefer.
Thank you for considering this request!”
Make It Easy:
Offer to provide bullet points they can use if they’re busy.
Additional LinkedIn Strategies
Be Active:
- Share relevant industry articles with your thoughts
- Post about what you’re learning
- Comment meaningfully on others’ posts
- Congratulate connections on achievements
- Join relevant groups and participate in discussions
Content Ideas:
- Share a key learning from your course
- Post about a marketing campaign you admire
- Share quick tips or insights
- Write short articles about digital marketing topics
- Share your project results (with screenshots if possible)
Networking:
- Connect with classmates and instructors
- Follow companies you want to work for
- Connect with digital marketing professionals
- Personalize connection requests (don’t use default message)
- Engage with your network’s content
Optimize for Search:
- Include keywords in all sections
- Complete all profile sections (aim for “All-Star” level)
- Use relevant hashtags in posts
- Add location (important for local opportunities)
- Keep URL customized (linkedin.com/in/yourname)
Section C: Essential Certifications

Certifications add credibility and show commitment to learning. Many are free and can be completed in days.
Must-Have Free Certifications
Google Analytics Individual Qualification (GAIQ)
- Provider: Google
- Cost: Free
- Duration: 3-4 hours study + 90-minute exam
- Value: Essential for any digital marketer. Shows you can analyze website data.
- Link: skillshop.withgoogle.com
- Validity: 12 months (renewable)
Google Ads Search Certification
- Provider: Google
- Cost: Free
- Duration: 4-5 hours study + 75-minute exam
- Value: Proves you can create and optimize search campaigns.
- Covers: Search advertising, bidding, optimization, measurement
- Validity: 12 months
Google Ads Display Certification
- Provider: Google
- Cost: Free
- Duration: 3-4 hours
- Value: Shows understanding of display advertising strategies
- Validity: 12 months
Facebook Blueprint Certification
- Provider: Meta
- Cost: Free courses; certification exam costs money (optional)
- Duration: Self-paced
- Value: Demonstrates Facebook and Instagram advertising expertise
- Covers: Campaign creation, audience targeting, optimization
HubSpot Content Marketing Certification
- Provider: HubSpot Academy
- Cost: Free
- Duration: 4-5 hours
- Value: Teaches content creation and distribution strategies
- Includes: Planning, creation, promotion, measurement
- Certificate: Downloadable immediately after completion
Google Digital Garage
- Provider: Google
- Cost: Free
- Duration: 40 hours (self-paced)
- Value: Good foundation covering digital marketing basics
- Covers: SEO, SEM, social media, analytics, e-commerce
- Recognized: Especially valuable in India
SEMrush Academy Certifications
- Provider: SEMrush
- Cost: Free
- Duration: Various courses, 2-4 hours each
- Options: SEO Toolkit, Content Marketing, PPC Fundamentals
- Value: Industry-recognized tool certification
HubSpot Social Media Marketing Certification
- Provider: HubSpot Academy
- Cost: Free
- Duration: 3-4 hours
- Value: Covers social media strategy, content, monitoring
- Certificate: Recognized by employers globally
Paid Certifications Worth Considering
Facebook Certified Digital Marketing Associate
- Cost: $99 USD
- Value: Official Meta certification, highly valued
- Recommended: Once you have some experience
Google Ads Certification Bundle
- Cost: Free to study, exam is also free
- Multiple specializations: Search, Display, Video, Shopping
- Strategy: Complete all available certifications
Certification Strategy for Freshers
Week 1-2: Foundation
- Complete Google Digital Garage for overall foundation
- Get Google Analytics Individual Qualification
Week 3-4: Specialization
- Google Ads Search Certification
- HubSpot Content Marketing Certification
Week 5-6: Advanced
- Facebook Blueprint courses
- SEMrush Academy certifications
- Additional Google Ads certifications
Display on Resume:
- List under “Certifications” section
- Include certification name and year
- Add “Certified” to your LinkedIn headline if relevant
Section D: Job Search Strategy
Finding the right opportunity requires strategy, not just applying randomly to hundreds of jobs.
Where to Find Digital Marketing Jobs
Job Portals:
- LinkedIn: Best for professional roles, easy to apply
- Naukri.com: Large database, especially for India
- Indeed: Aggregates from multiple sources
- Internshala: Great for internships and entry-level
- Shine.com: Good for freshers
- Monster India: Established portal with many listings
- Freshersworld.com: Specifically for entry-level positions
Company Websites:
- Check “Careers” page of companies you admire
- Set up job alerts on their sites
- Often get responses faster than portals
Social Media:
- LinkedIn job search feature
- Twitter (follow #digitalarketingjobs #hiring)
- Facebook groups for digital marketing jobs
- Instagram (some companies post openings)
Networking:
- Inform your course instructors you’re job hunting
- Connect with alumni working in digital marketing
- Attend marketing meetups and events
- Join digital marketing communities online
Startup Platforms:
- AngelList (for startup roles)
- Cutshort (quick apply platform)
- Hirect (direct chat with founders)
Freelancing Platforms (to build experience):
- Upwork
- Fiverr
- Freelancer
- PeoplePerHour
Application Strategy
Quality Over Quantity:
Don’t apply to 100 jobs with the same generic resume. Apply to 20 carefully selected roles with customized applications.
Customize Each Application:
- Read job description carefully
- Identify key requirements
- Adjust your resume to highlight relevant skills
- Use keywords from job posting
- Reference specific points from job description in cover letter
Application Tracking:
Create a spreadsheet to track applications:
- Company Name
- Position
- Date Applied
- Application Method
- Status (Applied, Interview Scheduled, Rejected, Offer)
- Follow-up Date
- Notes
Follow-Up:
- If no response in 1 week, send polite follow-up email
- Keep it brief and professional
- Express continued interest
- Don’t be pushy or demanding
Sample Follow-Up Email:
“Subject: Following Up – Digital Marketing Executive Application
Dear [Hiring Manager Name],
I hope this email finds you well. I applied for the Digital Marketing Executive position on [date] and wanted to follow up on the status of my application.
I remain very interested in this opportunity and believe my skills in SEO, social media marketing, and analytics would be valuable to your team. I would welcome the chance to discuss how I can contribute to [Company Name]’s marketing goals.
Please let me know if you need any additional information from my end.
Thank you for your consideration.
Best regards,
[Your Name]
[Phone Number]”
Setting Realistic Expectations
Application-to-Interview Ratio:
Expect roughly 1 interview call for every 10-20 applications as a fresher. This is normal. Don’t get discouraged.
Interview-to-Offer Ratio:
You might need to attend 5-10 interviews before getting an offer. Each interview is practice and learning.
Timeline:
Job search as a fresher typically takes 1-3 months. Some find faster, some take longer. Stay persistent.
Salary Expectations for Freshers (India, 2025):
- Tier 1 cities (Mumbai, Bangalore, Delhi): ₹15,000 – ₹30,000/month
- Tier 2 cities (Hyderabad, Pune, Chennai): ₹12,000 – ₹25,000/month
- Tier 3 cities and smaller companies: ₹10,000 – ₹20,000/month
- Internships: ₹5,000 – ₹15,000/month
Factors affecting salary:
- Company size and reputation
- Your skills and certifications
- City and location
- Previous internship experience
- Negotiation skills
Section E: Interview Preparation Checklist
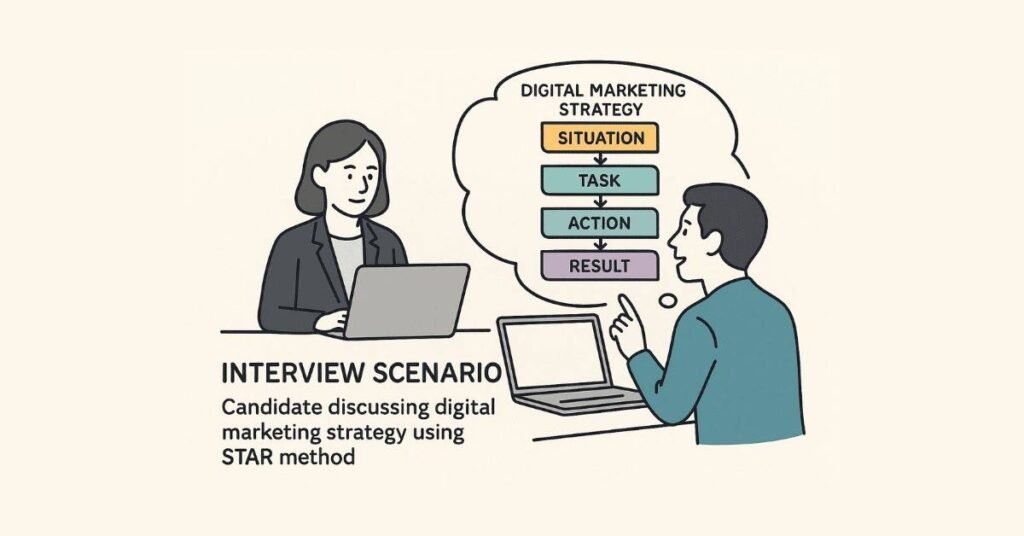
One Week Before Interview
Research Deep-Dive:
- Study company website thoroughly
- Read their blog if they have one
- Check their social media presence and recent posts
- Look up recent news about the company
- Understand their products/services
- Identify their target audience
- Note their marketing style and messaging
- Research competitors
Prepare Your Stories:
- Write down 5-6 experiences from projects or internships
- Practice explaining them using STAR method
- Prepare specific examples for common questions
- Quantify your achievements
- Practice out loud, not just in your head
Update Materials:
- Print 5 copies of resume on quality paper
- Prepare portfolio samples (digital or physical)
- Update LinkedIn profile
- Prepare list of references with contact info
- Organize certificates
Practice:
- Conduct mock interviews with friends or family
- Record yourself answering questions
- Practice in front of mirror
- Time your answers (keep under 2-3 minutes each)
- Prepare questions to ask them
Day Before Interview
Logistics:
- Confirm interview time and location
- Plan your route and transportation
- Check traffic patterns for that time
- Have backup transport plan
- Save interviewer’s contact number
- Know where to park if driving
Final Preparation:
- Review your resume and be ready to explain everything
- Re-read job description
- Prepare outfit and keep it ready
- Charge phone and laptop fully
- Test Zoom/video call setup if virtual
- Get good sleep (at least 7 hours)
Mental Preparation:
- Visualize success
- Stay positive
- Remember you’re qualified or they wouldn’t interview you
- Prepare to learn from experience regardless of outcome
Interview Day
Morning Routine:
- Wake up early, don’t rush
- Eat a proper breakfast
- Dress fully (even for video interviews)
- Arrive 10-15 minutes early (not too early, not late)
- Visit restroom before entering
- Turn off phone or keep on silent
What to Bring:
- Multiple resume copies
- Notepad and working pen
- Portfolio or work samples
- Certificates folder
- Photo ID
- Water bottle
- Breath mints
- Tissues
- Phone with interviewer’s number saved
During Interview
First Impression:
- Confident entry with smile
- Firm handshake (if offered)
- Wait to be offered a seat
- Good posture, eye contact
- Phone completely off or silent
Active Engagement:
- Listen carefully to each question
- Take brief pause before answering
- Be honest if you don’t know something
- Ask for clarification if question is unclear
- Show enthusiasm and genuine interest
- Take notes when appropriate
Red Flags to Avoid:
- Speaking negatively about previous employers
- Appearing desperate
- Being arrogant or overconfident
- Checking phone
- Interrupting interviewer
- Lying or exaggerating
- Not having questions for them
- Bad-mouthing competitors
Closing the Interview
Before Leaving:
- Thank them for their time
- Express continued interest in role
- Ask about next steps and timeline
- Get business card or email address
- Firm handshake and smile
- Confident exit
Within 24 Hours After:
- Send thank-you email
- Mention specific discussion points
- Reiterate interest
- Keep it brief and professional
Sample Thank-You Email:
“Subject: Thank You – Digital Marketing Executive Interview
Dear [Interviewer Name],
Thank you for taking the time to meet with me yesterday to discuss the Digital Marketing Executive position. I enjoyed learning about [Company Name]’s innovative approach to content marketing and the exciting campaigns your team is working on.
Our conversation reinforced my enthusiasm for this opportunity. I’m particularly excited about the possibility of contributing to your SEO and social media initiatives, and I believe my skills and passion align well with your team’s needs.
Please don’t hesitate to reach out if you need any additional information from my end. I look forward to hearing about the next steps.
Best regards,
[Your Name]”
Section F: Negotiation Basics
When the Offer Comes
Don’t Accept Immediately:
Even if excited, say “Thank you, I’d like to review the offer details. Can I have 24-48 hours to think it over?”
What to Review:
- Base salary
- Working hours
- Probation period terms
- Performance review schedule
- Benefits (if any)
- Growth opportunities
- Team structure
- Notice period
- Leaves and holidays
Research Before Negotiating:
- Know market rates for the role
- Consider your minimum acceptable salary
- Identify your priorities (salary vs learning vs growth)
- Be ready to justify your ask
How to Negotiate
If Salary is Lower Than Expected:
“Thank you for the offer. I’m very excited about this opportunity and believe I can contribute significantly to your team. Based on my research of market rates for this role and considering my certifications and project experience, I was hoping for something in the range of ₹[X] to ₹[Y]. Is there flexibility in the salary for this position?”
What to Do:
- Be polite and professional
- Justify with market research and your value
- Give a range, not a fixed number
- Be prepared for them to say no
- Know your walk-away point
If They Can’t Increase Salary:
Ask for alternatives:
- Earlier performance review
- Additional responsibilities
- Professional development budget
- Flexible working options
- Clear growth path timeline
If They Hold Firm:
You have three options:
- Accept the offer
- Decline politely
- Request time to decide
Decision Factors:
- Is the learning opportunity valuable?
- Will it build your career?
- Can you afford to live on the salary?
- Are there clear growth prospects?
- Does the company culture fit you?
Accepting or Declining
Accepting:
Get everything in writing before resigning from current position (if applicable) or declining other offers.
“Thank you for the offer. I’m delighted to accept the Digital Marketing Executive position at [Company Name]. I’m excited to join the team and contribute to your marketing goals. Please send the formal offer letter, and let me know the next steps regarding joining date and documentation.”
Declining:
Be professional – you never know when paths might cross again.
“Thank you very much for the offer. After careful consideration, I’ve decided to pursue another opportunity that aligns more closely with my career goals at this time. I appreciate your time throughout the interview process and hope our paths cross again in the future.”
🎯 Follow the Complete Digital Marketing Learning Path!
🧭 See Career Roadmap →
Section G: First 90 Days on the Job
Week 1: Orientation and Learning
Your Goals:
- Understand company culture
- Learn team structure
- Grasp basic processes
- Make positive first impression
- Ask lots of questions
Action Items:
- Arrive early every day
- Take detailed notes in all meetings
- Set up all accounts and tools
- Introduce yourself to everyone
- Learn everyone’s names and roles
- Ask about communication preferences
- Review past campaigns and reports
- Understand current projects
Questions to Ask:
- What are the team’s current priorities?
- How is success measured in this role?
- What tools and platforms do we use?
- How does our workflow process work?
- What should I focus on learning first?
- Who should I go to for different types of questions?
Month 1: Absorb and Contribute
Your Goals:
- Complete initial assignments successfully
- Demonstrate reliability
- Build relationships
- Learn company’s marketing approach
- Understand KPIs and metrics
Action Items:
- Deliver small tasks perfectly
- Meet all deadlines
- Proofread everything multiple times
- Ask for feedback regularly
- Offer help to team members
- Start contributing ideas (but don’t overwhelm)
- Document your learnings
What Good Looks Like:
- You understand the brand voice
- You know where to find information
- You complete tasks without multiple corrections
- You communicate proactively
- You show initiative within your scope
Month 2: Growing Confidence
Your Goals:
- Take ownership of specific tasks
- Start suggesting improvements
- Build deeper expertise
- Become more independent
- Expand your responsibilities
Action Items:
- Volunteer for new projects
- Share relevant articles or insights
- Suggest small process improvements
- Request additional responsibilities
- Network within company
- Start establishing your value
Signs of Success:
- Manager trusts you with independent work
- Colleagues seek your input
- You’re included in strategy discussions
- You understand the why, not just the what
- You’re making meaningful contributions
Month 3: Establishing Your Value
Your Goals:
- Have measurable impact
- Be seen as reliable team member
- Identify your niche or strength
- Plan your growth path
- Prepare for performance review
Action Items:
- Document your achievements and metrics
- Request feedback session with manager
- Discuss growth opportunities
- Identify skills you want to develop
- Set goals for next quarter
- Build case for any promotions or raises
Questions for Your Manager:
- How am I performing relative to expectations?
- What areas should I focus on improving?
- What opportunities exist for growth?
- How can I add more value to the team?
- What skills should I develop next?
Building Professional Relationships
With Your Manager:
- Communicate regularly and proactively
- Ask for feedback frequently
- Update on progress without being asked
- Bring solutions, not just problems
- Be honest about challenges
- Show appreciation for guidance
With Colleagues:
- Be helpful and supportive
- Share credit generously
- Collaborate willingly
- Respect boundaries
- Maintain professionalism
- Build genuine connections
With Other Departments:
- Understand their priorities
- Make their jobs easier
- Communicate clearly
- Respect their expertise
- Build bridges
Section H: Common Mistakes to Avoid
Resume and Application Mistakes
Mistake 1: Generic Applications
Sending same resume to every company without customization.
Fix: Customize resume for each application, highlighting relevant skills for that specific role.
Mistake 2: Typos and Errors
Spelling mistakes or grammatical errors in resume or emails.
Fix: Proofread multiple times. Use Grammary. Have someone else review.
Mistake 3: Lying or Exaggerating
Claiming skills you don’t have or inflating achievements.
Fix: Be honest. Highlight what you can do, not what you can’t. Growth mindset matters more than knowing everything.
Mistake 4: Unprofessional Email Address
Using emails like coolboy123@gmail.com or partylover@yahoo.com
Fix: Create professional email: firstname.lastname@gmail.com
Mistake 5: Missing Contact Information
Forgetting to include phone number or having incorrect details.
Fix: Double-check all contact information is current and correct.
Interview Mistakes
Mistake 6: Poor Preparation
Not researching company or not preparing answers to common questions.
Fix: Spend at least 2-3 hours researching and practicing before every interview.
Mistake 7: Arriving Late
Being late shows disrespect for interviewer’s time.
Fix: Plan to arrive 10-15 minutes early. Account for traffic and parking.
Mistake 8: Talking Too Much or Too Little
Either rambling for 10 minutes or giving one-word answers.
Fix: Practice concise 2-3 minute answers. Use STAR method for structure.
Mistake 9: Badmouthing Previous Employers
Complaining about past jobs, managers, or companies.
Fix: Frame everything positively. Focus on what you learned and what you’re seeking.
Mistake 10: Not Asking Questions
Saying “No questions” when asked if you have any.
Fix: Always prepare 3-5 thoughtful questions showing genuine interest.
Mistake 11: Focusing Only on Salary
Asking about money before showing interest in work.
Fix: Show enthusiasm for role and company first. Discuss compensation when they bring it up.
Mistake 12: Poor Body Language
Slouching, avoiding eye contact, fidgeting, checking phone.
Fix: Practice confident body language. Record yourself in mock interviews.
On-the-Job Mistakes
Mistake 13: Not Asking for Help
Struggling silently instead of asking questions when confused.
Fix: Ask questions early. It’s better to clarify than make mistakes.
Mistake 14: Overpromising
Saying yes to everything and missing deadlines.
Fix: Be realistic about what you can deliver. Better to under-promise and over-deliver.
Mistake 15: Not Taking Feedback Well
Getting defensive when receiving constructive criticism.
Fix: Thank people for feedback. Ask clarifying questions. Implement suggestions.
Mistake 16: Office Gossip
Participating in negative talk about colleagues or company.
Fix: Stay professional. Don’t participate in gossip. Focus on work.
Mistake 17: Not Documenting Work
Failing to track achievements or save work samples.
Fix: Keep folder of your work, metrics, and achievements for future reference.
Career Development Mistakes
Mistake 18: Staying in Comfort Zone
Only doing assigned tasks and not learning new skills.
Fix: Continuously upskill. Take courses. Volunteer for new projects.
Mistake 19: Not Networking
Keeping head down and not building professional relationships.
Fix: Attend industry events. Connect with professionals. Build your network.
Mistake 20: Ignoring Personal Brand
Not maintaining active LinkedIn or professional online presence.
Fix: Post regularly on LinkedIn. Share insights. Build your professional brand.
Section I: Confidence and Mindset
Overcoming Interview Anxiety
Understanding Nervousness:
Everyone gets nervous before interviews. It’s normal and natural. Some anxiety actually helps you perform better by keeping you alert.
Reframing Anxiety:
Instead of thinking “I’m so nervous,” think “I’m excited about this opportunity.” Research shows this simple reframe improves performance.
Preparation Reduces Anxiety:
The more prepared you are, the more confident you’ll feel. When you’ve practiced answers 20 times, they flow naturally.
Breathing Techniques:
Before interview, practice deep breathing:
- Breathe in for 4 counts
- Hold for 4 counts
- Breathe out for 6 counts
- Repeat 5 times
This activates your calm nervous system and reduces anxiety physically.
Power Posing:
Research suggests standing in powerful poses (hands on hips, chest open) for 2 minutes before interview can boost confidence.
Positive Visualization:
Spend 5 minutes visualizing yourself succeeding in the interview – confident, articulate, connecting well with interviewer.
Handling Rejection
Rejection is Normal:
Even highly qualified candidates face multiple rejections. It’s part of the process, not a reflection of your worth.
Learn from Each Experience:
After rejection, ask yourself:
- What went well?
- What could I improve?
- Did I adequately prepare?
- Was it genuinely bad fit?
- What will I do differently next time?
Don’t Take It Personally:
Rejection often has nothing to do with you. They might have:
- Internal candidate in mind
- Different needs than posted
- Budget changes
- Hiring freeze
- Found someone with specific experience
Request Feedback:
Politely ask for feedback: “Thank you for considering my application. If possible, I would appreciate any feedback that could help me improve for future opportunities.”
Keep Momentum:
Don’t dwell on rejections. Acknowledge the disappointment, then move forward. Apply to next opportunity.
Growth Mindset for Digital Marketing
Embrace Continuous Learning:
Digital marketing changes constantly. Algorithms update, new platforms emerge, best practices evolve. Your learning never stops.
See Challenges as Opportunities:
When you face something you don’t know, think “I get to learn something new” rather than “I can’t do this.”
Value Effort Over Natural Talent:
Digital marketing success comes from persistent practice and learning, not innate ability. Anyone willing to put in work can succeed.
Learn from Mistakes:
Every mistake is data. Every failure teaches something. Successful marketers have failed more times than unsuccessful ones have tried.
Celebrate Small Wins:
Increased engagement rate by 5%? Celebrate it. Got first interview call? That’s progress. Acknowledge every step forward.
Impostor Syndrome
What It Is:
Feeling like you don’t deserve success or that you’re faking your way through despite evidence of competence.
Why It Happens:
Common among career beginners and when learning new skills. Your brain focuses on what you don’t know rather than what you do.
How to Combat It:
- Document your achievements and review them regularly
- Remember that everyone was a beginner once
- Recognize that you were hired because you’re qualified
- Share your feelings with mentors or peers
- Focus on continuous improvement, not perfection
- Accept that you won’t know everything, and that’s okay
Perspective:
That senior marketer who seems to know everything? They felt exactly like you when they started. Experience builds confidence.
Section J: Resources and Tools
Learning Resources
Blogs to Follow:
- Neil Patel Blog (neilpatel.com/blog)
- Moz Blog (moz.com/blog)
- HubSpot Marketing Blog (blog.hubspot.com)
- Search Engine Journal (searchenginejournal.com)
- Social Media Examiner (socialmediaexaminer.com)
- Content Marketing Institute (contentmarketinginstitute.com)
- Backlinko (backlinko.com)
YouTube Channels:
- Neil Patel
- Ahrefs
- SEMrush
- HubSpot Marketing
- Google Analytics
- Social Media Examiner
Podcasts:
- Marketing School (Neil Patel & Eric Siu)
- The GaryVee Audio Experience
- Social Media Marketing Podcast
- Online Marketing Made Easy
- Perpetual Traffic
Communities:
- Reddit: r/digital_marketing, r/SEO, r/socialmedia
- Facebook Groups for Digital Marketers
- LinkedIn Groups
- GrowthHackers Community
- Inbound.org
Free Tools
SEO Tools:
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics
- Ubersuggest (limited free version)
- Answer the Public
- Google Trends
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider (free up to 500 URLs)
Keyword Research:
- Google Keyword Planner (free with Google Ads account)
- Keyword Surfer (Chrome extension)
- Keywords Everywhere (limited free version)
Content Tools:
- Grammarly (free version)
- Hemingway Editor
- Google Docs
- Canva (free version)
- Unsplash (free stock photos)
- Pexels (free stock photos and videos)
Social Media:
- Buffer (free for limited posts)
- Later (free Instagram scheduler)
- Canva (for social graphics)
- Bitly (link shortener and tracking)
Analytics:
- Google Analytics
- Facebook Page Insights
- Twitter Analytics
- LinkedIn Analytics
- Instagram Insights
Email Marketing:
- Mailchimp (free up to 500 subscribers)
- Sender (free up to 2,500 subscribers)
- MailerLite (free up to 1,000 subscribers)
Project Management:
- Trello (free)
- Asana (free for basic use)
- Google Sheets
- Notion (free personal plan)
Section K: 30-Day Interview Preparation Plan
Week 1: Foundation
Days 1-2: Self-Assessment
- List all your skills
- Document all projects and achievements
- Identify strengths and weaknesses
- Determine career goals
- Research digital marketing roles
Days 3-4: Resume Building
- Create/update resume
- Write compelling professional summary
- Quantify all achievements
- Get feedback from mentors
- Create multiple versions for different roles
Days 5-7: Certification Prep
- Start Google Analytics certification
- Begin Google Ads Search certification
- Complete at least one certification by week end
Week 2: Knowledge Enhancement
Days 8-10: Technical Knowledge
- Review all course materials
- Practice explaining concepts simply
- Create flashcards for terminology
- Study common technical questions
- Take online quizzes
Days 11-12: Company Research
- List 20 target companies
- Research each thoroughly
- Follow their social media
- Read their blogs
- Understand their marketing approach
Days 13-14: More Certifications
- Complete Google Ads certification
- Start HubSpot Content Marketing
- Add certifications to resume and LinkedIn
Week 3: Interview Skills
Days 15-17: Answer Preparation
- Write answers to 30 common questions
- Practice STAR method stories
- Record yourself answering
- Time your responses
- Refine and practice again
Days 18-19: Mock Interviews
- Conduct mock interviews with friends
- Record video mock interview
- Review and critique yourself
- Practice with different question types
- Get feedback from others
Days 20-21: Soft Skills
- Practice body language in mirror
- Work on eye contact
- Practice handshake
- Improve voice modulation
- Work on confident posture
Week 4: LinkedIn and Applications
Days 22-23: LinkedIn Optimization
- Update all sections
- Add keywords throughout
- Request recommendations
- Start posting content
- Connect with professionals
Days 24-25: Cover Letter Templates
- Create 3 cover letter templates
- Prepare customizable paragraphs
- Write compelling opening lines
- Prepare strong closing paragraphs
Days 26-28: Job Applications
- Apply to first 10 jobs
- Customize each application
- Set up tracking spreadsheet
- Follow up on previous applications
- Network with company employees
Days 29-30: Final Preparation
- Review all materials one final time
- Practice power poses
- Prepare interview outfit
- Mental preparation and visualization
- Stay positive and confident
Final Words of Encouragement
Starting a career in digital marketing is exciting. Yes, you’ll face challenges, rejections, and moments of doubt. But remember:
Everyone Started Where You Are:
Every expert was once a beginner. Every successful digital marketer faced the same uncertainties you’re feeling now.
Your Willingness to Learn Matters Most:
Companies hire freshers not because they know everything, but because they’re eager to learn, adaptable, and bring fresh perspectives.
Persistence Pays Off:
Every application brings you closer. Every interview makes you better. Every rejection teaches you something. Don’t give up.
You Have Valuable Skills:
You’ve completed comprehensive training. You understand concepts that most people don’t. You’re qualified.
The Industry Needs You:
Digital marketing is growing rapidly. Companies need talented marketers. There’s space for you.
Believe in Your Journey:
Your path is unique. Don’t compare your beginning to someone else’s middle. Focus on your growth, your progress, your goals.
You’ve Got This:
You’ve prepared thoroughly. You’ve learned extensively. You’re ready. Now go show them what you can do.
Complete Interview Preparation Checklist
Knowledge Preparation:
- ☐ Completed comprehensive digital marketing course
- ☐ Understood all technical concepts (SEO, SEM, SMM, Content, Analytics)
- ☐ Can explain concepts in simple terms
- ☐ Know current industry trends
- ☐ Familiar with major tools and platforms
Certifications:
- ☐ Google Analytics certified
- ☐ Google Ads certified (at least Search)
- ☐ At least one HubSpot certification
- ☐ Additional relevant certifications
Documents:
- ☐ Updated, error-free resume
- ☐ Multiple resume copies printed
- ☐ Cover letter template ready
- ☐ Portfolio of work samples
- ☐ Certificates organized
- ☐ Reference list prepared
Online Presence:
- ☐ LinkedIn profile optimized with keywords
- ☐ Professional profile photo
- ☐ Compelling About section
- ☐ All sections completed
- ☐ Recommendations received
- ☐ Active on LinkedIn with regular posts
Interview Preparation:
- ☐ Researched target companies thoroughly
- ☐ Prepared answers to 50+ common questions
- ☐ Practiced STAR method stories
- ☐ Conducted mock interviews
- ☐ Prepared questions to ask interviewers
- ☐ Reviewed own resume thoroughly
- ☐ Can explain every point confidently
Soft Skills:
- ☐ Practiced body language and eye contact
- ☐ Worked on clear, confident speaking
- ☐ Prepared professional attire
- ☐ Learned anxiety management techniques
- ☐ Ready to handle different question types
Job Search:
- ☐ Identified target companies and roles
- ☐ Created job application tracking system
- ☐ Customized applications for each role
- ☐ Applied to multiple opportunities
- ☐ Following up on applications
- ☐ Networking actively
Mindset:
- ☐ Confident in abilities
- ☐ Ready to learn and grow
- ☐ Prepared for possible rejections
- ☐ Maintaining positive attitude
- ☐ Committed to continuous improvement
Congratulations on completing the entire Digital Marketing Interview Preparation Guide!

You now have:
- 210+ technical questions and answers covering all aspects of digital marketing
- 60 ChatGPT prompts for self-directed learning
- 25+ behavioral questions with detailed STAR method answers
- Comprehensive communication skills guidance
- Complete career preparation resources
Remember: Preparation builds confidence. Confidence builds performance. Performance builds careers.
Go land that dream digital marketing job. You’re ready! 🚀
🎓 Your Digital Marketing Journey Starts Here !
📘 All Resources • 📘 All Courses • 🧭 Roadmap • 🚀 Join Course
